Path of digestive system (Castleman) Flashcards
Pathologic dzs of oral cavity
Developmental dz
- Developmental dz
- cleft palate
- prognathism
- brachygnathism
Cleft palate
- due to delayed development and fusion of lateral palatine arches
- genetic or toxic etiology
- plant tox
- steroids during pregnancy
- veratrum californicum in sheep
- poison hemlock in pigs
- Common complication
- aspiration pneumonia
Brachynathia and Prognathia
- Brachy (short); prognathia (long jaw)
- Growth abnormalities various causes (usually unknown)
- Genetic abnormalities
- Calcium deficiency
- Chondrodysplasia
- Complications are species dependant
- malocclusion
- tooth growth and wear abnormalities
Inflammatory lesions
Oral cavity
- vesicular
- erosive/ulcerative
- proliferative
- other
- pseudomembranous
- granulomatous
Inflammatory dzs
Vesicular stomatitis/esophagitis
- Large, fluid-filled lesions in mucosa
- blood
- neutraphils
- Lesions are short lived, progress rapidly to erosions/ulcers
- Causes
- viral (usual)
- thermal, toxic (rare)
When you see erosive stomatitits in cattle
Always have to consider Foot-in-mouth as a ddx
Inflammatory dzs of oral cavity
Erosive/Ulcerative Stomatitis
- Causes
- viral infection
- calicivirus
- BVD
- bluetongue virus in sheep
- Toxic dz
- phenylbutazone
- uremia
- immune mediated disease
- pemphigus vulgarus
- SLE
- viral infection
*often also esophageal involvement
Inflammatory lesions of oral cavity
Proliferative stomatitis/esophagitis
- Causes
- parapox viruses
- bovine papular stomatitis: calves
- contagious ecthyma - sheep, goat
- parapox viruses
Inflammatory lesions of oral cavity
Necrotizing stomatitis
- causes
- bacterial
- oral necrobacillosis/fusobacterium necrophorum
- actinobacillus (wooden tongue, osteomyelitis)
- infarctive
- NSAIDS: obstructs small capillaries
- bacterial
Inflammatory lesions of the oral cavity
Granulomatous
Pseudomembranous
- Granulomatous
- cryptococcal stomatitis
- Pseudomembranous
- Simian immunodeficiency virus
- then something about yeast and hyphae take over, I think
Vesicular oral lesions can be induced by all of the following except
- A. Foot and Mouth Disease virus
- B. Thermal injury
- C. Vesicular stomatitis virus
- D. Swine vesicular disease virus
- E. Bovine papular stomatitis virus
- E. Bovine papular stomatitis virus
Ulcerative oral lesions can be induced by
- A. Chronic uremia
- B. Calicivirus
- C. Bovine virus diarrhea virus
- D. Foot and mouth disease virus
- E. All of the above
- E. All of the above
Oral cavity
Neoplastic dzs dogs and cats
- Periodontal fibromatous epulis
- Acanthomatous ameloblastoma
- Melanoma
- Fibrosarcoma
Periodontal Fibromatous Epulis
Dogs
- Age:
- usually over 3 years of age
- mean 8.5 years
- Location
- anywhere on the gingiva
- Histological features
- mesenchymal spindle to stellate cells (periodontal ligament)
- odontogenic epithelium (cell rests of Malassez)
- variable matrix with characteristics of bone, dentin or cementum
- Behavior if untreated
- expansile and non-invasive
- excision is usually curative
Acanthomatous ameloblastoma
aka: Acanthomatous epulis
Dogs
- Age
- older than three years of age
- mean 8.8 years
- Location
- anywhere on the gingiva
- Histologic features
- interconnecting, invasive sheets of odontogenic epithelium
- Behavior if untreated
- invasive into bone
- no metastasis
Squamous Cell carcinoma
Dog
- Age
- mean: 8 yrs old
- Location
- Tonsil, gingiva, lip, tongue, palate, pharynx
- Gross features
- nodular, firm, oten ulcerated
- Behavior if untreated
- Tonsillar: metastasis to regional nodes early (98%) with frequent more distant metastasis (63%)
- Others: locally invasive, lower percentage 5-10% metastasize
Squamous cell carcinoma
Cat
- Most common oral tumor in the cat
- Age
- median: 12 yo
- Location
- tongue, and gingiva most common
- Gros and histo features
- same as dog
- Behavior if untreated
- locally invasive and mass producing
- destructive to bone
- 15% metastasis rate to local nodes (one study)
Oral malignant melanoma
- age
- mean: 11 yo
- Location
- Gingiva and lips most common
- Behavior if untreated
- 70% metastasize to regional lymph nodes
- 67% to distant sites
- lung, brain, eyes, liver, kidney
- May be amelanotic
Fibrosarcoma
Dog
- Age
- mean: 7.2 years
- Location
- gingiva, hard/soft palate, lip, tongue
- Behavior if untreated
- local infiltration and tissue destruction
- metastasis in 20% to local lymph nodes
- 10-20% to lungs
Which of the following oral neoplasms in dogs has the greatest pobability of metastasis?
- A. Tonsillar squamous cell carcinoma
- B. Periodontal fibromatous epulis
- C. Acanthomatous ameloblastoma
- D. Squamous papilloma
- E. Leiomyoma
- A. Tonsillar squamous cell carcinoma
Which of the following oral neoplasms in dogs has the least probability of invasion and/or metastasis?
- A. Melanoma
- B. Periodontal fibromatous epulis
- C. Acanthomatous ameloblastoma
- D. Fibrosarcoma
- E. Leiomyomasarcoma
- B. Periodontal fibromatous epulis
Calf: Morphologic diagnosis
Most likely cause is trauma and infection by?

- Stomatitis
- Focal
- Necrotizing
- Chronic: deep, rounded edges
- Likely cause: fusobacterum necrophorum
Cow: Morphologic diagnosis
Most likely cause?

- esophagous, esophagitis
- Multifocal: some spots are not affected
- Ulcers and erosions
- Most likely cause: BVD
Pathology of the Esophagus
- Inflammatory disease
- Megaesophagus
- Impaction / obstruction
- Neoplasia
Esophageal inflammation
- Generally comparable to inflammation in the oral cavity due to infectious agents
- Exceptions of note
- reflux esophagitis
Esophageal impaction
- lots of dry, poorly masticated feed
- Regurge, bloat, choke
- pressure induced necrosis
- esophageal damage
Esophageal neoplasms
- papillom
- leiomyom/leiomyosarcoma
- squamous cell carcinoma
Pathology of rumen/reticulum/omasum
- Infectious inflammatory diseases
- Chemical ruminitis
Infectious rumenitis/omasitis/reticulitis
- Erosive/Ulcerative
- Proliferative
- Necrotizing
- Other
- Pseudomembranous
- Granulomatous
Rumenitis
Lactic Acidosis
- Carbohydrate overload
- Lactic acid burn of mucosa
- Acidosis
- Chronic complications
- scars
- mycotic infection
- bacterial infection—hepatitis
Pathology of Stomach/Abomasum
- Ulcers
- Inflammatory dz
- Rupture
- Neoplasia
Ulcers
Associated conditions
- Trauma, chemical injury
- High acidity
- Local ishemia
- Helicobacter spp
- Parasites
- Neoplastic dz
- mast cells and gastrin producing tumors
Gastritis/abomasitis
causes
- Infectious
- Clostridial
- Fungal
- mycotic, animals on abx have changed gastral flora
- Parasitic
- ostertagia ostertagie – protein abomasopathy
- Helicobacter spp
- Toxic
Gastric/abomasal neoplasia
- Adenocarcinoma
- Leiomyoma/Leiomyosarcoma/GIST
- Lymphoma
- cats: stomach
- dogs: stomach
- Squamous cell carcinoma-horse
Most likely cause
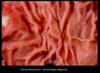
- Chronic, diffuse, hyperplastic abomasitis
- also widely disseminated, multifocal
- ostertagia ostertagia
Most likely etiologic diagnosis

- Acute multi-focal hemorrhagic and necrotizing omasitis
- Mycotic omasitis
Most likely morphologic diagnosis?

- leiomyoma or gastrointestinal stromal tumor
GI obstruction/vascular obstruction
- Gastric/abomasal volvulus
- Intestinal volvulus/torsion
- Intestinal external herniation
- Itenstinal internal herniation/entrapment
- Intussusception
- Intestinal stenosis/atresia
- Intestinal stricture
- Enteroliths and impactions
Gastric/abomasal volvulus
- Twist of stomach/intestine on self and mesentery
- Consequences
- obstruction of lumen
- obstruction of vascular supply and hemorrhagic infarction
Predisposing factors
Gastric Dilation and Volvulus in Dogs
- Initial gastric dilation
- gas accumulation
- dietary and feeding/exercise may influence
- Volvulus that may be associated with
- deep chested body configuration
- relaxation/stretching of gastrohepatic ligament
Right displaced abomasum
Predisposing Factors
- Displacement of Abomasum (LDA and RDA)
- Conditions during first 6 weeks of lactation
- High production of volatile fatty acids with diet
- GI stasis allowing abomasal stasis and gas accumulation and decrease in size of rumen
- Deep body cavity
- Unknown factors contribute to vovlulus following right sided displacement
def: Torsion
def: Volvulus
- Torsion
- twist around the long axis of the intestinal segment
- Volvulus
- twist in axis outside the long axis of the organ and involving the mesentery
Herniation/Vovulus dz examples
- Internal herniation through epiploic foramen
- Mesenteric rents
- Strangulating lipoma
- Intussusception
- Intussusceptum goes in Intussuscipiens
Intussusception
Predisposing factors
- Enteritis/altered motility
- Intestinal foreign body
- Intestinal polyp/neoplasm
Stenosis and Atresia
- Stenosis
- Membrane atresia
- Cord atresia
- Blind end atresia
Vascular Obstruction
- Thrombosis/thromboembolism/infarction
- horses: secondary to strongilus vulgaris
- Intestinal lymphangiectasia

- Intestinal linear foreign body obstruction

- Internal herniation of small intestine through epiploic foramen with infarction

- Mesenteric volvulus
DZ affecting intestinal Crypts
- Parvovirus replication
- BVD
- Rinderpest
- Mycotoxin
- Radiation
Dzs affecting Villar tip
- Rotavirus
- Coronavirus replication
- Cryptosporidium attach, replicate
Mechanisms of Diarrhea in Enterocolitis
- Maldigestion/Malabsorption - Osmotic
- epithelial surface area loss via villous atrophy and other mechanisms
- Secretory mechanisms - Cl- Secretion
- Many infectious agents act at the level of the intestinal crypts
- Increased permeability
- Mucosal epithelial damage
- Inc vascular permeability
Morphologic classification of enterocolitis according to Exudate
- Necrotizing (gross and microscopic)
- Fibrinonectic
- Proliferative
- Granulomatous
ecrotizing Enterocolitis Resulting in Villous atrophy
- viral
- protozoal
Known causes of infectious diarrheal dz in calves with villous atrophy
- Bovine corona virus
- Bovine rotavirus
- Cryptosporidia sp.
- Bovine enteric calicivirus
- Bovine norovirus
- Bovine enteric syncitial virus
- rotavirus grp B
- Bovine parvovirus
- Astrovirus
- Some E. Coli
Parvovirus can also cause
lymphoid atrophy
BVD can also cause
Acute multifocal erosive enteritis with necrosis of Peyer’s patches
Which of the following infectious agents induces villous atrophy?
- A. Rotavirus
- B. Coronavirus
- C. Cryptosporidia sp.
- D. Parvovirus
- E. All of the above
- E. All of the above
Which of the following infectious agents induces necrosis of crypt epithelial cells?
- A. Rotavirus
- B. Coronavirus
- C. Cryptosporidia sp.
- D. Parvovirus
- D. Parvovirus
Enteric salmonellosis
- classic disease resulting in fibrinonectroic lesions and fibrin casts
Pathogenic mechanisms
Salmonella
Not exam question
- Attach to M-cells, enterocytes and goblet cells
- Survive in phagosome
- neutralize NO through SPI-2
- Toxins inducing necrosis
- Enterotoxin
- Verotoxin
- Endotoxin
- Upregulate chloride ion secretion via PGE2
Salmonella
Pathogenesis
- Forms
- Peracute septicemia: sudden death
- Vasculitis, thrombosis
- common in rodents and pigs
- diamond skin lesions
- Acute enteric salmonellosis
- Enterocolitis: fibrinonecrotic lesions
- Septicemia: hepatocellular necrosis, lymphadenomegally, splenomegally, fibrinous cholecystitis
- Chronic enteric salmonellosis
- Enterocolitis
- Thrombosis
- Rectal strictures in pigs
- Peracute septicemia: sudden death
DDX for fibrinonectrotic intestinal lesions
- salmonellosis
- enterotoxigenic E. coli - calves
- clostridium difficile - horses, other sp.
- lawsonia intracellularis - classic in pigs
- brachyspira hyodysenteriae and anaerobes - swine dysentary
Hemorrhagic Enterocolitis
Causes
- Clostridial perfringens type C and other clostridia
- Shigellosis in primates
- Lawsonia intracellularis in pigs
- Coccidiosis
- Eimeria bovis in colon- calves, lambs and rabbits
Hyperplastic Enterocolitis
Causes
- Lawsonia intracellularis - proliferative ileitis in a pig
- Coccidiosis
Granulomatous Enterocolitis
Causes
- Mycobacterial infection
- Histoplasmosis, other deep mycoses
- Less well defined entities
- granulomatous enteritis in horses
*Johne’s dz classic example
- Chronic diffuse granulomatous enteritis and lymphangitis
Which of the following infectious agents most commonly induces fibrinonecrotic enterocolitis?
test question
- A. Rotavirus
- B. Salmonella sp.
- C. Cryptosporidia sp.
- D. Mycobacteria sp.
- E. Lawsonia intracellularis
- B. Salmonella sp
Which of the following infectious agents most commonly induces proliferative enteritis?
- A. Rotavirus
- B. Salmonella sp.
- C. Cryptosporidia sp.
- D. Mycobacteria sp.
- E. Lawsonia intracellularis
- E. Lawsonia intracellularis
Intestinal Neoplasia
- Lymphoma
- Epithelial tumors
- adenoma
- adenocarcinoma
- Leiomyoma/Leiomyosarcoma/GIST
- Carcinoid
Intestinal adenocarcinoma
Dog
- Age
- mean: 9 yo
- More common in males
- Location
- colon/rectum > 55%
- Small intestine < 45%
- Gross features
- plaque like or ulceratied
- may be partially polypoid in colon/rectum
- small intestine: almost always annular and constricted
- Behavior if untreated
- spread to local nodes and implant throughout peritoneum and liver
Intestinal Adenocarcinoma
Cat
- Age
- mean: 11 yo
- More common in males
- Siamese cats may be more susceptible
- Location
- small intestine (90%)
- Gross features
- small intestine: almost always annular and constrictive/obstructive
- Behavior if undetected
- usually spread to local nodes and implant throughout peritoneum by time noted clinically


