Male repro path (Dark) Flashcards
1
Q
Structure
A
- Testicles
- Epididymis
- Scrotum
- Urethra
- Prostate
- Penis
- Perineum
- +/- bulbourethral gland
2
Q
Histology
A
- Seminiferous tubules
- spermatids
- sertoli cells
- estrogens
- Interstitial (leydig) cells
- produce testosterone
3
Q
Function of testicles
A
- Produce sperm
- temperature dependent
- species-specific timeframe
- Produce hormones
4
Q
Accessory glands
A
- Prostate gland
- present in all male domestic mammals
- Seminal vesicles
- important in bulls
- absent in dogs
- Bulbourethral glands
- absent in dogs
5
Q
Testicle pathology
A
- Hypoplasia
- Cryptorchidism
- Degeneration
- Inflammation
- Neoplasia
6
Q
Hypoplasia vs Degeneration
A
- Hypoplasia
- regular circumference
- regular sertoli cell lining
- thickened but even basal lamina
- no inflammation
- no lipfuscin
- Degeneration
- Irregular tubular circumferences
- lack of tubular lining and collapse
- thickened, wavy basal lamina
- secondary inflammation
- presence of lipofuscin in tubular cells
7
Q
Inflammation
A
- Periorchitis
- Brucella
- Orchitis
- Sperm Granuloma
8
Q

A
- Brucella!
- Causes periorchitis
- Zoonotic
9
Q

A
- Sperm granulosa
- immunologically privilaged
- haploid, not diploid and rearranged compared to rest of the body’s genetic make up
- If body gets access to sperm it may react
- immunologically privilaged
10
Q
Neoplasia
A
- Seminoma
- Sertoli cell tumor
- Interstitial cell tumor
- Teratoma
- just like teratoma in ovary (2 germ cell layers)
11
Q

A
- Interstitial cell tumor
- most common testicular tumor in dogs, cats, bulls
- almost always benign
- can produce estrogen
- Gross Morph typically
- spherical
- well demarcated
- tan to orange
- possible hemorrhages
- generally firm-ish
12
Q
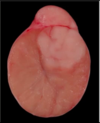
A
- Seminoma
- Gros morph usually
- homogenous
- pink/gray to white
- softish
- bulge when cut
13
Q

A
- Sertoli cell tumor
- produce estrogen
- Gross morph typically
- well circumscribed
-
firm, white, lobulated masses
- more fibrous connective tissue
- Can metastasize to regional lymph nodes and other structures in region
- not often
-
CS
- Males: gynecomastia, hair loss, attractive to male dogs, atrophy of contralateral testicle
14
Q

A
- Granuloma with a spermatocele
- granuloma with accumulation of sperm
- backup can cause fibrosis and disruption of testicle
- granuloma with accumulation of sperm
15
Q
Scrotum pathology
A
- Frostbite
- causes peripheral vasoconstriction
- Ergot
- causes peripheral vasoconstriction
- Dermatitis
16
Q
Epidydimitis
A
- bacterial
- sperm granulomas
- etc….
17
Q
Prostate path
A
- Prostatitis
- VERY PAINFUL
- Benign prostatic hyperplasia
- most common
- NON PAINFUL on palpation
- SYMMETRICAL
- Prostatic carcinoma
18
Q

A
- Left: normal
- Right: benign prostatic hyperplasia
19
Q
Prostatic carcinoma
A
- Lumpier
- Usually from transitional cells from urothelium
- Can met
- lymph nodes
- spinal column
- CS
- stranguria
- problems with defectaion
20
Q
Penis and prepuce problems
A
- Developmental anomalies
- persistent frenulum
- hypospadias: Failure of urinary tract to develop
- Trauma
- penile rupture (corpus cavernosu rupture)
- Inflammation
- Habronema
- Neoplasia
- Squamous cell carcinoma
- fibropapilloma (viral ush)
- TVT (Transmissible venereal tumor)
21
Q
Persistent frenulum
A


