Path Lab-Infectious Diseases II Flashcards
(31 cards)
A 10 year old boy developed coryza, conjunctivitis and high fever with white spots on his oral mucosa. Three days later a widespread maculopapular rash appeared with continued fever. Temp 102°F. Blotchy, reddish-brown rash on face trunk and proximal extremities. Ulcerated mucosal lesions in the oral cavity consistent with Koplik spots. What is causing his condition?

The rash of measles is due to immune response causing dilation of blood vessels.
An 8 year old girl developed non-specific flu-like symptoms with fever, followed by bilateral swelling of the parotid glands accompanied by abdominal pain and headache. Temp 101°F. The parotid glands are swollen bilaterally. Increased serum amylase. What other presentation might you look for if this were a boy?

Inflammation in a closed space like the testicle leads to decreased blood flow, infarction and necrosis. Orchitis is commonly seen in males with mumps. Note that mumps can also cause pancreatitis (confirm by checking lipase or p-amylase).
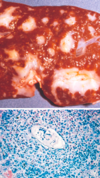
A 25 year old male medical student who recently returned from Mexico with his wife after spending spring break in Cancun, complained of painful defecation. His stools have changed color and have white purulent areas and occasionally are blood tinged. His bowels are active and his abdomen is tender to palpation, no guarding is present. Parasites are found in his bowel as shown below. What is likely causing his condition?

Entamoeba histolytica has cysts that resist gastric acid. They then wedge into the GI mucosa and cause ulcerations. Note the red blood cells phagocytosed by the amoeba.

A 32 year old male had unprotected sexual intercourse with a woman he picked up at a bar. Before he left the bar he had already drank 6 bottles of Sam Adams Boston lager. Three weeks later he noticed a single firm, non-tender, raised, red lesion on his scrotum. Healthy appearing male in no apparent distress with a slightly elevated firm reddened papule on his scrotum of 2 cm in diameter, with a clean-based shallow ulcer. Dark-field microscopy is shown below. What are the stages of this disease?

1) Chancre, infectious 2) Rash of palms and soles, condyloma lata, infectious 3) Neurosyphilis, aortitis/aneurism (most common complication), gummas (foci of delayed type hypersensitivity against the organism with fibrosis in bone, skin, oral cavity etc.)

A 65 year old male with diverticulitis underwent segmental sigmoid resection. He was doing well post operative until hospital day 5 when he developed fever, abdominal pain, and diarrhea. PMH of Diverticulosis. Ill appearing male with diffuse abdominal pain. T 102 °F, P 87, RR 18, BP 145/88. His HB 12, Hct 38, WBC 17,500, 340,000 platelets. Gram stain and biopsy are shown below. What is causing his condition? What are characteristics of this family of bacteria?

Note the gram-positive boxcar rods that indicate clostridium. These are spore-forming rods that produce spores resistant to the environment that persist in soil, canned foods and in hospitals. When they take root in humans they form toxins and enzymes: C. botulinum (toxin prevents release of ACh, comes from canned food), C. perfringens (comes from wound infection, forms bubbles, myonecrosis and gas gangrene), C. tetani (toxin inhibits release of GABA, muscles can’t relax and spasm, comes from dirt) and C. difficile (loss of normal flora + antibiotics, produce toxins A and B that cause mucosal cell apoptosis, inflammation, colitis and pseudomembrane made of necrotic cells).

An 11 year old boy was in a horseback riding summer camp in North Carolina. During the course of the camp he had several ticks on his legs. He developed fever and malaise associated with a generalized rash. Initially they thought he had a viral syndrome, but then developed a rash which started in his distal extremities and progressed centrally. Temp: 101.8°F, 120/ 78, P 78. Rash with hemorrhages over the entire body with edema in the ankles and wrists. The palms and soles are involved. Hb 11, HCT 34, WBC 8, Platelets 140. CK and LDH are slightly increased. Microscopic stain is shown below. What is causing his condition?

Rickettsia rickettsii causes Rocky Mountain Spotted Fever (RMSF). Note the obligate, intracellular, gram negative organism in sloughed endothelial cells seen on the Brown and Hopps stain. Rickettsia target endothelial cells and cause vasculitis, thrombosis, ischemia, infarction (petechial rash), damage of blood vessels and leakage of fluid (edema).

A 45 year old women from Nantucket recently returned from Africa with fever. She had spent three weeks there on a medical mission. She became delirious several hours after admission. T 102.5°F, P 91, RR 20, BP 140/89. She was ill appearing. Despite aggressive treatment the patient died several hours after hospitalization. Peripheral smear is shown below. Why is this patient prone to thrombosis?

If he has P. falciparum, knobs will form on the RBCs that bind to CD36 and I-CAM 1 on endothelial cells.

How can you tell if a rash needs your urgent medical attention?
Blanching occurs with a maculopapular rash that is from swollen vessels. If no blanching occurs, it’s blood and needs more attention.
Why is measles vaccination so important, especially in the developing world?
Immunosuppression can lead to severe pneumonia and encephalitis.

When are people most infectious with measles?
2-4 days before the maculopapular rash develops
Measles rash vs. RMSF rash
Measles starts on the face and spreads to the trunk. RMSF starts on the extremities and spreads to the trunk.
What are these cells from in an unvaccinated child that presents with a maculopapular rash and pneumonia?
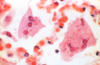
Measles infects epithelial cells of the upper respiratory tract and promotes giant cell formation. Note the eosinophilic inclusions in the nucleus and cytoplasm (Warthin-Finkeldey cells).
What parasite causes the lesions shown below in the GI tract? What other complications can arise form this infection?

Note the “flask-shaped” ulcer, typical of entamoeba histolytica. It gets to the liver via the splanchnic vessels and causes abscesses. Liver abscesses can also break through the diaphragm and enter the pleural space.

Treatment for entamoeba histolytica colitis
Metronidazole. It targets an enzyme used in fermentation used by the amoeba only.
You treat a patient with PCN G that has syphilis. He suddenly develops symptoms of shock. What caused this?
Jarisch-Herxheimer reaction: spirochetes are gram - bacteria and massive release of LPS can cause shock after treatment.
Why do people with syphilis get aortitis?
It causes a proliferative endarteritis (proliferation of endothelial cells and damage to blood vessels).

What syphilitic lesion is this?

Gumma. Type IV hypersensitivity causing fibrosis in many different areas of the body.
What inflammatory cell is highest in intensity in syphilis?
Plasma cells
What disease is transmitted by each tick shown below?

Left (Deer tick) = Lyme disease, Ehrlichiosis and Babesia. Right (Dog tick) = R. rickettsia and RMSF.

What are the stages of Lyme disease?

1) Erythema chronic migrans, lymphadenitis 2) Meningoencephalitis, neuritis, heart block, pericarditis, myocarditis 3) Destructive chronic arthritis, acrodermatitis atrophicans and neuropathy.

What organism causes typhoid nodules in the brain? What are they?

Rickettsia prowazeki causes typhus fever. The nodule is composed of focal microglial proliferation, T-cells and macrophages.
How do you diagnose a patient with RMSF?
Not antibody test, that takes a week and the patient will die by then.
What causes cerebral malaria?
Blood cells stick to walls, clog them and cause ischemia and ring hemorrhages.

This patient presented with diarrhea, bloating and malabsorption. GI biopsy is shown below. What is the life cycle of this organism?

Strongyloides infects through the skin, goes through the lungs and into the GI tract. It is the only parasite that can complete its lifecycle in humans. It can go on to disseminate to the brain, liver and kidneys in immunosuppressed patients, especially when they are given corticosteroids.