Papulosquamous Disease Flashcards
Pathogenesis of psoriasis.
Acanthosis (proliferation of keratinocytes in the epidermis) resulting from some external or autoimmune cause.
Condition linked to psoriasis.

Psoriatic Arthritis: immune-mediated disease that often presents in patients with pre-existing psoriasis

Condition linked to psoriasis

Psoriatic Erythroderma
Condition linked to psoriasis

Acropustular Psoriasis
Describe This Picture

Auspitz Sign: “pinpoint” bleeding sites when psoriasis plaques are scraped off. Occurs in locaitons where there is acanthosis along with extended projections of dermal papillae that protrude very superficial against a thin epidermis.

What is seen here?

Koebner Phenomenon: refers to skin lesions appearing on “lines” of trauma. The lesions can be vitiligo, erythematous macules, papules, plaques etc.
Name and describe type of dermatitis is seen here?

Atopic Dermatitis: Type I hypersensitivity, associated with asthma and allergies. This rash results from pruritic sensation (patient feels the itch, scratches, the rash is produced) so treatment involves stopping the itch.
Most common location of atopic dermatitis.
Flexor surfaces
Consequence of scratching eczematous lesions in atopic dermatitis.

Lichenification: thickened rough skin at the site of repeated rubbing or scratching.
Describe this dermatitis.

Cradle Cap: seborrheic dermaitis seen in infants (most seborrheic dermatitis cases result from fungal infection)
Name the causative agent of these lesions and an associated condition that predisposes patients to this type of infection.

Umbilicated lesions from molluscum contagiosum. Usually occurs in immunocompromised patients (HIV).
Conditions often associated with Seborrheic Dermatitis

Down Syndrome, Parkinson Disease, other neurological disorders
Name the condition and causative agent.

Pityriasis (previously Tinea) versicolor: caused by Malassesia furfur fungus
Way to diagnose Pityriasis versicolor.
Copper-Orange Fluorescence on Woods Lamp or “Spaghetti and Meatball” hyphae appearance on KOH prep.
What is the condition and most likely causative agent?

Tinea Corporis caused by Trychophyton rubrum. Lesions (no matter which location on the body) tend to have an annular border with raised edges a slightly hypopigmented center.
Describe the condition and possible cause.
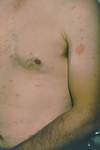
Pityriasis Rosea: Classically, it begins with a single “herald patch” lesion, followed in 1 or 2 weeks by a generalized body rash. The initial lesion is usually larger than the subsequent lesions. As of now it is an autoimmune condition possibly linked to viral infection trigger.
What is an important test to run in a patient that presents with Pityriasis Rosea lesions?

VDRL to rule out secondary syphilis infection. The rashes look very similar.
Describe the condition

Secondary syphilis rash. Distinguished from Tineas because the lesions are on the scrotum. Can also have mucous pathces in the mouth.

Describe the condition and the treatment.

Pityriasis Rubra Pilaris: reddish orange, scaling plaques and keratotic follicular papules surrounding “islands of normal tissue” or “skip spots”. Treatment is isotretinoin or methotrexate.

Describe the rash in this picture.

Subacute Cutaneous Lupus Erythematosus: lesions are scaly and evolve as polycyclic annular lesions or psoriasiform plaques on sun exposed skin. Patients advised to use UV protection. Lab tests often show ANA negative results.

Describe the Lesions and diagnosis

Lichen Planus: pruritic, purple, polygonal, planar, papules, plaques. Often see Koebner phenomenon due to scrathcing. May also see oral lesions.
Describe the condition.

Pityriasis lichenoides et varioliformis acuta: a disease of rashes and skin lesions caused by varicella and rashes. PLEVA erupts insidiously and is a chronic condition despite its name.
Describe this condition and its pathogenesis.

Crusted Scabies: caused by the mite Sarcoptes scabiei. The mite burrows into the skin and an immune response occurs to the mite, eggs, or feces. Crusted scabies is much more noticable than classic scabies in that millions of mites infest a crusted scabies patient.
Which patients will most likely develop a crusted scabies infection?
IC patients. Often seen in nursing homes with the elderly.
Treatment is Ivermectin



