Pain Management for Childbirth Flashcards
Nurses educate & support patients during the childbirth process
What makes childbirth pain different from other types of pain?
* Part of a normal process
* Able to prepare for pain
* Has a foreseeable endpoint
* Intermittent
* Emotional impact w/birth
If this pain is normal and short-lived, why do we need to intervene?
When pain exceeds a client’s tolerance, it can have negative effects on both the mother & her fetus
* Increases the woman’s metabolic rate & her need for O2
* Pain & anxiety can escalate this & increase catecholamine production (body enters fight-or-flight); resulting in fetal metabolic acidosis
* Reduces blood flow to uterus & placenta
* Protection of brain, heart, & adrenals in mother; triggers hypoxic status in fetus in dysfunctional labor patterns & prolonged pain
> Puts mother @ risk for C-section
* Alleviate pain & reduce anxiety
Poor pain control disrupts the pleasure of the birthing experience for both partners
- Mother can have difficulty bonding w/her newborn; reduces sexual desire; partner feels inadequate; may not want to experience childbirth again (negative memory)
What factors contribute to a woman’s response to labor pain?
Physical & psychological factors
Physical Factors Affecting Childbirth Pain
Sources of Pain
Tissue ischemia
Cervical dilation
Pressure & pulling on pelvic structures
Distension of the vagina & perineum (common during pushing)
Factors Influencing the Perception or Tolerance of Pain
Intensity of labor
Fetal position & size
Characteristics of the pelvis
Fatigue
Intervention of caregivers
Types of Pain
___ (a deeper, more generalized pain, can’t quite pinpoint from where) versus ___ (e.g. directly related to stretching of perineal tissue & adjacent structures; happens at delivery; localized to the area)
visceral
somatic
Psychosocial Factors Affecting Childbirth Pain
Culture (i.e. loud & vigorous expressions of pain versus stoicism)
Anxiety & fear
Previous pain experience
Preparation for childbirth
Support system
So we know it is important to manage labor pain, but how do we do it?
Nonpharmacologic Pain Management
Nonpharmacologic Pain Management Techniques
* Support general comfort
* Reduce anxiety & fear
* Promote relaxation
* Utilize mind-body stimulation
* Supplement w/hydrotherapy
* Distract w/mental stimulation
* Educate on proper breathing techniques
- Hydrotherapy can reduce BP & edema & increase diuresis; you CAN continuously monitor the fetus during this (note that textbook stated you could not)
Nonpharmacologic Pain Management Techniques - Advantages
* Do not slow labor progress
* No side effects
* No risk of allergies
* No sedative effects
* Can be used in combination w/pharmacologic measures
Nonpharmacologic Pain Management Techniques - Disadvantages
* May not achieve desired level of pain control
Pharmacologic Pain Management - Special Considerations When Medicating Pregnant Women
* Any rx taken by a pregnant woman may affect her fetus (direct vs indirect effects)
* Rx’s may have effects during pregnancy that they do not have in someone who is not pregnant
* Rx’s can affect the course & the length of labor
* Complications may limit the choice of pharmacologic pain management
* Women who need other therapeutic rx’s, use herbal or botanical preparations, or practice substance abuse may have few safe choices for labor pain relief
Regional Pain Management Techniques
* Paracervical Anesthesia
* Pudendal Block
* Local Infiltration Anesthesia
* Epidural Block
* Combined Spinal-Epidural Anesthesia
* Subarachnoid (Spinal) Block
?
Provides comfort during 1st stage of labor; does not help for pushing
Does not affect labor progress or sensory motor function; mother can be up, moving, walking, etc.
Helps to diminish the sensation of cervical dilation; the visceral pain that may be felt
Does not provide relief for 2nd stage of labor = ?

Paracervical anesthesia
pushing
?
Done for suturing or cutting
Injected into perineal tissues to provide anesthetic response
There is a short delay between the administration & the onset of the numb feeling
This can burn at injection but is NORMAL

Local Infiltration Anesthesia
?
Used to anesthetize the lower vagina & part of the perineum
Helps an individual who needs an episiotomy; helps provide anesthesia for vaginal birth
Contractions & pain will still be felt; used during pushing & after delivery for repair of lacerations
* Use local anesthesia on the perineum

Pudendal Block
?
Can be used for vaginal & Cesarean birth
Typically has an indwelling catheter
Epidural Block
Epidural space is between the dura & spinal cord; filled w/fat, veins, & connective tissue
L3 to L4 entry
Give a test dose (any numbness of tongue or lips? lightheadedness? tachycardia?)
Rx is an anesthetic (i.e. bupivacaine) & an opioid (i.e. fentanyl) combination
Operative delivery rates are higher
Note than an epidural catheter can migrate >it’s inserted
Epidural-associated fever that can be present in the neonate as well
Know if baby was born by use of an epidural or not
Rx’s can cause nausea, vomiting, pruritus, respiratory depression
If large dose administered into subarachnoid space versus epidural space, may experience rapid, intense motor & sensory block
If dura gets punctured, can cause CSF leak = spinal headache
Adverse effects of maternal hypotension & possible reduction in placental perfusion
Position mother on left, lateral side; give bolus of crystalloid IV fluids; anesthesiologist can opt to give patient IV ephedrine
Giving maternal O2 does not treat fetal tissues
Foley or straight cath can increase risk of infection but assist w/voiding
Risk for prolonged 2nd stage

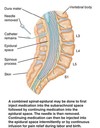
?
For quick, Cesarean birth
NO catheter in place
No pain relief during labor
Local anesthetic & opioid used
Subarachnoid (Spinal) Block
?
Couples an epidural & a spinal block
Involves an injection of an opioid anesthetic into the intrathecal space 1st, then the epidural catheter is inserted into the epidural space to have continuation of pain management throughout labor
Good when you need a rapid onset of pain relief w/o sedating client
> Remember issue of dura puncture = spinal headache
Combined Spinal-Epidural Anesthesia
* Do not use in those w/bleeding disorders, systemic/local infection (same as spinal block)
Adverse Effects of an Epidural Block
* Maternal hypotension (can happen within the first 15 min)
* Bladder distension
> Reduced sensation to void; increased IV intake; retention of fluid
> Catheter increases risk of UTI
* Prolonged second stage
* Migration of the epidural catheter
* Fever (in mother & neonate [don’t overtreat for sepsis])
* Nausea & vomiting (especially w/opioid analgesics)
* Pruritus
* Respiratory depression (risk persists for up to 24 hrs > epidural opioid administration)
?
Occurs when a woman sits or gets up and experiences an awful, 10/10 headache; feels better laying down
Can do a blood patch; prevents leakage of CSF
Spinal headache

Levels of anesthesia for cesarean versus vaginal birth


Systemic Medications for Labor
* Inhalants (i.e. nitrous oxide)
* Opioid analgesics
* Opioid antagonists
* Adjunctive medications
* Sedatives (not given often in labor due to prolonged depressive effects on neonate)




