paeds Flashcards
(104 cards)
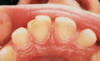
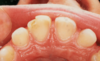
what age is this patient

6 or 7
which other permanent teeth should be present at this time

first permanent molars (6s)
what is the name given to the space between the upper central incisors

midline diastema
what has caused this in this particular case

low frenal attachment
what is the likely cause of the general appearacnnce of the lower central incisors

fluorosis
how is fluorosis likely to have arisen

excessive ingestion of fluoride during development of the teeth
what other permanent teeth are likely to affected by fluorosis

upper centrals
lateral incisors
canines
first premolars
second premolars
first molars
give 3 tx options for lower central incisors

microabrasion
composite restoration
strip crowns
which primary teeth are still present

55
54
53
63
then adults 16, 12, 11, 21, 22, 25, 26
what age is this pt

10/11/12 years
tx option for retained primary teeth on RHS
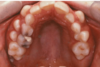
extraction
in which caries risk category would you place this pt
and why (3)

high risk
existing restorations
new carious lesions
early loss of primary tooth (64)
which radiographs would you take to further investigate caries in posteiror teeth
bitewings
bitewings confim no caries in FPM
what preventative tx would you provide

fissure sealants
which caries risk category
why (3)

high
existing restorations in 85, 84, 74
buccal swelling adjacent to 85
new carious lesion in 75
which 2 teeth have been temporised

85
84
which tooth is erupting distal to the last tooth on patients RHS

46
at what age do 6s usually erupt
6 years
what preventative tx would you provide for 46 when erupted

fissure sealant
5 possible fluoride containing preparations and doses, which would be suitable for this pt who lives in an area with less than 0.3ppm fluoride in drinking water

- fluoride toothpaste (1000ppm)
- fluoride toothpaste (1450ppm)
- duraphate/fluoride varnish (22600ppm)
- fluoride mouthwash (225ppm)
- fluoride tables (1mg)
which primary teeth are still present

55, 53
63, 65
which primary teeth have been extracted early

54
64
name for forward movement of teeth into an extractions space
mesial drift
caries risk category
why (3)

high risk
early loss/extraction of primary molars
existing restorations
new carious lesions