Paediatrics Upper and Lower GI Disorders Flashcards
What is chronic constipation?
This is infrequent passage of stool, but varies person to person:
- Normal stool frequency ranges from 4 per day to 1 per week, depends on age and diet
What does normal stool frequency range between, and depend on?
- Normal stool frequency ranges from 4 per day to 1 per week, depends on age and diet
Describe the bristol stool chart?

What are signs and symptoms seen with constipation?
- Type 1/2 Bristol stool chart
- Poor appetite
- Irritable
- Lack of energy
- Abdominal pain or distension
- Withholding or straining
- Diarrhoea
What are possible causes of constipation?
- Social
- Poor diet
- Insufficient fluid
- Excessive milk
- Potty training/school toilet
- Poor diet
- Physical
- Intercurrent illness
- Medication
- Psychological (secondary)
- Organic
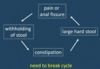
Describe the psychological viscous cycle of paediatric constipation?
Constipation - treatment
- Social
- Explain treatment to parents
- Diet – increase fibre, fruit, vegetables, fluids, decrease milk
- Psychological
- Reduce aversive factors – make going toilet pleasant experience
- Reward good behaviour – general praise, STAR charts
- Soften stool and stimulate defication
- Osmotic laxatives (lactulose)
- Stimulant laxatives (senna, picosulphate)
- Isotonic laxatives (movicol/laxido)
- For severe constipation (megarectum)
- Empty impacted rectum
- Empty colon
- Maintain regular stool passage
What are different kinds of laxatives?
- Osmotic laxatives (lactulose)
- Stimulant laxatives (senna, picosulphate)
- Isotonic laxatives (movicol/laxido)
What are examples of:
- osmotic laxatives
- stimulant laxatives
- isotonic laxatives
- Osmotic laxatives (lactulose)
- Stimulant laxatives (senna, picosulphate)
- Isotonic laxatives (movicol/laxido)
What is a complication of severe constipation?
Megarectum
What is megarectum and what can it cause?
- Megarectum
- Lots of faeces collected in rectum, causing it to dilate and push forward on urethra
- Can cause urinary retention or urinary tract infections
What are the conditions that form inflammatory bowel disease?
- Crohn’s disease
- Ulcerative colitis
Describe how the epidemiology of inflammatory bowel disease differs between children and adults?

How does the location of ulcerative colities different between adults and children?
- Different areas of ulcerative colitis
- Proctitis
- 40% adults
- 4% <5 years, 17% 5-17 years
- Left sided colitis
- 40% adults
- 14% children
- Pancolitis
- 20% adults
- >60% children
- Proctitis
How does the location of Crohn’s disease involvement differ between children and adults?
- Different areas of Crohn’s disease
- Isolated ileal
- 36% adults
- 6% children
- Ileocolonic
- 50% adults
- 45% children
- Upper GI/panenteric
- Extremely rare adults
- 51% children
- Isolated ileal




