P5 - Forces Flashcards
What is a vector quantity?
A quantity that has a magnitude and a direction.
What is a scalar quantity?
A quantity with only a magnitude, no direction.
What is the difference between mass and weight?
Mass is the amount of ‘stuff in an object’, whereas weight is the force acting on the object due to gravity.
How do you work out the weight of an object?
Weight (N) = Mass (kg) x Gravitational Field Strength (N/kg)
What is a free body diagram?
All the forces acting on an object.
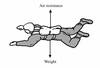
What is the resultant force?
The resultant force is the overall force of an object (consider horizontal and vertical forces seperatley)
How do you find the work done of an object?
Work done (j) = Force (N) x Distance (m)
What is the conversation rate of joules and newton metres?
1 joule = 1 Nm
Describe the forces if an object is in equilibrium?
If all objects acting on an object equal a resultant force of 0, then the object is in equilibrium.
How do you find the force of an object?
Force (N) = Spring constant (N/m) x Extension (m)
How do you work out the elastic potential energy of an object?
Elastic potential energy (j) = ½ x spring constant (N/m) x extension2 (m)
What is displacement?
It measures distance and direction in a straight line from an object’s starting point to its finishing point.
What is velocity?
Velocity is speed in a given direction.
Define acceleration in terms of velocity and time.
Acceleration is the change in velocity in a certain amount of time.
How do you work out the speed of an object?
Spped = distance/time


