Overlapping generations model Flashcards
(16 cards)
Model skeleton
- Individuals live for two periods:
- youth
- old age
- Number of individuals born at time t is N_t, there is an exponential population growth
-
Young age
- They work and decide how much to consume and and save.
-
Old age:
- They don’t work, so they just consume their savings.
Household problem

Savings and labor income
If individuals don’t work in second period
Labor income only generates income effect => increases consumption in both periods.
- It also increases savings
Savings and interest rate
- Generates two opposing forces:
- Substitution effect => cost of consumption today increases => I save more
- Income effect => increases intertemporal income (if I save) => consume more in both periods.

Firm problem
Usual structure, there are no capital gains

Equilibrium

Law of motion of capital per capita

Properties of the steady state

Properties of the steady steady state (non-oscilatory trajectories)
Then income effect shouldn’t be too strong

Overlapping generations and pareto optima
- In the overlapping generations oversaving (dynamic inefficiency is possible)
- There is scope for a Pareto improving government intervention
- This happens because there is a market missing (intergenerational transfers)
- Whenever r<n></n>
Problem under altruism
Individuals care about themselves and the utility of their children

Altruism and dynamic efficiency
- Non negativity of the bequests isn’t binding
- With altruism there is no over accumulation: decentralized solution is Pareto efficient.
Fully funded system
- There is no effect over the consumption levels.
- Notice now the market clearing condition includes the Government saving
- Both forms of savings yieldthe same return and the household is indifferent between them
- Fully funded system can change the consumption allocations if households can’t borrow against future pensions and the government sets very high contributions
PSYG system
- Imposed steady state condition is equal contributions per person accross periods:
d1t=d1,t+1
- Here, there is no savings from the government, it is just a transfer from the young to the old intra-period

Savings and PAYG
- PAYG system has a lower level of capital per capita in the SS
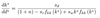
Transition from a PAYG to a fully funded
- Government issues debt that is refinanced perpetually
- Government now competes for private savings
- If we are at the golden rule, there is no change in the final allocations from the pension system reform



