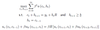Life cycle Flashcards
1
Q
Consumption-retirement puzzle
A
- Retirment is associated with consumption drops
2
Q
Possible explanations for the humped-shaped profile
A
- Uncertainty about future income when young is high: Jensen inequality might explain this if BR<1
- Survival probabilities: might work if BR>1
- Non-separable leisure: if consumption and leisure are substitutes, this might help to explain the drop of consumption at retirement

3
Q
Becker model
A
- Time and expenditures are inputs in the production of non-tradable consumption services
- Two constraints
- Time constraint
- Budget constraint
- Usual assumptions over the production function
- F_xl(x,l)>0

4
Q
Household problem
A

5
Q
Implications FOC
A
- Ratio of factors is independent of the level of consumption and independent of the wealth of the household
- With CES function, x/l tracks the ratio of w/p
- x/l will be hump shaped over the life cycle
- changes in consumption services and the change in the ratio of factor x/l move in opposite directions
- Allocation into the production of domestic consumption services will be U-shaped over the life cycle

6
Q
Elasticity of substitution between expenditure and time def
A
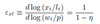
7
Q
Life cycle profile of consumption expenditure
A
It depends on the relationship of the elasticity of intertemporal substitution and elasticity of substitution between time and consumption services

8
Q
Habit formation problem
A
Habit formation break the link between IES and RA
- Remember that breaking this link is important for the equity premium puzzle