Ortho Flashcards
What to suspect if kids fracture in odd places?
osteosarcoma
(or abuse)
What to worry about if injury at fingertip, e.g., slammed in car door?
Tuft fracture, risk of osteomyelitis
Get Xray
Imaging for finger dislocation?
yes! X-ray to r/o fracture
generally have a low threshold for x-rays/suspicion of fracture in kids
(will need digital block to reset dislocated finger)
How are children different, in terms of ortho?
- anatomy & physiology
- more bones
- physeal and metaphyseal regions
- bones are often weaker than ligaments
- Fracture before sprain
- Always X-ray!
- Fracture before sprain
- born mostly cartilage - “x-ray of foot is mostly nothing”

Parts of the growing bone

Adult vs kid’s elbow
Adult: 3 bones
Child: 3 bones w/more pieces. Ossification centers can be mistaken for fractures. 11-12yo elbow pictured

Which regions of bone tend to break more in kids?
metaphyseal (darker on imaging, less dense)
What are the Salter Harris fracture types?
- Through growth plate: most common, best prognosis.
- can be displaced or non-displaced. Nondisplaced looks nl radiographically
- Usually return in 1 week to see if growth reaction - definitevely fracture
- metaphysis and physis
- Epiphysis and physis
- All
- obliterates the growth plate: least common, worst prognosisM
MNEMONIC in relation to physis (growth plate): Separation, Above, Lower, Through, Reduction

What is FOOSH?
Fall On Outstretched Hand
axial and lateral force
What should you think if tenderness over growth plate?
Even w/o radiographic evidence of fracture, consider Salter Harris type I or V
What should you consider if joint effusion associated w/trauma?
occult fracture
Mechanism for cervical spine fractures?
Fall, diving accident, MVA
Signs of a cervical spine fracture?
tenderness, any neuro deficits
risk factors - see “mechanism”

- CT
- can see C2 b/c of dens (“funky piece sticking up”)
- C1 is fractures - this was d/t axial loading to top of head, fell down stairs
- Risk: SCI d/t bleeding - no invasion in this pic; risk for vertebral artery dissection (circle at left)

15yow
Can see C1 (a ring) - Dens process of C2 sticking up past C1 = fracture through dens.
She became left hemiplegic d/t vertebral artery dissection
Mechanism for compression fracture of thoracolumbar spine
MVA, sports injury
Signs of compression fracture of thoracolumbar spine
point tenderness, loss of function
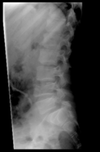
L4 vertebra is “squished”
This child was properly restrained in back seat, but tucked shoulder belt behind him, hit head forward
Will not be paralyzed - spinal cord ends around L1, thus will have chronic back pain but no neuro sx
Most commonly fractured bone?
clavicle!
Common injuries to shoulder/clavicle?
anterior dislocation
clavicular fracture
*it takes a lot of force to dislocate shoulder - this force would likely fracture before growth plates close)

Shoulder dislocation
No growth plates! 18yo.
If you see GPs - think fracture first.
Nursemaid’s elbow: what happens?
- Lecture:
- Bicep tendon gets caught between radial head and distal humerus (capitellum). Should feel tendon pop out when reduce. Must have hand on top of humerus to feel tendon.
- Not a dislocation - bill as one and you get paid more ;)
- UpToDate:
- portion of the annular ligament slips over the head of the radius and slides into the radiohumeral joint, where it becomes trapped.
- By the age of five years, the annular ligament has become thick and strong and is unlikely to tear or be displaced.

Common injuries to arm/elbow
nursemaid’s elbow
supracondylar fracture (need assessment of neurovascular status!)

Supracondylar fracture of humerus!
Urgent - straight to ED!
Blood supply through arm is brachial, runs along humerus. Nerves run alongside - will have white arm d/t artery severed/compressed

- Humerus, radius, ulna
- No obvious fracture. Can move arms.
- BUT = can see posterior fat pad and anterior sail sign
- Posterior fat pad: fat pushed away (usually have a swollen elbow) Can also use U/S
Scaphoid fracture
- tiny fracture – important d/t blood supply to bone
- if not pinned, may get avascular necrosis. You will lose significant mobility.
- PE: tenderness over snuffbox.
- Even if xray neg, splint and send to ortho.
- Mechanisms usually FOOSH.
- Usually happens in older adolescents, not young kids.

How common are forearm and wrist injuries?
Very common!
Importance of bowing deformities in forearm/wrist injuries
can lead to significant loss of pronation and supination!
U & R need to cross
Cast them and they heal quickly

Ulnar fractures are usually associated with…
(+example)
radial fractures or dislocations - almost never on own

Montaggia’s fracture – ulna broken and radial head dislocates
Common hip problems
Developmental dysplasia of the hip
SCFE
AVN (Legg-Calve-Perthes disease)
How common are knee injuries in kids?
Uncommon!
but fractures + improper healing can cause significant length discrepancies
Evaluate for joint stability!
Ankles in kids: sprains vs fracture?
Imaging?
Sprains uncommon
multiple different fractures
need 3 views to adequately visualize joint
What does knee pain usually indicate?
Referred pain from hips

- Buckle fracture at distal radius
- Splint x 2 weeks (or nothing if resource limited). Will heal on its own.
- optional cast
- Buckle fracture more common in kids
- compression fracture on one side of a bone that causes the bone to bend or buckle toward the damaged side

- Fooshed – tender over distal radius. Epiphysis of radius is dorsally displaced
- = displaced salter I – must push on so will line up again. Don’t miss!
normal pictured to contrast - epiphysis squarely on top


- Greenstick fracture. Not seen in adults often. One part broken the other not.
- Must straighten – but also must complete fracture or will only grow back in broken part.
- (broken part of arm grows longer than nonbroken – one way to add height is to break bones)
DDx for nursemaid’s elbow?
Clavicle fracture! They hold themselves in the same way!
SO - alway examine clavicle and humerus before trying to reduce
12 y/o obese boy w/complaint of BL knee pain, progressively worsening, no hx trauma
You are thinking…
Slipped capital femoral epiphysis (SCFE)
- classic presentation is that of an obese adolescent with a complaint of nonradiating, dull, aching pain in the hip, groin, thigh, or knee and no history of preceding trauma
- May present before radiographic evidence but proceed to obvious slipping later
What is SCFE?
- a chronic salter I fracture
- Misnomer: actually the proximal femur that is displaced (UpToDate)
SCFE: tx
- Fix by putting pin through, opposite side as well since 50% of time is BL!
- Most serious complication: avascular necrosis (rare and more likely 2/2 pinning) (UpToDate)
12 yo gymnastic student w/BL knee pain, beginning of season, no hx acute injuries
Pain at tibial area
Osgood Schlatter!
Rx: NSAIDs and rest
(UpToDate: continue activity as tolerate, risk of deconditioning and further injury if stop. Strengthen quads and hamstrings.)

Important considerations when ordering radiographs/imaging for kids
1 - kids fracture then sprain, so don’t be stingy
2 - comparison views are helpful! Kids tend to be symmetric
Treatment for fractured clavicle?
Tx: put in a sling and they find each other
What is the ACL?
one of four major ligaments that stabilize the knee joint during activity

When does ACL tear risk increase
during adolescent growth spurts, starting at age 12 in girls and age 14 in boys.
Recommended approach to ACL tear in teens?
Recommended: Early surgery!
But some acute acl tears don’t require surgery: quadriceps and hamstring exercises can helps and also reduce the risks of meniscus tears and osteoarthritis.
Risks to ACL surgery
surgical techniques may involve drilling into the growth plate, which introduces a risk of complications such as premature closure and limb-length discrepancy.
newer surgeries spare the growth plate
Future risks associated w/ACL tear?
Up to 10 times more likely to develop degenerative knee osteoarthritis within 10 to 20 years.
Quadriceps and hamstring exercises can help reduce this risk
How to reduce risk of acl tear
plyometric exercises, like repetitive jumping, to build stronger muscles and stretching and balance training.
Why do children often buckle instead of fracturing transversely?
bones are soft
What is a galeazzi fracture?
fracture of the radius with dislocation of the distal radioulnar joint



