Ophthalmology Flashcards
Disadvantage if mast cell stabilisers in eyes?
Takes time to work need loading dose
What is shown?

Pappiloedema blurred disc
Non proliferative severe retinopathy no macula oedema?
If proliferative?
Consider Photocoagulation (laser)
urgently do if proliferative or very high risk
Risks for corneal ulcers?
Contact lense wear and overnight wear
Immune compromise
What is this?
What grade or hypertensive retinopathy has this?

Grade iv pappiloedema
What is shown? firstline treatment?
What makes this the diagnosis rather than another similar?

Stye- warm compress unless associated conjunctivitis
Likely to be painful wheras chalazion is nto and not inflamed also a stye not blepharitis because it features a small area that is white and bulging
What investigation will find a cataract?
Slit lamp examination, normal fundus and optic nerve seen on ophthalmoscopy
Features of acute glaucoma?
Severe pain- occular and or headache
Reduced visual acuity
Symptoms worse with mydriasis dilation(big word)
Semi dilated pupil (non reactive), halos around lights
Syetmic upset- unwell nausea
Hazy cornea- red eye
Eyelids burn, itch, and stick together.
Symptoms are worse in the mornings.
Both eyes are affected.
Symptoms come and go and flare?
Blepharitis
Proliferative vs non proliferative retinopathy?
comparison shown

Complications of cataract surgery?
Poterior capsule opacification, retinal detachment, inflammation of vitreous humour
AV nipping grade of hypertensive retinopathy?
Grade II silver/copper wiring
What is this what may cause it? Symptoms?

Dendritic ulcer often caused by herpes simplex- refer to ophthal and give topical aciclovir
See a defect in red reflex in elderly adult think?
Cataract as light can not reach retina
What has happened here?

Old laser burns from treatment of diabetic retinopathy (proliferative)
How to perform an RAPD test?
Swing lgiht from eye to eye, eye with problem will consistently start dilating whne light is shone on it and signifies a problem on that side with optic nerve
Initial treatment acute glaucoma?
Beta blockers (caution asthma) and steroids applied topically and pilocarpine (constrict pupil)
IV acetazolomide is used (caution sickle cell)
Surgery: peripheral iridotomy
Offer analgesia and antiemtic also
Non proliferative non-severe retinopathy and no macula oedema?
Observe
Most common blindness cause 35-65 years?
Diabetic retinopathy
Causes of cataract?
Smoking, alcohol, diebetes, trauma, steroids
What is this? best treatment?

Cataract- surgery
Symptoms of diabetic retinopathy?
Spots or dark strings floating in your vision (floaters)
Blurred vision.
Fluctuating vision.
Impaired color vision.
Conservative management of cataracts?
Stronger lenses.glasses, brighter lighting, does not slow progression, only improves vision for a while
What is shown? ?causes and treatment

Corneal ulcer focal staning with fluorescein
Give antibiotics, often gent and a quinolone
Commonly staph or pseudomonas
Cataract presentation?
Reduced vision, faded colour vision, glare and halos around lights
What is this? usual treatment?

Blepharitis, good lid hygiene and warm compresses
ABX not usually needed unless evidence of infection such as crusting which may indicate staph
Signs of hypertensive retinopathy on pictures?
Flame haemorrhages, dots and blots, lots of cotton wool spots
Retinal photo features of diabetic retinopathy (non proliferative) ?
microaneurysms
blot haemorrhages
hard exudates
cotton wool spots,
venous beading/looping and intraretinal microvascular abnormalities
Grade iv hypertensive retinopathy?
Pappiloedema present
Thickened macular oedema treatment?
Anti VEGF
What type of glaucoma can present suddenly?
Acute angle closure
Usual first test for evaluationg ocular trauma?
CT
Possible xrays if clear history of radio-opaque injury eg hammering nail or iron filings
Causes of RAPD?
Optic neuritis
Glaucoma
Optic nerve lesion
Retinal detachment
Ischaemic optic disease
What is shown? Diagnosis and why?

Proliferative retinopathy due to new vessel formation in disc and overlying vessels everywhere
Recent URTI presents with gritty painful red eye?
Likely viral conjuncitivitis self limiting condition
Purulent red eye, eyes stuck together?
Treatment?
Acute bacterial conuncitivitis
Self limiting often given ABX chloramphenicol or fusidic acid in pregnancy
Symptoms of corneal ulcer?
watery eyes, discharge, visual acuity loss, painful, red eye, photophobia
Cataract type with diabetes?
Dot opacities
What is this what can be seen?

HTN retinopathy lots of cotton wool spots and haemorrhages
Subscapular cataract?
Steroid use
What should BP be in diabetics with end organ damage eg eye involvement?
130/80
Red eyes
Itch is prominent
the eyelids may also be swollen
May be history of atopy
What and first line treatment?
Allergic conjunctivitis often associated with hayfever
topical antihistamines first line
sodium cormiglicate second line
Factors that predispose to angle closure glaucoma?
Long sightedness, pupil dilation and lense growth with age
Most common type of cataract and cause?
Nuclear changes refractive index of lenses common old age
Most common cause of cataract?
Ageing
Patient presents with this eye, feels sick has had ocular pain too … diagnosis?

Acute glaucoma- note reddening and mid dilated pupil with history of vision loss and pain
What features are shown? Likely cause?

macular oedema: exudate (yellow arrow), microaneurysms (red arrow), thickened retina (white circle), cystic change at macula (blue arrow)
Non-proliferative diabetic retinopathy
Inherited cataract type?
Polar
Presentation of scleritis and episcleritis? Differentiate?
Both conditions present with a red eye which may be painful
Episcleral vessels can be moved with a cotton bud. When phenylephrine 10% is applied, they blanch
Scleral vessels appear darker, follow a radial pattern, are immobile and do not blanch.
Specific pain of scleritis?
Boring eye pain
Onset of episcleritis vs Scleritis?
Epi acute scler insidious
Associated symptoms of sclertiis and episcler?
scleritis Yes, nausea vomiting
Episcleritis no
Visual problems scleritis or episcleritis?
Scleritis
Associated diseases with episcleritis?
Often idiopathic but may be common in IBD
rarely RA or connective
Episcleritis management?
Artificial tears may provide some relief, particularly in nodular disease.
The use of topical non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) can be helpful in more symptomatic patients.
Scleritis associated disease? How common?
Very common up to 50% usually RA
Suspect scleritis do what? What investigations?
Refer immediately to ophthal think about underlying pathology as very often there is some
Scleritis treatment?
Nsaids initially Ibuprofen and then if not effective steroids 80mg
If necrotising steroids and immunosupression immediately
Anterior uveitis/iritis associated with?
HLA b27 Ank spon
What condition is shown?
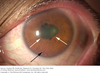
Uveitis
Presentation of anterior uveitis?
Usually unilateral.
Pain, redness and photophobia are typical.
Eye pain is often worse when trying to read.
excessive tearing
headache, unreactive and irregular shaped pupil
What is entropion?
Invertion of the eyelashes irritating the eyes
Types of ARMacDegen and which more common?
Wet and dry- wet 10% dry 90%


