Nutrient Digestion and Absorption 2 Flashcards
(33 cards)
What form does most of the digested fat take?
Triacylgycerol
What is responsible for fat digestion?
•All fat digestion in small intestine by pancreatic lipase
What is the effect of lipase on triacylglycerol?
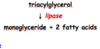
Desribe the solubility of triacylglycerol and lipase
- Triacylglycerols present as large lipid droplets which are insoluble in water
- Lipase = water-soluble enzyme
- digestion can only take place at surface of droplet - very slow
What is meant by emulsification?
dividing large lipid droplets into smaller droplets (~1 mm diameter) - increased surface area and accessibility to lipase action.
What are the two requirements for emulsification?
Mechanical disruption and an emulsifying agent
What is responsible for the mechanical disruption?
(The process of changing large lipid droplets into small droplets)
- smooth muscle contraction grinds and mixes lumenal contents. (muscle within muscularis externa)
What is the function of an emulsifying agent?
•prevents small droplets reforming into large droplets.
What are the emulsifying agents?
Bile salts and phospholipids
What type of molecule are phospholipids?
Amphiphatic
What portion of the phopholipid is exposed to the water?
The polar portion
How do these exposed polar portions prevent the reforming of large lipid droplets?
Polar portions repel other small lipid droplets
What is the funciton of micelles?
Enhance absorption of lipase digestion products
What is the difference between micelles and emulsion droplets?
•Micelles similar to emulsion droplets but much smaller (4-7 µm diameter)
What are the components of a micelle?
•bile salt + monoglycerides + fatty acids + phospholipids
What composes the micelle core?
Non-polar portions
What happens when micelles breakdown?
Release of small amounts of free fatty acids (FFA) and monoglycerides into solution - diffusion across plasma membrane of absorbing cells.
Fatty acids and monoglycerides are in dynamic equilibrium between micelles and solution. The digestion products are held in solution whilst being replenished as they are being absorbed.
Look

What happens to the fatty acids and monoglycerides after they are absorbed by the epithelial cells?
They enter the smooth endoplasmic reticulum where they are reformed into triacylglycerols by enzymes located within the SER.
What happens to the triacylglycerol formed by the SER?
Coated with amphiphatic protein (emulsification) and then transported through the cell in vesicles formed from the sER membrane, they are processed through the golgi apparatus and exocytosed into the extracellular fluid at serosal membrane
What is the name given to extracellular fat droplets?
Chylomicrons
What do Chylomicrons contain?
phospholipids, cholesterol & fat-soluble vitamins
and of course triacyglycerol
What is larger chylomicrons or micelles?
Micells are 4-7 µm diameter
Chylomicrons are ~1 µm diameter
What is the movement of chylomicrons?
They pass into the lacteal between endothelial cells (they cannot pass through the capillary basement membrane - tight junctions).




