Nucleotides and Nucleic Acids Flashcards
Readings: Chapter 19 pp 573-586
What are four processes in which mono and dinucleotides are involved in?
- oxidation-reduction reactions
- Energy transfer
- intracellular signalling (cAMP)
- Biosynthetic reactions (ATP - energy transfer | NADPH - redox reactions)
How are polynucleotides used (2)
- storing and decoding genetic information (DNA/RNA)
- enzymes - ribozymes (eg ribosomes)
What are nucleotides composed of?
- Phosphate(s)
- Sugar
- Nitrogen-containing aromatic base (Heterocyclic rings)

How does the number of phosphates differ between nucleotide polymers and mononucleotides
Nucleotide polymers often have 1 phosphate for each sugar and base
BUT
Mononucleotides may contain multiple phosphates
What determines the structure of the nucleic acids?
The structure of nucleotides incorporated into nucleic acids determines the structure of the nucleic acids.
ie structure of monomers influences polymers
What is the image?
How do you know?

A basic pyrimidine
- 6-member ring
- N at positions 1 and 3
What is the image?
How do you know?

Basic Purine
- 6-member ring with 5-member ring
- N at positions 1, 3, 7, 9
What is the molecule in the image?
How do you know?
How many hydrogen bonds can it form?

Uracil:
- pyrimidine
- 6-membered ring with N at 1 and 3
- Substituents at positions 2, and 4 (in this case 2 carbonyl groups)
- Can form 6 H-bonds
- 2 as donor
- 4 as acceptor

What is the molecule in the image?
How do you know?
How many hydrogen bonds can it form?

Thymine
- Pyrimidine: 6-member ring with N at 1,3
- Substituents at 2,4 (in this image, carbonyl groups)
- methyl group at 5
- Can form 6 H bonds
- 2 donor
- 4 as acceptor

What is the molecule in the image?
How do you know?
How many hydrogen bonds can it form?

Cytosine
- Pyrimidine: 6 member ring with N at 1 and 3
- Carbonyl at C2
- NH2 at C4
- Can form 6 H-Bonds
- 3 donor
- 3 acceptor

What is the molecule in the image?
How do you know?
How many H-Bonds can it form?

Adenine
- Purine: 6 member ring + 5 member ring
- N at 1, 3, 7, 9
- NH2 at C6
- 6 H-bonds
- 3 acceptor
- 3 donor

What is the molecule in the image?
How do you know?
How many H-bonds can it form?

Guanine:
- Purine
- 6C ring + 5C ring
- N at 1, 3, 7, 9
- Carbonyl at C4
- NH2 at C2
- 7 H-bonds
- 3 acceptor
- 4 donor

How do Uracil and thymine differ in the pattern of H-bond potential?
They don’t.
Uracil and thymine have the same pattern of H-Bond potential
Why can the N at C3 in Cytosine be a H-bond acceptor?
The N at C3 has no H associated therefore it is sp2 hybridized with a lone pair

Hydrogen attached to nitrogen can always act as a __________
Hydrogen attached to nitrogen can always act as a Hydrogen bond donor
Can a nitrogen within a ring be a hydrogen bond acceptor?
Not unless it has a lone pair within sp2 hybridized orbital such as the case with N1,3,7 in adenine, N7 in guanine and N3 in cytosine
All H-bond potential for Purines and pyrimidines is localized to the _______
All H-bond potential for Purines and pyrimidines is localized to the equatorial region of the bases
- ie around the edge of a planar structure of either purine based ring or pyrimidine based ring
What is the difference between thymine and uracil?
Thymine has a methyl group at C5

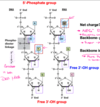
What is a nucleoside?
Base + Sugar
-Purine or Pyrimidine base linked to a 5C sugar (pentose)
Purine and pyrimidine bases are linked to a five-carbon sugar to form _______
Purine and pyrimidine bases are linked to a five-carbon sugar to form nucleosides

How are pyrimidines attached to pentose?
N1 in pyrimidines attaches to the 1’ C of the sugar (loses h-attachment)

How do purines attach to the 5C sugar to form nucleosides?
Through N9 to 1’C in the sugar
- N9 will no longer be able to form an H-bond when attached to sugar

How are ribose and deoxyribose different?
In ribose there is 2’ OH and a 3’ OH
In deoxyribose there is a 3’ OH but NO 2’OH
- therefore, in DNA, the sugar is 2’ deoxyribose

How do you name nucleosides?
Purines:
Pyrimidines:
How do you name nucleosides?
- Purines:
- Adenine+ribose = adenosine (ribonucleoside)
- Adenine+deoxyribose = deoxyadenosine
- Guanine + ribose = guanosine
- Guanine+deoxyribose = deoxyguanosine
- Pyrimidines:
- Cytosine
- +ribose = cytidine
- Thymine
- +deoxyribose = deoxythmidine
- +ribose (RARE) = thymidine or ribothymidine
- Uracil
- +ribose + uridine
- Cytosine