6 Biological Membranes Flashcards
Lipids are compounds that are primarily:
- ______
- ______
- _______ (beh in water)
Compounds that are primarily:
- Non-polar (or amphipathic)
- Hydrophobic
- Insoluble in water
What are four types of lipids?
- Fatty acids
- Triacylglycerol
- Membrane lipids
- Cholesterol
What are Fatty acids?
- Long chain hydrocarbon carboxylic acid
- up to 24 carbons long (16 & 18) most common
- General formula (for a saturated Fatty Acid) CH3(CH2)NCOO-
- Amphipathic (Amphiphilic)
- Polar and non-polar portions
- May be saturated or unsaturated
- Saturated = no double bonds
- Unsaturated = double bonds
- Mono- or polyunsaturated (1+ DB’s)
- usually cis (z) double bonds
FATTY ACIDS are:
- Long-chain _____________\_
- up to __\_carbons long (__\_ & __\_ most common)
- General formula (for a saturated Fatty Acid) ________\_
-
_____\_(_____\_)
- Polar and non-polar portions
- May be _____\_or _____\_
- _____\_ = no double bonds
-
_____\_ = double bonds
- Mono- or polyunsaturated (1+ DB’s)
- usually _____\_ conformation double bonds
FATTY ACIDS are:
- Long-chain hydrocarbon carboxylic acid
- up to 24 carbons long (16 & 18 most common)
- General formula (for a saturated Fatty Acid) CH3(CH2)NCOO-
-
Amphipathic (Amphiphilic)
- Polar and non-polar portions
- May be saturated or unsaturated
- Saturated = no double bonds
-
Unsaturated = double bonds
- Mono- or polyunsaturated (1+ DB’s)
- usually cis (z) conformation double bonds
What type of molecules are shown in the image?

Fatty acids (Lipids)
(a) is saturated
(b) is monounsaturated (1 double bond between C9 and C10)
(c) is polyunsaturated (>1 double bond)
* ALL in Z or CIS configuration
Would CIS or TRANS conformation of Fatty acids be more favourable? Why?

- TRANS appears more energetically favourable
- HOWEVER impact of of CIS = Creates a kink in the structure
- affects melting point (lowers mp) = liquid at room temperature
- Most naturally occurring db’s are in the cis conformation
- Most naturally occurring double bonds are in the ___\_ conformation
- impact of __\_ = Creates a kink in the structure
- affects _______\_ = liquid at room temperature
- Most naturally occurring double bonds are in the cis conformation
- impact of CIS = Creates a kink in the structure
- affects melting point (lowers mp) = liquid at room temperature
What is the shorthand notation of fatty acids and what does it identify about the structure?
- Shorthand notation identifies: (#C):(#double bonds)Δ(locations of the double bonds)
- eg:
- CH3CH2CH2CH2CH2COOH is 6:0 (5 carbons, no double bonds)
- carbon 1 is associated with the -OOH (carboxyl group)
In a fatty acid, what Carbons would be designated alpha α, beta β, and omega ω?
Alpha: Carbon 2 (the carbon attached to the carboxyl group (COOH))
Beta: Carbon 3 - follows alpha
Omega: The last carbon in the chain

Give the shorthand notation for the fatty acid in the image
- Is it a cis or trans double bond?

16:1 Δ7
Cis double bond

Provide the shorthand notation for the fatty acid in the image:

16:1 trans Δ7

If a shorthand notation for a fatty acid doesn’t indicate cis or trans explicitly, what can you assume it’s configuration is?
CIS
How do double bonds affect fatty acids?
Double bonds alter the shape of fatty acids
As length of the fatty acid chain increases, what happens to the Melting Point?
Melting point increases with length
How does melting point change with increased degrees of unsaturation?
Melting point decreases with increased degrees of unsaturation (more double bonds)
What two properties affect the fatty acid melting points and how?
- Length
- longer fatty acids melt at higher temperatures
- shorter fatty acids melt at lower temperatures
- Unsaturation
- Saturated fatty acids melt at higher temperatures
- Unsaturated fatty acids melt at lower temperatures
- Has a greater effect on melting point than length
Does length or unsaturation have a greater effect on melting point (fatty acids)
Unsaturation has a greater effect
Why does unsaturation have such a dramatic effect on melting point of fatty acids?
- Saturated fatty acids can align closely to maximize van der waal’s interactions
- Unsaturated fatty acids are bent = interferes with close packing
- Trans fatty acids are able to pack better than Cis ones

What is triacylglycerol (TAG)?
Molecule that contains fatty acids as part of its structure; also contains glycerol
- Very hydrophobic (NOT amphipathic)
- way of storing fatty acids
- Three (ester-linked) acyl chains attached to glycerol

Three acyl chains attached to glycerol make up what molecule?
Triacylglycerol
- Acyl chains from fatty acids (ester linked)
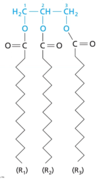
What is the molecule in the image?

Triacylglycerol
- 3 acyl chains attached to glycerol
- acyl chains from fatty acids (ester-linked)

TAG (triacylglycerol) is extremely ________ (not amphipathic). Why?
TAG (triacylglycerol) is extremely Hydrophobic (not amphipathic). Why?
- This is due to the Ester-linkage between the polar hydroxyls of glycerol and the polar carboxylates of the fatty acids.
- TAG (triglycerides) are hydrophobic, non-polar, and insoluble in water
Forms droplets in aqueous environment.

Melting points for triacylglycerols will be lower for those containing ________ or ________
Melting points for triacylglycerols will be lower for those containing unsaturated fatty acids or Shorter chains
What are the three lipids found in the membrane (ie membrane lipids)?
- Glycerophospholipids
- Sphingolipids
- Cholesterol
Glycerophospholipids and sphingolipids contain fatty acids as part of their structure and are structurally similar