Neurotransmisores y Receptores Flashcards
Secreción y difusión de norepinefrina, serotonina, dopamina y acetilcolina.
Estructuras que secretan (nor)epinefrina
The chemical transmitter present at most sympathetic postganglionic endings is norepinephrine.
It is stored in the synaptic knobs of the neurons that secrete it in characteristic small vesicles that have a dense core.
Norepinephrine and its methyl derivative, epinephrine, are secreted by the adrenal medulla, but epinephrine is not a mediator at postganglionic sympathetic endings.
Each sympathetic postganglionic neuron has multiple varicosities along its course, and each of these varicosities appears to be a site at which norepinephrine is secreted.
There are also norepinephrine-secreting and epinephrine-secreting neurons in the brain. Norepinephrine-secreting neurons are properly called noradrenergic neurons, although the term adrenergic neurons is also applied. However, it seems appropriate to reserve the latter term for epinephrine-secreting neurons.
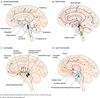
The cell bodies of the norepinephrine-containing neurons are located in the locus ceruleus and other medullary and pontine nuclei (Figure 7–2).
From the locus ceruleus, the axons of the noradrenergic neurons form the locus ceruleus system. They descend into the spinal cord, enter the cerebellum, and ascend to innervate the paraventricular, supraoptic, and periventricular nuclei of the hypothalamus, the thalamus, the basal telencephalon, and the entire neocortex.



