Neuro 1 Flashcards
Components of neurological examination
- Assessment of awareness/level of consciousness
- Posturing
- Mental Status
- Speech Assessment
- Cranial Nerve Examination
- Cerebellar/Coordination Testing
- Gait Examination
- Motor and Strength Examination
- Reflex Testing
- Sensory Examination
Components of the Mental Status Exam (MSE)
- General appearance, behavior, and attitude
- Level of consciousness and orientation
- Speech and language
- Mood and affect
- Thought process, Content, and Perceptions
- Memory and cognition
- Judgment and insight
What level of consciousness?
- Patient is able to open eyes, look at you, and responds fully and appropriately
Alert
What level of consciousness?
- Patient is drowsy, but can open eyes, look at examiner, and respond. Falls back to sleep easily.
Lethargic
What level of consciousness?
- Patient opens eyes and looks at you, offers confused responses, has lack of interest in environment
Obtunded
What level of consciousness?
- Patient wakens only with painful stimuli. Verbal responses slow or absent. Falls back into unresponsive state when stimuli ceases
Stuporous
What level of consciousness?
- Patient is unarousable to any stimuli
Comatose
What posture is this?
–Upper extremities flexed at the elbows and held closely to the body
–Lower extremities are internally rotated and extended
Decorticate posture
___________
–Thought to occur when the brain stem is not inhibited by the motor function of the cerebral cortex.

Decorticate posture is thought to occur when…..

–Thought to occur when the brain stem is not inhibited by the motor function of the cerebral cortex.

What posture is this?
- Rigid flexion;
- upper arms held tightly to side of body;
- elbows, wrists, and fingers flexed;
- feet are plantar flexed
- legs extended and internally rotated;
- may have fine tremors or intense stiffness
Decorticate

What is the site of lesion for decorticate posture?
corticospinal tracts, above the brainstem

What posture is this?
–Seen in persons with extensive brain stem damage to the pons and lesions that compress the lower thalamus and midbrain
Decerebrate Posture

What posture is this?
- Rigid extension
- arms fully extended
- forearms pronated
- wrists and fingers flexed
- jaws clenched
- neck extended
- back may be arched
- feet plantar flexed
- may occur spontaneously, intermittently, or in response to a stimulus
Decerebrate

What is the site of lesion for the decerebrate position?
brainstem
3 questions of Orientation?
- Name
- Day or date
- Where are we?
Assessing speech and language. You are assessing:
- Talkative or silent?
- Does the patient speak spontaneously or only when directly questioned?
What aspect of speech and language is that?
Quantity
Assessing speech and language. You are assessing:
- Is the speech too fast, too slow, or just right?
What aspect of speech and language is that?
Rate
Assessing speech and language. You are assessing:
- Is the speech too loud, too quiet, or just right?
What aspect of speech and language is that?
Volume
Assessing speech and language. You are assessing:
- Can you understand what the patient is saying physically? If not, why not?
What aspect of speech and language is that?
Articulation
Assessing speech and language. You are assessing:
- Is the rate, flow, melody, and content of speech within normal limits?
What aspect of speech and language is that?
Fluency
Assessing speech and language:
If the rate, flow, melody, and content of speech are not within normal limits, what should you suspect?
If not, suspect an aphasia.
Speech and Language/Fluency
What are you testing?
- Ask patient to follow one or two step command
Word comprehension
Speech and Language/Fluency
What are you testing?
- Ask patient to repeat, “No ifs, ands, or buts”
Repetition
Speech and Language/Fluency
What are you testing?
- Ask patient to name the parts of a watch
Naming
Speech and Language/Fluency
What are you testing?
- Ask patient to read a paragraph out loud
Reading
Speech and Language/Fluency
What are you testing?
- Ask patient to write a sentence
Writing
________ is the external expression of emotion visible to the clinician
Affect
What are you assessing?
•Are the pts responses and body language devoid of emotion?
Affect
What are you assessing?
•Are their responses hyper-emotional?
Affect
What are you assessing?
•Do the pts responses change dramatically through the interview?
Affect
What are you assessing?
•Are the responses appropriate to the patient’s situation or what they are saying?
Affect
What are you assessing?
•Does the pt have poor eye contact?
Affect
Mood tends to alter quickly and spontaneously; unstable. This is called ______
Labile mood
How do you assess the patient’s mood?
To assess mood, you need to ask the patients how they are feeling
Assessment of Thought Process
Identify:
– speech shifts from one topic to another that is not clearly related to the first topic without the patient realizing that the topics are unrelated.
Derailment or loose associations
Assessment of Thought Process
Identify:
•– only partially relevant or irrelevant responses to questioning
Tangentiality
Assessment of Thought Process
Identify:
•– Patient speaks more and more quickly than would be ordinarily expected. Patient gives long answers to brief questions and may not finish one thought before starting another.
Pressured speech
Assessment of Thought Process
Identify:
•– speech makes no sense at all (aka “word salad”)
Incoherence
Assessment of Thought Process
Identify:
•– speech is delayed in reaching goal because of unnecessary detail, however components are properly related
Circumstantiality
Assessment of Thought Process
Identify:
•– During the course of a discussion, pt changes subject in response to something unrelated in the environment.
Distractable speech
Assessment of Thought Process
Identify:
•– persistent repetition of specific words or ideas
Perseveration
Assessment of Thought Process
Identify:
•– word choice doesn’t make any sense because words are chosen based on the sound they make (often rhyming), not their meaning.
Clanging
Assessment of Thought Process
Identify:
•– Fabrication of facts to fill in gaps of memory
Confabulation
Assessment of Thought Content
Identify:
•– Recurrent, uncontrollable thoughts or images that are unwanted and unpleasant to the pt.
Obsessions
Assessment of Thought Content
Identify:
•Repetitive behaviors or mental acts that the pt. feels driven to perform to produce relief or to prevent some future consequence (although that consequence is unlikely)
Compulsions
Assessment of Thought Content
Identify:
•– False, fixed personal beliefs that are not shared by others in the pts community
Delusions
Assessment of Thought Content
Identify:
•– Persistent, irrational fears accompanied by desire to avoid the stimulus
Phobias
Assessment of Thought Content
The below are all examples of _______:
–Persecution
–Grandiosity
–Delusion of being controlled externally
–Somatic delusions
–Jealousy
Delusions
Assessment of Thought Content
Identify:
•– A sense that things in the environment are unreal, strange or remote
Feelings of Unreality
Assessment of Thought Content
Identify:
•– A sense that the inner self has become detached from the mind or body
Feelings of Depersonalization
Assessment of Thought Content
Identify:
•– Fears, tensions, or uneasiness that may be focused or free-floating
Anxiety
Assessment of Perceptions
Identify:
•– misperception of real external stimuli
Illusions
Assessment of Perceptions
Identify:
•– false perceptions. Pt hears, sees, smells or feels something others cannot.
Hallucinations
Assessment of Memory
Identify:
- Can pt. learn something new and repeat it back?
Registration
Assessment of Memory
Identify:
•Can the patient correctly remember things that happened today?
Recent Memory
Assessment of Memory
Identify:
•Can the patient correctly remember things that happened or information from long ago?
Remote Memory
Assessment of Cognition
Identify:
•Can the patient focus enough to be able to perform tasks?
Attention
Assessment of Cognition
Identify:
•Assess patient’s apparent intelligence by assessing the degree to which they are informed and the complexity of their vocabulary
Information and vocabulary
Assessment of Cognition
Identify:
•– Ask the patient to interpret a commonly used proverb
Abstract Thinking: Proverbs
Assessment of Cognition
Identify:
–Ask the patient to tell you how two things are alike
Abstract Thinking: Similarities
Assessment of Judgment
What are the two ways to assess judgment?
–Ask patients to propose a solution to their current problems: “How will you get follow up care after you leave here today?”
–Ask patients to propose a solution to a hypothetical problem: “What would you do if you found a stamped, addressed letter on the ground?”
___________ is the ability to evaluate a situation and form an appropriate response
Judgment
________ is the ability of patients to understand and acknowledge their illness or situation.
insight
Standardized way to test mental status that is:
- Validated many times
- Easy to administer
- Results reproducible across examiners
- Brief and well-tolerated by patients
Mini Mental State Exam (MMSE)/ “Folstein” test

How do you score MMSE?
- 27 – 30 = Normal
- 20 – 26 = Mild Dementia
- 10 – 19 = Moderate Dementia
- < 10 = Severe Dementia
**For pts > 80 years old, 25 or more is normal.
**Patients with low levels of education (less than 8th grade) will score lower from the start
Assessment of Speech Disorders
Identify:
•– loss of ability to speak because of damage to larynx or throat
Aphonia
Assessment of Speech Disorders
Identify:
– Difficulty speaking due to abnormalities of the oral and facial muscles that produce speech. Cause can be central or peripheral. Speech sounds “sloppy”.
Dysarthria
Assessment of Speech Disorders
Identify:
•– loss of comprehension or power of expression of speech.
Aphasia
Assessment of Speech Disorders
Identify:
–Pt can comprehend perfectly, but not speak fluently. You know that they understand because they can nod or shake head appropriately.
Broca’s aphasia – is an expressive aphasia.
Assessment of Speech Disorders
Identify:
– Pt cannot comprehend language, but is able to speak fluently. Patient usually speaks gibberish.
Wernicke’s aphasia – is a receptive aphasia.
Cranial nerves are _____ nerves
Peripheral
Cranial Nerve I Exam
•I = OLFACTORY
–One nostril at a time!!!
–Don’t Use A Noxious Stimulus
–Coffee, Cinammon, Mint
Cranial Nerve II Exam
- II = OPTIC NERVE
- Evaluation:
–Visual Acuity Test
–Visual Fields by Confrontation
–Funduscopic Exam
Cranial Nerve III/IV/VI Exam
•III = OCULOMOTOR
–Observe lids for ptosis
–Pupillary response to light (CN II & III) and accommodation (PERRLA)*
–Extraoccular movements (EOMs)
- CARDINAL POSITIONS
- IV = TROCHLEAR – superior oblique muscle
- VI = ABDUCENS – lateral rectus muscle
Ptosis is which cranial nerve?
CN III (three) oculomotor
Cranial nerves and eye muscles: what statement to remember?
•“LR VI, SO IV, all else III”

Assessing Pupillary Response To Light. Which CNs?
•Assesses CN II & III
Cranial Nerve V Exam
•V = TRIGEMINAL
MOTOR :
–Masseter & Temporalis
–movement & strength
SENSORY :
–Light touch and sharp /dull – all 3 divisions bilaterally
–Corneal Reflex
Cranial Nerve VII Exam
VII = FACIAL
Observe for:
–Facial asymmetry
–Strength of facial muscles
- Raise eyebrows
- Smile
- Show teeth
- “Puff out cheeks and don’t let me push them in”
- Purse lips
- Close eyes against resistance
Identify:
–Forehead wrinkling preserved
–Mild weakness of eye closure
–Flat nasolabial fold
–Most common cause is stroke
Central Seventh Nerve Paralysis
Identify:
–Entire side of face affected
–Forehead not wrinkled on affected side
–Severe weakness of eye closure on affected side
–Flat nasolabial fold on affected side
–Cause: cranial neuropathies. Most commonly, Bell’s Palsy
Peripheral Seventh Nerve Paralysis
Cranial Nerve VIII Exam
VIII = VESTIBULOCOCHLEAR
–Auditory Acuity
•Document stimulus used (Weber, Rinne, hair rub, whisper)
Cranial Nerve IX/X Exam
•IX = GLOSSOPHARYNGEAL
–Gag reflex and ability to swallow
–Can the pt taste sour and bitter tastes?
X = VAGUS
–Say “ahhh” - uvula elevates symmetrically /deviates AWAY from side of lesion
–Observe ability to swallow
Cranial Nerve XI Exam
XI = ACCESSORY
• Assessment of muscle
strength bilaterally
• Trapezius:
–Shoulder shrug against resistance
• Sternocleidomastoid:
–Left/right rotation of neck against resistance
Cranial Nerve XII Exam
XII = HYPOGLOSSAL
•Observe tongue at rest, then protruded. In both:
–Inspect for fasciculations
–Tongue should be in midline
–Unilateral paralysis-the tongue deviates TOWARD the affected side.
•Press tongue against inside of cheek and you attempt to push it away to assess strength.
–
Coordination / Cerebellar Testing
Testing assesses integration of:
Cerebellar system:
–rhythmic movements and posture
Coordination / Cerebellar Testing
Testing assesses integration of:
Vestibular system
––balance, & eye, head & body movements
Coordination / Cerebellar Testing
Testing assesses integration of:
Sensory system
––position sense (aka proprioception)
What does the below test?
•Rapid Alternating Movements (RAM)
Coordination testing
What does the below test?
•Point-to-point Testing (Finger to Nose and Heel-Knee-Shin)
Coordination testing
What does the below test?
•Romberg testing
Coordination testing
What does the below test?
•Pronator Drift
Coordination testing
Rapid movement testing results in non-fluid movements or inability to keep track of the order. What is this called?
(i.e. abnormal rapid movement testing)
Dysdiadochokinesis
Point to point testing results in inability to find the finger /nose, or to smoothly run down leg . What is this called?
(i.e. abnormal point to point testing)
Dysmetria
What are the two tests for point-to-point testing?
- –Finger-to-nose
- –Heel-knee-shin
What does the ROMBERG TEST assess?
–CEREBELLAR FUNCTION
–PROPRIOCEPTION (position sense)
What is a positive ROMBERG TEST?
•pt stands well with eyes open but loses balance with eyes CLOSED
–this result is abnormal–
What does PRONATOR DRIFT test?
- Part 1: Holding up a pizza box with eyes closed ONLY
–Upper Motor Neuron Function
–PROPRIOCEPTION (position sense)
If you do the PRONATOR DRIFT test, what is a clear indication a patient is faking?
•Patients who are faking will let their arm fall, but will not pronate
If you do the PRONATOR DRIFT test, what is a clear indication of upper extremity weakness?
•the arm will begin to pronate and fall
What does PRONATOR DRIFT test?
- Part 2: Tapping the arms and watching recoil
–PROPRIOCEPTION (position sense) only
What does PRONATOR DRIFT test?
- Part 2: Tapping the arms and watching recoil
What’s a normal response? Abnormal response?
–PROPRIOCEPTION (position sense) only
- Normal = rapid return to baseline position
- Abn = unable to quickly return to baseline position
Gait Assessment
What does the below test?
- Walk casually across room and include turns
gait abnormalities
Gait Assessment
What does the below test?
- Walk On toes
distal muscle weakness
Gait Assessment
What does the below test?
- Walk On heels
–distal muscle weakness
Gait Assessment
What does the below test?
- Rise from sitting position
–proximal muscle weakness
6 assessments of Gait
- Casually walk across room and include turns
- On toes
- On heels
- Tandem
- Hopping on one foot in place
- Rise from sitting position
Gait Abnormalities
Identify:
–Shuffling gait with leg extended and held stiff
•Spastic Gait
–Unilateral corticospinal tract injury such as stroke or traumatic brain injury

Gait Abnormalities
Identify

•Spastic Gait

–Unilateral corticospinal tract injury such as stroke or traumatic brain injury
–Shuffling gait with leg extended and held stiff
Gait Abnormalities
Identify

•Scissors Gait

–Bilateral corticospinal tract injury
–Adductor spasm, knees pulled together, knees and thighs hit each other
–Seen in cerebral palsy, MS
Gait Abnormalities
Identify:
–Adductor spasm, knees pulled together, knees and thighs hit each other
•Scissors Gait

–Bilateral corticospinal tract injury
–Seen in cerebral palsy, MS
Gait Abnormalities
Identify:
–Hip and knee are elevated excessively high to lift the foot off the ground. The foot is brought down to the floor with a slap.
–Patient cannot walk on heels
•Steppage Gait
–Cause: Loss of ability to dorsiflex ankle
–Seen in neuropathies/ radiculopathies

Gait Abnormalities
Identify:

•Steppage Gait

–Cause: Loss of ability to dorsiflex ankle
–Hip and knee are elevated excessively high to lift the foot off the ground. The foot is brought down to the floor with a slap.
–Patient cannot walk on heels
–Seen in neuropathies/ radiculopathies
Gait Abnormalities
Identify:

•Cerebellar Gait

–Feet set wide apart and steps are unsteady, uncertain and of variable length
–Indicator of cerebellum damage (including severe alcohol intoxication)
Gait Abnormalities
Identify:
–Feet set wide apart and steps are unsteady, uncertain and of variable length
•Cerebellar Gait

–Indicator of cerebellum damage (including severe alcohol intoxication)
Gait Abnormalities
Identify:
–Small steps and is decreased arm swing when walking
–Head and body are flexed and arms are semi-flexed and abducted
•Basal Ganglia Gait (Parkinson’s or Festination gait)
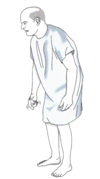
Gait Abnormalities
Identify:

•Basal Ganglia Gait (Parkinson’s or Festination gait)
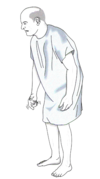
–Small steps and is decreased arm swing when walking
–Head and body are flexed and arms are semi-flexed and abducted
Gait Abnormalities
What does this indicate?
•Spastic Gait
–Unilateral corticospinal tract injury such as stroke or traumatic brain injury
Gait Abnormalities
What does this indicate?
•Scissors Gait
–Bilateral corticospinal tract injury
–Seen in cerebral palsy, MS
Gait Abnormalities
What does this indicate?
•Steppage Gait
–Cause: Loss of ability to dorsiflex ankle
–Seen in neuropathies/ radiculopathies
Gait Abnormalities
What does this indicate?
•Cerebellar Gait
–Indicator of cerebellum damage (including severe alcohol intoxication)
Gait Abnormalities
What does this indicate?
•Basal Ganglia Gait
–Indicator of Parkinson’s or Festination gait
Gait Abnormalities
A person with Steppage Gait cannot walk on _____
heels
–Loss of ability to dorsiflex ankle


