Neoplasia 1 Flashcards
What is neoplasia?
an abnormal mass of tissue, that proliferates faster than the rest of the tissue, even without the stimuli
what is this?

carcinoma of the pancreas
what is the fourth leading cause of cancer deaths in the United States?
Pancreatic cancer - Infiltrating ductal adenocarcinoma of the pancreas
what are the 2 components that define neoplasia?
- proliferating neoplastic cells (parenchyma)
- supporting tissue (stroma)
- desmoplasia is seen: abundant collagenous stroma
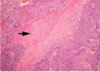
what is this?
what are the arrows pointing at?

neoplasia
Tumor cells in nests and surrounding fibro-collagenous stroma.
what is this picture an example of?

Desmoplastic round cell tumor:
what is this picture an example of?

Desmoplastic round cell tumor:
What is this picture an example of?

Desmoplastic round cell tumor:
who usually gets desmoplastic round cell tumor?
adolescent, young adults, male
where does dermoplastic round cell tumor grow usually?
Intra abdominal tumor
how aggressive is a desmoplastic round cell tumor? can it be removed?
very aggressive
complete removal is not possible due to infiltration of abdominal structures
benign tumors have what suffix?
-oma
what are 2 types of benign tumors?
- mesenchymal tumors
- epithelial tumors
what are 3 examples of benign mesenchymal tumors?
- fibroma
- osteoma
- chondroma
what are 3 examples of benign epithelial tumors?
- adenoma
- papilloma
- cystadenoma
what is this?

osteoma
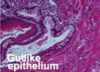
what is this?

adenoma or polyp
what is a adenoma?
a tumor composed of solid glandular tissue with structures closely arranged
what is important to remember of adenomas of the endocrine glands?
they may not show glands, but show cells resembling the respective tissue.
what is important to remember of adenomas arising in glands that grow into lumen?
they become pedunculated to form ‘polyps’.
what is a cystadenoma?
adenomas exhibiting cystic spaces into which papillary ingrowths of neoplastic epithelium protrude.
what is an example of cystadenoma?
papillary’ cystadenoma of ovary (can be mucous or serous)
what is a Fibroadenoma?
benign tumor seen in breast.
what is a fibroma?
common benign tumor arising mostly in oral cavity.