Negative Externalities Flashcards
(11 cards)
Define Negative Externalities.
When the consumption or production of a good causes a harmful effect to a third party.
Gice 3 examples of Negative Externalities.
- Loud music. If you play loud music at night, your neighbour may not be able to sleep.
- Pollution. If you produce chemicals and cause pollution as a side effect, then local fishermen will not be able to catch fish. This loss of income will be the negative externality.
- Congestion. If you drive a car, it creates air pollution and contributes to congestion. These are both external costs imposed on other people who live in the city.
Define Social Costs.
- Social cost is the total cost to society; it includes both private and external costs.
With a negative externality which is mostly effected Social Or Private Cost?
Social Cost > Private Cost
Define Production Negative Externality.
When producing a good causes a harmful effect to a third party.
Diagram of Production Negative Externalities.

In the free market, do producers ignore external costs to others?
YES!
At Q1 is it Socially efficient or inefficient?

Socially Inefficient becuase at Q1 - SMC (Social Marginal Cost) > SMB (Social Marginal Benefit)

Is there Social efficientcy at Q2?

YES, because the Social Marginal Benefit = Social Marginal Cost
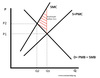
What does the RED area mean?

Is the Area of Deadweight Welfare loss, indicates the area of overconsumption. (Were SMC is greater than PMC)



