Economies of Scale Flashcards
1
Q
Define Economies of Scale
A
Is when increasing output leads to lower long-run average costs.
2
Q
Diagram of Economies of Scale
A
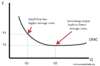
3
Q
Why are Economies of Scale important?
A
- Means that as firms increase in size, they can become more efficient.
4
Q
Example of Economies of Scale - SPECIALISATION AND DIVISION OF LABOUR
A
- Were workers do more specific tasks
- Becoming mroe specialised in a field improves the businesses efficientcy
5
Q
Examples of Economies of Scale - Technical
A
- To use a factory to its capacity
- Average costs are lower and efficientcy is improved
6
Q
Examples of Economies of Scale - Bulk Buying
A
- When you buy a large quatity average costs will be lower.
- Because of lower transport cost and packaging costs
7
Q
Example of Economies of Scale - Spreading Overheads
A
- Is if a firm merged, it could rationalise its operational centres.
- For example, it could have one head office rather than two.
8
Q
Examples of Economies of Scale - Risk-bearing Economies
A
- Some investments are expensive and risky
- So only large frims undertake this risk
- E.g. pharmaceutical industry needs to take risks in developing new drugs
9
Q
Examples of Economies of Scale - Marketing Economies of Scale
A
- Were there is little point a small firm advertising on a national TV campaign because the return will not cover the high costs.
10
Q
Examples of Economies of Scale - Financial Economies
A
- A bigger firm can get a better interest rate than smaller firms
11
Q
Examples of Economies of Scale - External Economies of Scale
A
- Is when firms benefit from the whole industry getting bigger.
12
Q
Internal Economies of Scale
A
- means the economies benefit the firm when it grows in size.


