Name that scan! Flashcards

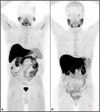
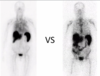
I-131 scan more metastatic thyroid cancer, beta minus decay
uptake in the thyroid shows star artifact along with multiple metastatic sites
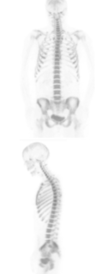
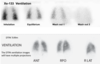
F18- NaF
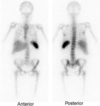
Tc-99m MDP scan,
MOA: adsorption to crystals in bone matrix
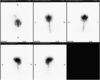
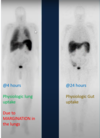
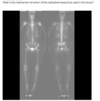
In-111 tagged WBC scan
hot spleen!!
two varieties of WBC scans: Tc-99m and In-111
Tc-99m WBC scan is preferred in kids because shorter half life (lower dose in kids) AND higher quality imaging (better spatial resolution for smaller parts)
In-111 has a longer half life –> more delayed imaging
In-111 –> less bowel uptake so preferred to evaluate for IBD


In-111 WBC in Crohns diseae with abscess


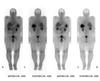
I-123 whole body pre-treatment
medium energy detector (not as crappy picture as I-131)

post thyroid ablation
what uptakes differs between pre and post treatment iodine scans?

post treatment: liver uptake (physiologic) is present in post treatment scan which is never present pre-treatment
can also see breast and colon uptake as in this case



normal distribution of Ga67


I-123 MIBG

I-123 MIBG scan. Normal or abnormal?
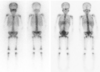
super abnormal. you shouldn’t see the bones at ALL. if you see bones on MIBG scan –> bone mets


tc99m O4 (pertechnetate)



Tc-99m MDP
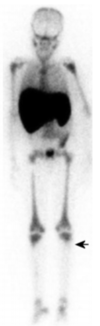
Tc-99m sulfur colloid

Tc-99m sulfur colloid scan, posterior image (spleen on screen left)
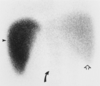
colloid shift = portal HTN
typically on SC scan the liver = spleen –> portal HTN the blood is shunted to the spleen –>
spleen > liver
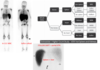

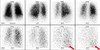
tagged RBC scan to look for bleed
Flow images of red blood cell labeled 99m-Tc gastrointestinal bleed scan: Chronological first site of bleed localized to distal ileum (arrow head) and proximal jejunum as primary site of bleed (arrow)
https://www.wjnm.org/viewimage.asp?img=WorldJNuclMed_2013_12_3_111_136735_f1.jpg

free tech in a meckel scan


altered biodistribution of MDP due to radiochemical impurity (free tech)
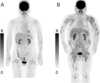
f-18 fdg pet

tc99m sestamibi