Musculoskeletal - Joints Flashcards
What is a joint?
A point where two or more bones interconnect
What are the functions of the joints?
Movement, force transmission and growth
What are the factors that affect joint movement?
The muscles that cross them
Ligament
Fat and skin
How do joints respond during force transmission compared to bone?
They are the weak points
What are the three main types of joints?
Synarthrosis, amphiarthrosis and diarthrosis
What is the relative stability and movement of the different types of joints?
Synarthrosis: high stability and low mobility amphiarthrosis: medium stability and mobility
diarthrosis: low stability and high mobility
Where do you find joints of high stability and low mobility?
In the axial skeleton
Where do you find joints of high mobility and low stability?
Appendicular skeleton
What happens to synarthrosis over time? What is this process called?
The joint will use, this is called ankylosis
What is an example of a synarthrosis joint?
The sutures in the skull –> no movement, only there to allow some growth during early development then fuse (ankylosis)
What is an example of an amphiarthrosis joint?
The vertebrate columns
How does the stability and mobility of the vertebrate change through the spine? Why?
At the top of the spine (i.e. the head) it has greater mobility and less stability. But further down the spinal cord there become more stability and less mobility
This is because lower down the spine it has more load bearing responsibilities so needs more stability
What limits the movement of the synarthrosis and amphiarthrosis joints?
The blocker tissue holding the joints together
What limits the movement of diarthrosis joints?
The attachment point of the articular capsule
What type of joint is a simply synovial joint?
Diarthrosis joint
Label the diagram, what is it showing?

A simple synovial joint

What prevents the bones from grinding on each other in a simple synovial joint? Why is it bad for the bones to grind on each other?
Articular cartilage
There are blood and nerve supplies near the joint
What attaches the bones together in a simple synovial joint? What is inside of this and what does it do?
Articular capsule (which forms a sleeve around the joint) contains synovial fluid to lubricate the joint
What are the four defining features of a diarhtorisis joint?
1 - Articular cartilage
2 - Articular capsule
3 - Joint cavity
4 - Synovial fluid
What is type of cartilage is articular?
It is a highly specialised type of hyaline cartilage
What are the different types of cartilage?
Hyaline, fibrous and elastic cartilage
What is the function of articular cartilage?
Protect the ends of bones in joints
Absorbs shocks in the joints
Can support heavy loads for long period of time
Near frictionless surface (when combined with synovial fluid)
What is the degradation of of articular tissue called?
Arthritis
What are the two main components of articular cartilage?
Cells and extracellular matrix
What kind of cells make up articular cartilage? What portion of the cartilage does this constitute?
Chondrocytes, ~5%
What is the function of the chondrocytes?
Build, repair and maintain cartilage
How does the amount of chondrocytes affect cartilage?
There is a low amount of cartilage growth and repair is very slow
Where are chondrocytes found in the joints? What is the distribution of these cells?
In lacunae
The can either be isolate cells or in groups called nests
What makes up the extracellular matrix of the articular cartilage?
Water and soluble ions
Glycosaminoglycans (GAG)
Proteoglycans
Collagen (mainly type II)
What is the function of the water in the extracellular matrix of the articular cartilage?
It is the fluid component that moves in and out o the tissue
What does the water, glycosaminoglycans and proteoglycans make up in the extracellular matrix of articular cartilage?
The ground substance (i.e. the solution of the connective tissue)
What is the function of the glycosaminoglycans (GAG) and proteoglycans?
Absorb the water in the cartilage to keep the tissue swollen with water
Part of the solid component that is fixed inside the tissue
What are some examples of GAG?
Hyaluronic acid, Chondroitin sulphate, Keratin sulphate
What is an example of a proteoglycan?
Aggrecan
What type of fibre makes up the articular cartilage?
Collagen type II
What is the difference between type I and type II collagen?
Type II is finer and more flexible than type I
Label the diagram of the articular cartilage


What site surface zone predominantly made of?
Very fine densely packed collagen
What is the orientation of the surface zone fibres?
Aligned in the direction of the forces
What kind of proteoglycans are found in the surface zone
Lubricating to reduce friction on the surface
Why does the shape of the chondrocytes change thought the material?
They are less compressed so become more spherical in shape
What is the purpose of the chondrocytes in the deep zone?
They chondrocytes grow in excess to serve as a stock for new chondrocytes to replace the ones on the surface zone as they get damaged
What happens below the tide mark in the articular cartilage?
The tissue types changes to a more calcified form of tissue where proteoglycans are replaced with hydroxyapatite (mineral component of the bone)
What does the cement line in articular cartilage do?
Connects the articular cartilage onto the underlying bone
What is the purpose of the calcified cartilage?
Has the stress bearing properties of the non-calcified zones (surface, middle, deep zone) and the strength of the calcified zone (i.e. bone) which allows for better connection of the non-calcified zones onto the bone during stress
What happens to the articular cartilage as you get older? How does this result in reduced mobility?
The tide mark becomes higher therefore there is less function zone (i.e. zones which can bear stress)
What is the middle and deep zone collagen arrangement? Why is it like this?
The collagen fibres run vertically attaching the cement line onto the surface zone
This is to tether the surface zone down so that as the articular cartilage swells up with fluid (water concentration changes FYI), the depth of the cartilage doesn’t change
What is the colour of the articular cartilage? Why?
It is white
This is because there it is avascular
Why is the articular cartilage avascular and aneural?
If there were capillaries in the cartilage they would constantly be crushed and would not be able be able to function
If there were nerves in the cartilage then every time weight was put onto the joint it would innervate them causing pain
What is the building blocks of GAG?
Repeating units of negatively charged disaccharides (disaccharide = 2 monomers connected)
What are some common GAG’s?
Hyaluronic acid, Chondroitin sulphate, Keratin sulphate
For chondroitin sulphate and keratin sulphate, what does the sulphate do?
It gives the molecule the negative charge
What do GAG’s attach to?
A proteoglycan protein core (i.e. Aggrecan)
When the GAG are attached to the proteoglycan, what is its response during compression? Explain.
When the protein compresses it will, when unloaded, spring back into tis original configuration
The GAG are negatively charged due to the addition of the negatively charged disaccharide’s. As the proteoglycan is compressed these GAG fibres become closer together and repel more so when unloaded it goes back to its original configuration
What is the difference between a proteoglycan and a proteoglycan complex?
Proteoglycan is the individual ‘brush’ where GAG attached to a core protein.
A proteoglycan complex is where multiple proteoglycan’s attach onto a long hyaluronic acid chain with hundred of proteoglycan
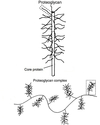
What does the proteoglycan complex attach to?
It attaches to the collagen fibres
What does the collagen fibres and proteoglycan complex in the articular cartilage make up?
Makes up the fixed solid component
What does the ‘fixed solid component’ of the articular cartilage mean?
It means that these are the components of articular cartilage that don’t move in and out
Explain what is the loading cycle (not the steps involved).
It is the process of water and ion movement in and out of the articular cartilage as it is put under/released from a load
What creates the negative charge of the deep zone in articular cartilage?
The glycosaminoglycans attached onto the proteoglycan complex
Where do the ions that move in and out of the articular cartilage during loading come from?
The synovial fluid
If the collagen fibres of the deep zone were cut, how would the articular cartilage respond? Why?
It would keep expanding as more water would be able to get into the cartilage
This is because the tension force of the collagen prevents complete swelling so when the tension force is removed, it can swell up fully
During loading, where does the fluid in the articular cartilage go?
It goes into the synovial fluid and to parts of the cartilage not loaded
During loading what is the initial response of the articular cartilage? What is the advantage of this?
The fluid does not leak out straight away
This allows the fluid component of the cartilage to protect the solid parts
As a load is applied on the articular cartilage, how does this change the lubrication? Why?
It increases the lubrication
This is because fluid released that goes into the synovial fluid increases the lubrication of the joint
What is the loss of volume in the articular cartilage called?
Creep
How does the loading and unloading of the articular cartilage help keep the cartilage alive? Why is this important in particular for the articular cartilage?
Unloading up of the articular cartilage allows nutrients (i.e. glucose, O2…) to be absorbed and loading helps to remove waste (i.e. CO2…)
This loading and unloading is critical for the chondrocyte survival because it is avascular and this is the only way for it to get sufficient nutrients
How does the loading and unloading of the articular cartilage help keep the cartilage alive? Why is this important in particular for the articular cartilage?
Unloading up of the articular cartilage allows nutrients (i.e. glucose, O2…) to be absorbed and loading helps to remove waste (i.e. CO2…)
This loading and unloading is critical for the chondrocyte survival because it is avascular and this is the only way for it to get sufficient nutrients
What is this a diagram of and label it

This is articular capsule

Label the cross-section of the articular cartilage


What is the joint cavity and outside the joint cavity considered relative to the capsule?
Joint cavity = inter-capsular
Outside joint cavity = extra-capsular
Where are articular capsules found?
They surround the synovial joint synovial fluid
What is the function of the articular capsule? How does it do this?
Limits the range of movement by becoming tight at the extreme ranges for motion
What is the fibrous layer?
The outer layer of the articular capsule
What is the fibrous layer made of?
Dense irregular (fibres are arranged in multiple directions) and regular (fibres are arranged in a single direction) connective tissue
How does the regular and irregular dense connective tissue function vary?
Regular is good at taking loads that are coming from a single direction
Irregular is good at taking loads that are coming from multiple directions
What is the function of the fibroblasts in the fibrous layer in the articular cartilage (and in other tissue types)?
Lays down collagen, reticular and elastin fibres
What is the function of the pro-prioreceptors in the articular cartilage?
They mesure the stretch of the capsule so that you know where your limb is in space
They also initiate reflexes
What is the function of the fibrous layer of the articular capsule?
Physically supports the synovial membrane and pretences the more delicate synovial membrane and joint
What is the location of the synovial membrane? Why this location
It lines all the non-articular surface inside the joint cavity
All the NON-articular surfaces because it is very delicate so if it connected to articular tissue then it would break
What are the two layers of the synovial membrane? What are their functions and locations?
Intima - Very thin layer (1-3 cells FYI) in direct contact with the synovial fluid that contains synovicytes that secrete some of the components of the synovial fluid
Subintima - Between the Intima and fibrous layer it helps maintain and protect the articular capsule during movement
What is the function of the joint cavity?
Contains the synovial fluid
What is the volume of the joint cavity? Explain the advantage of this size
Less than 2ml
This is because if there is a lot of fluid it becomes harder to do nutrient diffusion so only a little bit is used
What is an important product secreted by the synoviocytes?
Hyaluronic acid


