Digestive - 1 Flashcards
What is the the structure of the digestive system?
A gut tube (i.e. mouth, stomach, small intestine, large intestine) and two large glands (pancreas and liver)
What is the function of the digestive system?
Store, break down and absorb food
Label the diagram


What is dentine very similar to? How is it different?
It is very similar to bone
However the tissue producing cells, odontoblasts, are not found within the tissue, instead near the border
What makes enamel special within the body?
It is the hardest substance in the body
What is enamel made of?
Crystalline rods/prisms of calcium phosphate and calcium carbonate, there are NO cells
Because enamel has no cells in it, how does this affect its function?
It doesn’t receive any sensation
What is the function of the cementum?
It is the connective tissue covering the root
What are the periodontal ligaments?
They are collagen fibres linking the bone of the socket to the cementum
What is the function of the periodontal ligament?
They connect the bone into the socket
What is a property of the periodontal ligament that allows it have more than just tooth to jaw attachment properties?
It has a very large surface area
What is imbedded inside the periodontal ligaments and what is its functions?
Mechano receptors
Measures pressure and initiates a reflective paralytic response if sudden pressure is exerted on the teeth (i.e. stops the bone from further crushing itself = protection)
It allows for the teeth to readjust their position within the jaw by getting the osteoclasts (C for cut off) to break down and osteoblasts (B for build up) to build up bone is the direction needed
What vitamin is essential for periodontal ligament synthesis? What is the condition where there is a deficiency of this, what does it cause and why?
Vitamin C
Scurvy causes the teeth to fall out because there is high turnover of the collagen fibres in the periodontal ligament and without be able to synthesis new collagen fibres anchoring the teeth to the jaw, the will fall out
What is the function of the pulp?
It is the medium which blood vessels, nerves and lymphs travel through
What kind of muscle is the tongue made of?
Skeletal muscle
What are the different orientation of the muscle fibres in the tongue?
Longitudinal (i.e. running from the back to the front)
Vertical (i.e. from the top to the bottom)
Transverse (i.e. from side to side)
What is on the surface of the tongue?
Papillae and taste buds
Label the different types of papillae, which one has taste buds on it?

Vallate papillae have lots of taste buds on them

What are the three types of salivary glands?


What are the two types of cells that make up the salivary glands? What are their functions?
Mucous cells - Secrete mucous which help with moving food down into stomach
Serous cells - Secrete watery substance which contains amylase (breaks down starch around teeth) and lysozyme (breaks down bacteria)
What type of cells is each of the salivary glands made of?
Parotid (top) - Serous mainly
Sublingual - Mucous mainly
Submandibular - 50/50 of both
What are the different ways which the gut tube can increase its surface area?


Where would you predominantly find each type of surface area gaining method?
Plicae circular - Small intestine
Evaginations - Small intestine (i.e. villi)
Invagination - glands, stomach, small and large intestine
Convulsions - Small intestine
(FYI the SI has all of these features therefore shows that it is very important in maximising nutrient absorption)
What are the four layers/tunics of the small intestine?


What are each of the components of the small intestine (label the diagram)?
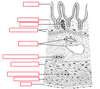

What is the function of the epithelium?
Protection, absorption and/or secretion
What is the function of the lamina propria?
It is what the epithelium is attached to and carries thieves, capillaries and immune cells
What is the function of the muscularis mucosae?
Provides the mucosa with movement independent of the external muscle (does NOT contribute to peristalsis)
What is the function of the submucosa?
Carriers large blood vessel, lymphatic vesses and nerves (submucosal plexus) to support the mucosa
What is the function of the external smooth muscle?
Constricts to produce peristalsis
What is the function of the serosa?
Provides lubrication surrounding the gut to reduce friction and separates the gut ( FYI is visceral peritoneum)
What is the enteric nervous system? What does it do?
It is the nervous system of the digestive tract and controls digestive processes
What parts of the nervous system can influence the enteric system? Explain
The sympathetic and parasympathetic
The sympathetic system turns off digestion (ie reduce blood flow, reduce salivation…)
Parasympathetic turns on digestion (ie increased movement, increased salivation…)


