Muscles Flashcards
(24 cards)
which muscle type? why?

skeletal muscle. has striations, myofibrils, each cell is multinucleated (peripheral), with many nuclei distributed throughout its cytoplasm
which muscle type? why?

cardiac muscle. microscopically has striations. individual cells are short & mononucleate
which muscle type? why?

smooth muscle. no striations. mononucleated, short, spindle-shaped
name the muscle architecture

- strap muscle 2. spindle-shaped muscle 3. pennate muscle 4. bipennate muscle 5. multipennate muscle
cross- sectional area of muscle provides what?
power
what is Isometric contraction?
When tension is generated in a muscle, i.e. muscle tone is increased, but the muscle does not shorten
what is Isotonic contraction?
When a muscle actually moves or shortens
name the structures & briefly define

Origin – The starting point of a muscle is its origin. By convention this generally closest to the centre of the body. It moves the least during contraction
muscle belly - fleshy central area the belly that tapers to tendons at either end
Insertion – Distal end where a muscle inserts on bone
Aponeurosis (flat broad tendons) - An attachment of a flat muscle that is drawn out into a flat sheet

This muscle runs from one region of the body to another. Thus the origin and insertion are in different parts of the body. type of muscle?
extrinsic muscle
This muscle lies completely within one region of the body where they have their origin and insertion. muscle type?
intrinsic muscle
Name some muscles with extrinsic origins & their functions
Trapezius - Draws the leg forward and protracts the limb
Pectorals – Adduct the limb and hold the forelimb against the body
Latissimus dorsi - Retracts the forelimb
Brachiocephalicus – When limb is on the ground it flexes the neck and bends the neck laterally; when the limb is not weight bearing it draws the foreleg forwards or protracts the limb (similar to trapezius)
name the muscles & briefly describe their roles

Supraspinatus – Extends the shoulder and stabilises the shoulder joint
Infraspinatus: Flexes the shoulder joint and helps stabilise the shoulder joint
Triceps brachii – Extends the elbow joint
Biceps brachii – Flexes the elbow joint
Brachialis – Flexes the elbow joint
name these muscles


name these muscles
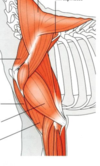

name these muscles


Muscles of the caudal aspect, main muscles of propulsion…what are they? describe their roles
Biceps femoris – Extends hip, flexes stifle and extends the hock
Semitendinosus – Extends hip, flexes stifle and extends the hock
Semimembranosus – Extends hip and flexes stifle
Gluteal muscles. function?
hip extensors
Tensor fascia latae. function?
Aid in extension of the hip
name these muscles


describe the function of intrinsic EXTENSOR GROUP muscles: cranial tibial, Long digital extensor, Fibularis longus, Lateral digital extensor

Cranial Tibial – flexes the hock and rotates the paw medially.
Long digital extensor – Flex tarsus and extend the digits.
Fibularis longus – flex tarsus and rotate paw medially.
Lateral digital extensor – Flex tarsus and extend lateral digits
describe the function of intrinsic FLEXOR GROUP muscles: Gastrocnemius, Superficial digital flexor, Deep digital flexor
Gastrocnemius – By virtue of its origin extends the tarsus and flexes the stifle
Superficial digital flexor – Flex digits, extend the tarsus flex stifle
Deep digital flexor – Flex digits and extend tarsus
name these muscles


position & function of Epaxial muscles?
above the vertebral column. Arranged in three groups and function to support the spine, extend the vertebral column and allow lateral flexion
position & function of Hypaxial muscles?
below the vertebral column. One region is associated with the neck, another with the back. The hypaxial muscles flex the neck and tail, and contribute to flexion of the vertebral column


