MSK types of fractures Flashcards
What type of fracture is this?

Transverse
What type of fracture is this?

Spiral
What type of fracture is this?

Segmental
What type of fracture is this?

Oblique
(non-displaced and displaced)
What type of fracture is this?

Linear
What type of fracture is this?

Impacted
What type of fracture is this?

Greenstick
What type of fracture is this?

Comminuted
What type of fracture is this?

Avulsion
Which fracture is associated with dinner fork deformity?
Colles fracture
What does displacement desribe?
The direction of translation of the distal fragment in a fracture
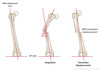
What does angulation describe?
The direction in which the distal frament points towards and the degree of deformity

Describe a Colles fracture
(which bone, intra- or extra-articular and direction angulation / displacement)
Distal radius
Dorsal displacement
Dorsal angulation

What’s the classic history for a Colles fracture?
Fall onto outstretched hand
Describe a Smith fracture?
(which bone, intra- or extra-articular, and angulation / displacement)
Distal radius, extra-articular
Volar / ventral displacement and angulation

Smith’s fractures tend to be stable.
TRUE / FALSE?
False! Highly unstable
Treatment of Smith’s fracture?
ORIF for all of them
If the fracture heals with flexion it will result in profound weakness and reduced grip strength

What is a Barton’s fracture?
(which bone, intra- or extra-articular, and direction of displacement / angulation?)
Distal radial fracture
Intra-articular with subluxation or dislocation at the radio-carpal joint
Can be dorsal or volar
Treatment of Barton’s fracture (and subluxation of carpals)?
ORIF with plate and scews
note: fracture is v unstable
Describe a Galeazzi fracture
(which bone, and what is dislocated?)
Fracture of the radius (distal third)
Dislocation of the ulnar at the distal radio-ulnar joint
(note: if the radius is fractured in isolation, suspect dislocaiton of the distal R-U joint)

Descibe a Monteggia fracture?
(which bone is fractured, and what is dislocated?)
Ulna is fractured
Dislocation of the radial head at the elbow

What is a nightstick fracture and when might it occur?
Fracture of the ulnar shaft
(with no associated radial head dislocation)
Occurs after a direct blow to the ulnar shaft
List three types of forearm fracture
Galezza: radial fracture with distal ulnar dislocation
Monteggia: ulnar fracture with radial head dislocation at the elbow
Nightstick: isolated fracture of the ulnar shaft
Treatment of a forearm fracture?
The exception to this is for an isolated fracture with no dislocation (Nightctick fracture) - how would this be treated?
ORIF with plate and screws
Nightstick / isolated fracture: manage conservatively


