MSK nuggets - lower limb Flashcards
Which fibular nerve is the nerve of the lateral compartment?
Superficial fibular
(common fibular supplies the anterior compartment of the leg)
What are the three compartments of the femoral sheath?
Lateral = femoral artery
Intermediate = femoral vein
Medial = femoral canal
What nerve supplies the adductor muscles in the leg?
Obturator nerve
This nerve exits the pelvis via the obturator canal which passes through the obturator foramen.
What is this ligament?

Pubofemoral
What is in the superficial compartment of the posterior compartment of the lower leg?
Gastrocnemius
(I think plantaris as well)
What is the purpose of the anterior cruciate ligament?
Prevents femur from sliding posteriorly on the tibia and prevents hyperextension of the knee
Look at the bursa that are on page 123
What are the attachments of the medial collateral ligament?
Medial epicondyle of the femur to the medial epicondyle and upper part of the medial surface of the tibia
Look at the superficial fibular nerve, deep fibular nerve, anterior ibial artery and dorsalis pedis artery on essential anatomy
What is this ligament?

Sacrotuberous ligament
During which movement of the subtalar joint are ankle sprains more common?
Inversion
What is this ligament?

Iliofemoral
What is the mnemonic for the door to the foot?
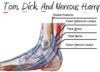
What are the three major structures found in the femoral triangle?
Femoral vein
Femoral artery
Femoral nerve
What type of joint is the ankle?
hinge type
What are the root values for the superior gluteal nerve?
L4, L5, S1
What is the action of the muscles of the anterior compartment of the lower leg?
Dorsiflexion of the ankle
Extensords of the toes
What are the functions of the gluteus maximus?
Extension and external rotation
Layer 1 muscles of the foot
Abductor digiti minimi
Abductor hallucis
Flexor digitorum brevis
Which meniscus is more commonly injured?
Medial meniscus
Which part of the fascia lata is called the iliotibial tract?
The lateral part
What is the name of the ring of cartilage that surrounds the acetabulum?
Acetabular labrum
What are the contents of the femoral canal?
Fat
Loose connective tissue
Lymphatic vessels - draining the deep inguinal lymph nodes
Deep lymph node the lacunar node
Empty space
How does a femoral hernia arise?
Abdominal contents push into the femoral canal within the demoral sheath.
What is the function of the arches of the feet?
Distribute body weight and act as shock absorbers
Which muscle does the sciatic nerve always lie under?
Piriformis
What are the borders of the femoral triangle?
Medially = adductor longus
Laterally = sartorius
Base = inguinal ligament
What are the dynamic factors that maintatin the integrity of the arches of the foot?
Intrinsic muscles of the foot
Long flexor tendons
Tendon of tibialis anterior and fibularis longus
What are the adductor muscles supplied by?
Obturator nerve (pectineus is supplied by the femoral nerve though)
Which action is likely to break both fibular and tibial bones?
Eversion
What is the function of the acetabular labrum?
Increases the depth of the joint
What are the muscles supplied by the femoral nerve?
PISR
Pectineus
Illiacus
Sartorius
Rectus femoris
What muscles are responsible for dorsiflexion?
Tibialis anterior
Extensor digitorum
Extensor hallucis longus
Pernoeus tertius
What are the two main branches of the sciatic nerve?
Tibial nerve and common fibular nerve
What are the contents of the popliteal fossa?
Fat
popliteal artery
small saphenous vein as well as popliteal vein
Tibial nerve
Common fibular nerve
Popliteal nodes and lymphatic vessels
What does the medial collateral ligament attach to?
Medial meniscus
Which sciatic foramen is responsible for structures leaving or entering the perineum?
Lesser
What is the highlighted nerve?

Common fibular nerve
What is the action of the gluteus medius and gluteus miminus?
They are abductors and medial rotators
What are the three main flexors of the hip?
Iliacus
Psoas major
Pectineus
Rectus femoris
Sartorius
What is the position of the obrutator nerve?
Traverses the interior surface of the pubis bone

What is the function of the lateral ankle ligament?
prevents over inversion
What muscles are in the deep compartment for the gluteal region?
Gluteus medius
Piriformis
Superior gemellus
Obturator internus
Inferior gemellus
Quadrator femoris
Which ligament of the ankle is named the deltoid ligament?
Medial ligament - resists over eversion
Which joint of the foot is responsible for inversion and eversion?
Subtalar and transverse tarsal joint
What are the contents of the adductor canal?
Femoral artery
Femoral vein
Nerve to vastus medialis
Saphenous nerve (this is the largest cutaneous branch of the femoral nerve)
What is the highlighted nerve?

Tibial nerve
What are the actions of the muscles in the lateral compartment of the leg?
They evert the foot weakly and plantar felx the ankle joint
Which bursa is assocaited with housemaids knee?
Pre patellar
What are the root values for the inferior gluteal nerve?
What does this nerve supply?
L5, S1, S2
Which digit of the foot has no abductors and no adductors?
Second digit
Does the sciatic nerve suply any muscles in the gluteal region?
No
What are the two main branches of the sacral plexus?
Sciatic nerve and the pudendal nerve
What muscles are responsible for plantar flexion?
Gastrocnemius
Soleus
Plantaris
Fibularis longus
Fibularis brevis
Tibialis posterior
Flexor hallucis longus
Flexor digitorum longus
Where do the lymphatic vessels that accompany the small saphenous vein drain?
They drain into the popliteal nodes
What are the two muscles of the iliotibial tract?
Tensor fascia lataw and the gluteus maximus
Layer 3 of foot
Adductor hallucis transverse head
Flexor hallucis brevis (medial and lateral heads)
Flexor digiti minimi
Adductor hallucis
When is the ankle joint unstable?
Generally unstable during platar flexion of the ankle joint
What are the three actions of the sartorius on the hip joint?
Flexion
Abduction
Laterally rotates the thigh at the hip
It also flexes the leg at the knee joint
So this means that it can flex the knee and the hip which is unusual.
What are the functions of the menisci?
Deepens the articular surfaces of the tibia - increases the stability of the joint
Shock absorbers
What are the passive factors that maintain the integrity of the foot?
Shape of the united bones
Plantar calcaneonavicular ligament
Long plantar ligament
Short plantar ligament and plantar aponeurosis
The lymphatic vessels that accompany the great saphenous vein end where?
They end in the superficial inguinal nodes
What are the two major nerves of the lumbar plexus?
Femoral
Obturator
What compartment does the obturator nerve supply?
Medial compartment
Layer 2 muscles of the foot
Flexor hallucis longus
Quadratus plantae
Lateral plantar nerve and artery
Medial plantar nerve
When does the external iliac become the femoral artery?
Inguinal ligament
What joints are responsible for inversion and eversion?
Subtalar, talocalcaneonavicular and calcaneocuboid
How do the 4 quadricepts muscles attach to the bone?
They unite to form a quadricepts tendon proximal to the patella. this continues as the patellar ligament distal to the patella to its attachment on the tibia (the tuberosity)
What movements are possible at the knee joint?
Flexion
Extension
Active and passive rotation movements can occur
What are the two terminal branches of the tibial nerve which innervates the intrinsic muscles of the foot?
Medial plantar and the lateral plantar nerves
What substance are the menisci made up of?
Fibrocartilage
What are the segmental root values for the femoral nerve and the obturator nerve?
L2-L4
What are the articular surfaces of the ankle joints?
Distal end of the tibia and fibula with the superior part of the talus bone
Which bursa comunicates with the articular cavity of the knee?
Suprapatellar
Clinically significatn because an infection of the bursa may spread to the knee
What innervates the gastrocnemius?
Tibial nerve
What compartment does the femoral nerve supply?
Supplies the anterior compartment
What are the muscles that make up the deep group in the posterior compartment?
Popliteus
Tibialis posterior (looks like feathers on an arrow)
Flexor hallucis longus (most lateral but becomes medial)
Flexor digitorum longus
What are the adductors of the hip?
adductors longus, brevis and magnus, pectineus and gracilis
Look up ankle ligaments on essential anatomy
What innervates the gluteus maximus?
Inferior gluteal nerve
What forms the lumbosacral trunk?
The union of L4 and L5
Which sex are femoral hernias more common in?
More common in females due to wider width of female pelvis
What type of joint is the superior and inferior tibio-fibular joint?
Superior tibio-fibular joint is a plane type of synovial joint
Inferior tibiofibular joint is a syndesmosis joint
What muscles are extensors of the hip?
Extension – gluteus maximus; semimembranosus, semitendinosus and biceps femoris (the hamstrings)
What muscles are involved with flexion of the knee?
Hamstrings (semitendinosus, semi-membranosus, biceps femorus)
Gracillis
Sartorius
Popliteus
What is the function of the posterior cruciate ligament?
Prevents the femur from sliding anteriorly on the tibia
Which leg bone is not involved in the knee joint?
Quadriceps femoris
Describe the location of the femoral nerve
Lies on the psoas major muscle and is lateral to the genitofemoral nerve

The femoral artery is a continuation of which artery?
External iliac
What is the main function of the plantaris?
Proprioception
Other functions include flexion of te knee and plantar flexion of the ankle
What are the nerve root values for the sacral plexus?
The sacral plexus is formed by the union of the ventral rami of spinal nerves L4, L5 as well as S1, S2, S3 and S4
Which nerve innervates the gluteus medius, minimus and the tensor fascia latae?
Superior gluteal nerve
What is this ligament?

Ischiofemoral
When is the malleolar grip strongest?
Dorsiflexion of the ankle joint
Which nerve innervates the posterior thigh muscles?
Tibial nerve
What are the two divisions of the sciatic nerve?
Tibial
Common fibular
Which vein is the femoral vein a continuation of?
Femoral vein is a continuation of the popliteal vein
What muscles are in the gluteal region, suerficial compartment?
Gluteus maximus, gluteus medius, gluteus minimus
What allows the femoral artery to go from anterior to posterior?
Adductor canal
Adductor hiatus
What muscles are medial rotators of the hip?
anterior fibres of gluteus medius and minimus, tensor fascia latae
What muscles form the popliteal fossa upper medially and upper laterally?
Upper medially = semimemembranosus
Upper laterally = biceps femoris
Which vessels accompany the 3 muscle tendons (tibialis posterior, flexor digitorum longus, flexor hallucis longus)
Tibial nerve
Posterior tibial artery and vein
What are the branches of the sacral plexus?
SLIP, DSP
S: superior gluteal nerve.
L: lumbosacral trunk.
I: inferior gluteal nerve.
P: posterior femoral cutaneous nerve.
D: direct branches to lateral rotators (including nerve to piriformis, nerve to obturator internus, nerve to quadratus femoris, etc), and pelvic floor.
S: sciatic nerve.
P: pudendal nerve.
Which nerve innervates the muscles of the anterior compartment of the leg?
common fibular nerve
What is the vein on the medial aspect of the foot?
The great saphenous vein
What musces are involved with extension of the knee
Quadriceps femoris
Which vein and artery runs in the popliteal fossa?
Artery = popliteal
Vein = short saphenous vein
What are the articular surfaces of the knee joint?
Medial and lateral condyles of the femur
Tibia
Posterior surface of the patella
What are the lower boundaries of the politeal fossa?
Medial and lateral heads of the gastrocnemius muscle
Which nerve innervates all the muscles of the posterior compartment of the leg?
Tibial nerve
What are the attachments of the lateral collateral ligament?
Extends from the lateral epicondyle of the femur to the lateral surface of the head of the fibula

Which branch of the popliteal artery supplies the posterior compartment of the leg?
Posterior tibial artery and fibular artery
Which nerve innervates the anterior group of muscles on the leg?
Femoral nerve
What are the two muscles of the lateral compartment of the leg?
Fibularis longus
Fibularis brevis
Which superficial vein empties into the femoral vein?
Great saphenous
How does the obturator nerve enter the medial thigh?
Through the obturator foramen
What separates the lateral meniscus from the lateral colateral ligament?
The tendon of the popliteus
Which nerve roots contribute to the sacral plexus?
(L4) L5-S4
Look at the bones of a foot
Which two important veins drain the femoral triangle?
Profunda femoris vein and the great saphenous vein
What is this ligament?

Sacrospinous
Which vein ascends posterior to the lateral malleolus?
Small saphenous vein
Where do testes drain?
Para-aortic nodes
Revise dermatomes of the leg

What are abductors of the hip?
gluteus medius, gluteus minimus, piriformis and tensor fascia latae
What6 muscles are responsible for lateral rotation?
biceps femoris, gluteus maximus, piriformis, assisted by the obturators, gemilli and quadratus femoris.
Which artery runs midway between the malleoli?
Dorsalis pedis
What is the large branch of the femoral artery which passes posteriorly toward the hamstrings?
Deep femoral
Which superficial vein empties into the popliteal vein?
Small saphenous vein
Which ligament plays an important part in maintaining the arch of the foot?
Calcaneonavicular
What are the 4 muscles of the anterir compartment of the leg?
Tibialis anterior
Extensor digitorum longus
Extensor hallucis longus
Fibularis tertius
What supplies the lateral rotators?
Sacral plexus
What are the actions of the deep muscles of the hip?
Deep muscles are lateral rotators of the hip
Superficial muscles are external rotators of the hip
What structures are involved in the unhappy triad?
Medial collateral
Medial meniscus
ACL
Which sciatic foramen is the route for structures entering or leaving the pelvis?
Greater
Which nerve roots contribute to the formation of the lumabr plexus?
T12-L4
The femoral artery enters the thigh midway between which 2 bony surface markings?
Pubic tubercule
Anterior superior iliac spine
Which ankle ligament is the weakest?
Lateral


