Module B: Biological Chemistry Flashcards
What determines the mass number of a molecule?
The number of protons plus the number of neutrons I.e. Carbon has six protons and six neutrons, therefore is 12
What is an isotope?
A molecule with extra neutrons in the nucleus. Carbon can have 7 neutrons for example; is called Carbon Thirteen
What are the electrons in the outer shell of an atom?
Valence electrons
What are the two types of chemical bonds?
Covalent and non-covalent
What is a covalent bond?
When two atoms share one or more pairs of electrons from valence shells.
What is the rule that states atoms like a complete outer valence shell?
The octet rule
What is electro-negativity?
The attraction of an atom for the shared electrons
What is a non-polar covalent bond?
Where there are two atoms of equal electro-negativity, there is a stand-off
What is a polymer?
A long molecule with similar building blocks (molymers)
What is a non-covalent bond?
A bond with no sharing of electrons
What is an ionic bond?
A bond where an atom donates an electron
What is a hydrogen bond?
An electrostatic attraction between an electronegative atom (O, N, F) and a hydrogen atom attached to an electronegative atom.
Three types of non-covalent bonds?
Ionic, hydrogen and Van Der Waals attractions
What are the three types of Van Der Waals attractions?
Permanent to permanent charge Permanent to induced interactions Instantaneous induced-induced interactions
What are instantaneous induced-induced interactions also referred to as?
London dispersion forces
What are the weakest intermolecular forces?
London dispersion forces
How do isotopes differ in electrons, protons and neutrons?
All isotopes of a given element have the same number of protons but different numbers of neutrons in each atom.
What is an element?
A substance that cannot be chemically broken down into another unit of measure. Distinguished into over one hundred categories of atoms.
What is a trace element?
A chemical present in only minute amounts
What is the difference between atomic mass and mass number?
Atomic mass is also known as atomic weight. Atomic mass is the weighted average mass of an atom of an element based on the relative natural abundance of that element’s isotopes. The mass number is a count of the total number of protons and neutrons in an atom’s nucleus.
Difference between molecule and compound?
They are used interchangeably; however, when a molecule consists of only one type of element (ie O2) it CANNOT be a compound.
What does VSEPR stand for?
Valence-Shell Electron-Pair Repulsion (Theory)
What is the VSEPR theory?
The pairs of electrons are spaced to minimise the repulsion between negative charges. This dictates the position of the atoms thereby influencing the overall shape of the molecule.
What is the electrical charge and mass of protons, electrons and neutron?
Protons have a positive charge and a mass of 1 unit, electrons have a mass of zero units and a negative charge and neutrons have a mass of one units ad no formal charge.
When an element is displayed with a bottom and top number to the left, what is the top number?
The top number is the total mass number; particles in an atom of an element that have mass are protons and neutrons. The bottom number is the atomic number i.e. number of protons and electrons
When an element is displayed with a bottom and top number to the left, what is the bottom number?
The bottom number is the proton number, it is simply the number of protons in an atom of the element.
How an atom behaves when it comes into contact with other atoms is determined by its
Electrons
What are ions?
Ions are atoms with extra electrons or missing electrons.
What is the difference between a positive and a negative ion?
When you are missing an electron or two, you have a positive charge. When you have an extra electron or two, you have a negative charge.
What is an ionic bond?
Ionic bonding is the complete transfer of valence electron(s) between atoms. It is a type of chemical bond that generates two oppositely charged ions.
Can non-polar molecules dissolve in water?
No, as they are hydrophobic
What intermolecular forces would hold two molecules of CH4 together?
CH4 is non-polar and doesn’t have any permanents dipoles because the spread of the charge is even across the tetrahedral molecules. Therefore, the force is only instantaneous induced-dipole-induced dipole interactions (London Forces)
What is hydrogen bonding?
Hydrogen bonding is a special type of dipole-dipole attraction between molecules, not a covalent bond to a hydrogen atom. It results from the attractive force between a hydrogen atom covalently bonded to a very electronegative atom such as a N, O, or F atom and another very electronegative atom.
Is hydrogen bonding covalent?
No, as there is no sharing of electrons. It is simply due to the attraction of electronegativity.
What are Van Der Waals attractions?
Van der Waals forces’ is a general term used to define the attraction of intermolecular forces between molecules. There are two kinds of Van der Waals forces: weak London Dispersion Forces and stronger dipole-dipole forces.
What molecules do Dipole-Dipole forces occur in?
Dipole Dipole forces occur in polar molecules, that is, molecules that have an unequal sharing of electrons.
Do isotopes have different masses?
Yes, as neutrons have mass (and isotopes differ in neutrons)
What is the symbol for mass number?
A
What is the mass number comprised of?
The total of protons and neutrons in the nucleus of an atom
What is the strength of London-Dispersion forces dependant on?
The polarisability: In essence, the more electrons, the stronger the potential of forces (as there is more opportunity for electrons to be imbalanced on one side of the atom)
Explain what makes a molecule hydrophobic
Water is a polar molecule, which means that it carries a partial charge between its atoms. Hydrophobic molecules are molecules that do not have a charge, meaning they’re nonpolar.
Three main factors effecting reactions?
Molecular collisions, concentration and temperature of the environment
The relative bond strengths of covalent, hydrogen and hydrophobic bonds (Van Der Waals) from weakest to strongest?
Van Der Waals Hydrogen Covalent
What factors affect the rate of a reaction?
Temperature, orientation of reactants, concentration and activation energy
In an equilibrium, what is the rate of the forward reaction equal to?
The rate of the reverse reaction
In an equilibrium, is the concentration of a reactant equal to the concentration of the product?
Not necessarily
Does the equilibrium constant, K, tell you how fast products are being made?
No
What is a solvent?
The dissolving agent
What is a solute?
The substance being dissolved
Why don’t non-polar molecules dissolve?
There are no charges for the molecule of water to interact with
What is Molarity?
A unit that describes the concentration (or amount of substance) with a volume of solution.
What is the formula for number of moles?
N = mass (g) / molecular mass (g/mol or Daltons)
What is the formula for concentration?
C = N (number of moles) / Volume (Litres)
What is the dissociation of water?
The dissociation of water occurs when a hydrogen atom in a hydrogen bond between two water molecules shifts from one to another. The water molecule with an extra proton is now a Hydronium ion.
Important properties of water?
Polarity, cohesion, adhesion, surface tension and a high boiling point (and thus, a evaporative cooling)
Difference between acids and bases in respect to protons?
An acid has a tendency to donate a proton (H+), while a base accepts a proton (H-)
Equation for pH?
pH = -log[H3+]
What is a buffer?
A buffer is a solution that can resist pH change upon the addition of an acidic or basic components.
Three types of isomers?
Structural, geometric and enantiomers
What are structural isomers?
Structural isomers have different covalent partnerships that hold all of their atoms together
What are geometric isomers?
Geometric isomers have the same covalent partnerships but differ in the spatial arrangements of groups that are positioned of double bonds. These are referred to as cis-trans isomers
What are enantiomers?
Enantiomers are essentially non-superimposable mirror images of each other. When written on 2D paper they look the same, but cannot be imposed upon one another in 3D space.
What are functional groups?
The chemically reactive groups of atoms within organic molecules
What is the chemical structure of a carboxyl group?
COOH
What is the chemical structure of a hydroxyl group?
OH
What is the chemical structure of a carbonyl group?
CO
What is the chemical structure of a amino group?
NH2
What is the chemical structure of a methyl group?
CH3
What is the chemical structure of a phosphate group?
H ₃ PO ₄
What are aldehydes?
An aldehyde is a compound containing a functional group with the structure −CHO, consisting of a carbonyl centre with the carbon atom also bonded to hydrogen and to an R group, which is any generic alkyl or side chain
What are ketones?
In chemistry, a ketone is a functional group with the structure RCR’, where R and R’ can be a variety of carbon-containing substituents. Ketones contain a carbonyl group.
What are chiral centres?
Chiral centres are carbons that have four different substituents attached
What is a hydrocarbon?
In organic chemistry, a hydrocarbon is an organic compound consisting entirely of hydrogen and carbon
The carbon atom is tetravalent; this means that:
A carbon atom can complete its valence shell by forming four covalent bonds
What is an aqueous solution?
An aqueous solution is a solution in which the solvent is water.
Variations in the properties of different organic molecules are most closely associated with
The presence or absence of functional groups
Although the structure of specific functional groups varies they all share one thing in common, they:
All are hydrophilic and increase the organic compound’s solubility
Ethanol, propanol and methanol are three simple alcohols. They can be grouped together because:
They all share the same function group - a hydroxyl
Why is testosterone considered a lipid?
It’s side chains are hydrophobic
What are enzymes?
A type of protein that acts as a catalyst to speed up chemical reactions
What determines the turnover number of enzymes?
Kcat
What are the side chains of amino acids called?
R groups
What is the isoelectric point?
The pH point where a zwitterion is formed
What is a zwitterion?
An amino acid in its neutral state i.e. a molecule or ion having separate positively and negatively charged groups
What are the amino acids with non-polar side chains?
Glycine Alanine Proline Valine Leucine Isoleucine Methionine
What are the amino acids with uncharged polar side chains?
Serine Threonine Cysteine Asparagine Glutamine
What are the amino acids with negatively charged side chains?
Aspartate Glutamate
What are the amino acids with positively charged side chains?
Lysine Arginine Histidine
What are the amino acids with aromatic side chains?
Phenylalanine Tyrosine Tryptophan
What are amino acids linked by?
Peptide bonds
What is a polypeptide?
A polymer of amino acids
Two regular arrangements of secondary structures?
Alpha helix and Beta sheet
What are Alpha helix secondary structures?
Secondary structures of proteins stabilised by hydrogen bonds between nearby residues
What are Beta sheet secondary structures?
Secondary structures of proteins stabilised by hydrogen bonds between adjacent segments that may not be nearby
What are random coils in regards to secondary structured proteins?
A protein with an irregular arrangement of the polypeptide chain
What is tertiary structure?
The overall three-dimensional shape of a polypeptide
What does the tertiary structure arise from?
Non-covalent interactions between amino acids and R groups (side-chains)
What is quaternary structure?
The assembly of the polypeptide chains. Can be identical or different in sequence
How does the heme group in haemoglobin attach to the polypeptide?
Via non-covalent bonds
Where does Fe2+ attach to in haemoglobin?
It is coordinated to the heme and to a Histidine side chain
How does Myoglobin and Haemoglobin reversibly bind O2?
Myoglobin + 02 <=> Myoglobin-02 Haemoglobin + 402 <=> Haemoglobin-402
What do saturation curves tell us?
The percentage of protein molecules that have oxygen bound at any one time
What is a saturation curve dependant on?
The amount varies depending on the partial pressure exerted by 02 (concentration [partial pressure] of 02)
What does the concentration of 02 [partial pressure] varied upon?
Dependant on the body part
P02 of active tissues?
20 torrs
At 20 torrs, how does the affinity of Myoglobin and Haemoglobin differ?
Myoglobin cannot release its 02 at this pressure, whereas Haemoglobin can release about 75% of its oxygen here
When does Myoglobin release its oxygen?
When P02 is 5 torrs This is as the last stores of 02 have been depleted
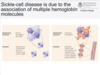
What is sickle-cell disease?
A condition where there are not enough healthy red blood cells to carry oxygen throughout the body. The abnormal blood cells have incongruity via their shape and textures
Where is the mutation in sickle-cell anaemia?
Glu - Val
What is the significant of Glu -> Val in sickle cell anaemia?
Glu is a negatively charged side chain. Val is non-polar: the substitution places a hydrophobic residue on the surface of the protein. This greatly reduces the solubility of the de-oxygenated form of haemoglobin. Val B6 forms a hydrophobic patch on the surface of the mutant protein.
What is proinsulin?
The inactive precursor form of insulin
Via what form of activation does insulin become active?
Proteolytic cleavage (activation)
When proinsulin is cleaved, what happens to the inactive form of insulin?
Disulphide bonds still hold it attached to the active form of insulin
What is denaturation?
The loss of the native protein structure
What can cause denaturation?
Alterations in pH Salt concentration Temperature Detergents
Opposite of denaturation?
Renaturation
Where are hydrophobic amino acids usually located?
Inside the core of the protein
Where are charged side chains of globular proteins usually located?
On the outside
Where do hydrogen bonding side chains usually reside in globular proteins?
In the core or located on the surface
What happens to globular proteins when hydrogen bonding side chains are disrupted?
They lose activity
Most abundant protein in vertebrates?
Collagen
What percentage of the body’s protein does collagen make?
~30%
Characteristics of collagen?
It is fibrous and not soluble in water
How many types of collagen are there?
28
What percentage of the body’s collagen is collagen 1?
90%
What does collagen 1 form?
Skin, tendons, vascular ligature, organs, bone
What does collagen 2 form?
Cartilage
What does collagen 3 form?
Connective tissue around the liver
How many amino acids does collagen have?
~1000
How long and thick is collagen?
300nM long and 1.5nM thick
How are collagen fibres aligned and linked?
Aligned in a staggered fashion (helical) and cross-linked (covalent bonds) for strength
Is collagen soluble in water?
No
Is collagen double or triple helixed?
Triple
What is the only side chain that points inside the triple-helix or collagen? Why?
Glycine - Because only the hydrogen is small enough to fit inside
What is Osteogenesis Imperfecta? (Brittle bone disease)
Osteogenesis imperfecta or brittle bone disease is a genetic disorder where a glycine side chain has mutated to cysteine. Makes helix unstable.
What amino acid in collagen is not one of the standard twenty amino acids?
Hydroxyproline
How is Hydroxyproline formed?
Hydroxyproline is formed by a chemical modification to the existing structure of an amino acid. Forces proline ring into a more favourable conformation for stabilising the triple helix. Offers more hydrogen bonding between the three strands of collagen.
Via what process is 4-Hydroxyproline formed?
Catalysed by Prolyl Hydroxylase in the presence of ascorbate (vitamin C)
What is a vitamin?
An organic compound required as a vital nutrient by an organism. Cannot be synthesised, thus must be obtained via diet.
What does Prolyl-4-Hydroxylase need to be fully active?
Fe2+
What type of enzyme is Prolyl-4-Hydroxylase?
A metalloenzyme
How does vitamin c active Prolyl-4-Hydroxylase?
Adds an electron to Fe3+, making it Fe2+ and activating Prolyl-4-Hydroxylase
Without vitamin C, what would happen to collagen?
It would have less of a tendency to become hydroxylayted. The collagen would thus be weaker.
What is scurvy?
A disease cause by a lack of vitamin C, in which one’s collagen becomes weaker


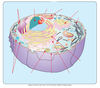
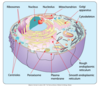


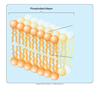


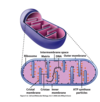










What is the main base of every amino acid?













Two main distinguishing features of a carbohydrate?
Feature 1: They contain 3-6 carbon atoms
Feature 2: They are aldoses or ketoses
What is a condensation reaction?
A condensation reaction, also known as a dehydration reaction, combines together small monomeric building blocks to make complex polymers.
A molecule of water is produced as a result of such a chemical reaction.
How can two monosaccharides form a disaccharide chemically? (where do they link)
Their two OH groups undergo a condensation reaction (losing water), and link via an oxygen molecule
Explain the difference structurally between amylose and amylopectin
Amylose - has a single chain polysaccharide consisting only of glucose
Amylopectin - also a polysaccharide, but the chain has occasional branch points where a singly monosaccharide may be attached to three other monosaccharides
Is glycogen soluble or non soluble?
Soluble
Is amylopectin soluble or non soluble?
Non soluble
Main difference between amylose and glycogen?
The main difference between Glycogen and Amylose is that the Glycogen is a polysaccharide and Amylose is a chemical compound.
Three main types of lipids?
Fats
Phospholipids
Steroids
How are triglycerides made?
Triglycerides are made from two components:
A molecule of glycerol + 3 molecules of the fatty acid.
How are triglyceride molecules linked?
The three fatty acid molecules are linked to glycerol by an ester bond (as the result of a dehydration reaction)
Key feature of an unsaturated fat?
Double bond in chain
What is a cis fat?
Means the carbon on either end of the double bond is on the same side
What is a trans fat?
Means the carbons on either end of the double bond are on opposite sides
Are monosaccharides polar or non-polar?
Polar
What chemicals would be in high concentration in hydrophobic molecules?
Carbon and hydrogen
What chemicals would be in high concentration in hydrophillic molecules?
Carbon, nitrogen, oxygen and hydrogen (with their bonds being polarised)
Structure of steroids?
The core part of their structure usually consists of two ring structures stacked on top of each other. This is in a stepwise fashion. The ring structures largely consist of carbon and hydrogen and so are lipophilic, or hydrophobic. Various polar groups can be found attached to the core providing a steroid with its unique properties.
Function of steroids?
There are two functions for steroids (i) is as a component of the cell membrane and (ii) signalingmolecules to transfer information(eg testosterone is the message molecule to make more musclecells).
What are glycosidic bonds?
A glycosidic bond or glycosidic linkage is a type of covalent bond that joins a carbohydrate (sugar) molecule to another group, which may or may not be another carbohydrate.
Out of amylose, amylopectin and glycogen; which have unbranched chains?
Amylose has unbranched chains, while amylopectin and glycogen have branched structures.
Structurally, what do polymer chains of amylose tend to form?
Helical structures
Three functional roles proteins can take?
Proteins can
(i) be catalysts to speed up chemical reactions (i.e. enzymes)
(ii) provide strength (e.g. collagen in skin, bone and cartlidge)
(iii) transport molecules (e.g. hemoglobin transports O2 from the lungs to the veins and arteries)
Aside from amino acids, what else can be found in proteins?
Metal ions, organic cofactors and every now and the nnoval chemical attachments
Does every amino acid have a centrally located carbon atom? To which groups is that central carbon bound?
Yes, the R-side chain, amino group, carboxyl group, and an hydrogen atom.
Explain what the prefix L or D refers to with respect to the structure of amino acids.
L, D are the two possible stereoisomers of amino acids. Stereocentres occur when there is a carbon atom with the different substituents attached (chiral).
Which part of the amino acid is the amino group?
The H3N+
What part of the amino acid is the carboxy group?
The COO-
Explain why glycine does not have two stereoisomers whereas all other amino acids can exist as stereoisomer pairs.
Because it’s side group has a simple H molecule, and thus is not a chiral molecule (there is already a simple H on the main carbon atom)
Describe the non covalent bonding of valine
It has a non-polar side chain, therefore it has hydrophobic (or vander waals) interactions
Describe the non covalent bonding of serine
The side group is polar (due to the presence of a hydroxyl group); therefore is has polar bonds (and possibly hydrogen if it can find it)
Another word for an ionic bond?
Salt bridge
Describe the non covalent bonding of aspartate
It has a carboxylate group (making it polar); therefore polar bonds or hydrogen bonds (if partner can donate a proton). If the partner is positively charged, it can form an ionic bond. (Because COO-)
What is the term to describe the new covalent bond that is formed by the chemical reaction of two amino acids?
Peptide bond.
Do the –R groups (side-chains) bound to the central carbons participate in theunion between amino acids
Not usually, but the cysteine side chains form covalent side-chain bonds. Chemical cross links can also involve covalent bonds between side chains (e.g. lysine).
How does cysteine’s side chains form a covalent bond?
By yielding disulfide bridges
Strongest chemical bond contributing to protein structure?
Covalent bonding
Does the chemical reaction to unite amino acids together incorporate or liberate atoms? What are the chemical entities incorporated or liberated in this reaction?
Liberate a molecule a water
In a substrate + enzyme complex, how does the enzyme catlyse the compund?
The enzyme will help to orient the substrates for optimal bond formation. Amino acids(or cofactors)can also supply protons or ions to facilitate reactions
Explain the term kcatas applied to enzymes. What is the unit used to describe kcat.
Kcat is the speed at which enzymes convert substrates into products.The unit is usually s-1.It indicates the rate at which a single enzyme molecule converts it substrate to product.
Explain the term substrate as it applies to enzymes. Explain how enzymes can be specific for a certain substrate
Substrates are the reactant molecules that enzymes work on.They have a shape and charge that is complementary to that of the substrate so they can bind to them. Enzymes can stretch bonds to make them easier to break or bring two substrates close together to allow catalysis to occur.
Using sucrase as an example; explain why a dipeptide is not likely to be a substrate for sucrase.
Sucrase has a complementary shape to accept sucrose into its active site. Other chemicals like a dipeptide don’thave a complementary shapeto match sucraseand therefore cannot fit in the active site.
What is the essential condition for a protein to be identical to another protein?Explain your answer.
The primary sequence must be the same.
What is the definition of the primary structure of a protein?
Primary structure = the amino acid sequence of the protein. It dictates the way in which the protein folds up into its three-dimensional structure and ultimately determines its function.
What is secondary structure in the context ofproteins?
Ordered regions of the polypeptide that form regular structural motifs (i.e. alpha helices and beta-sheets)
What type of non-covalent bonding can help to bring individual b-strands close to each other?If sheets were to stack on top of each other, how would they be stabilized?
b-sheets can stack on top of each other, by making use of the side-chainnon-covalent chemistry. Side chains that are hydrophobic on one layer, could interact with hydrophobic side chains on a different layer (this is how the b-sheets in spiders silk arranged)
What makes the sheets configeration in secondary strcutures of amino acids?
Random boils or turn links the strands to make sheets
In an alpha helix, which amino acides has the hydrogen bond?
Every 4th one
What is the tertiary structure of a protein? What are the two main types of tertiary structure?
The tertiary structure is the complete three dimensional structure of theprotein(ie its overall shape).
Main two types are globular and fibrous
Characteristics of a globular protein?
Spherical
Can have mixed secondary structure that is linked by coils
Characteristics of a fibrous protein?
Usually a single continous linear molecule, with one type of secondary structure
What is the common functionof hemoglobin and myoglobin?
Hemoglobin delivers O2 to tissues (active and resting)Myoglobin delivers O2 to muscles (especially active muscle cells).
What type of saturation curve does myoglobin have?
A hyperbolic saturation curve
What type of saturation curve does haemoglobin have?
A sigmoidal saturation curve
What does the saturation curve of myoglobin tell us?
The shape tells us that binding is “all or nothing”. This means myoglobin is fully loaded with O2 or it off loads it in one go. Off loading occurs at very low O2 concentrations, suggesting binding is strong.
What does the saturation curve of haemoglobin tell us?
This indicates cooperativity or chemical communication between subunits. The cooperativity allows the gradual release of the four O2 molecules from hemoglobin.
What has a stronger binding to oxygen; myoglobin or haemoglobin?
Myoglobin
What do homologous proteins have in common?
Homogolous proteins have:
1) similar amino acid sequences
2) similar secondary structure motifs
3) similar tertiary structures
Thus, similar functions
What DON’T homologous proteins have in common?
Quaternary structure
In sickle cell anemia, a hereditary disease, there is substitution of one amino acid by another in two of the polypeptide chains of hemoglobin. In this case, which structural levels of the protein are modified?
Primary sequence has been changed.
A single amino acid change may not alter the secondary structure of most proteins.
The tertiary structure will change in that local position.
In sickle cell anemia the quaternary structure alters from a tetramer to an aggregate.
Which of the following amino acids, if present at the sixth position of the β-globin chain, would yield a non-covalent aggregation of hemoglobin in a low-oxygen environment?
Threonine, Aspartic Acid, Serine and Isoleucine
Isoleucine
Explain with reference to the structures of the side-chains,Glu and Val,why the substitution of Gluto Val at position b6 of hemoglobin causes deoxy-hemoglobin to aggregate.
sickle cell anemia to also occur? With the help of a table of amino acids, explain your answer.The two hydrophobic valine side chains (on one deoxy-hemoglobin) fit perfectly into pockets on a second deoxy-hemoglobin. The pockets are formed by phenylalanine and leucine, two hydrophobic amino acids. Thus, multiple deoxy-hemoglobin assemble associate and aggregate.
Explain with reference to the structures of the side-chains,Glu and Val,why the substitution of Gluto Val at position b6 of hemoglobin causes oxygenated hemoglobin to aggregate.
There is no such exposed hydrophobic pocket in oxygenated hemoglobin (due to conformational change). Thus there is no aggregation in that case.
Explain with reference to the structures of the side-chains, Glu and Asp, why the substitution of Glu to Asp at position b6 of hemoglobin causes deoxy-hemoglobin to aggregate.
Aggregation will not occur as the same charge remains on the mutant as the original protein. Thus, it is likely that the hemoglobin will not aggregate. This is an example of a conservative mutation. In such a case there functional consequences are usually less dramatic that a non-conservative change.
What happens if someone doesn’t have insulin?
Without insulin, sugar is trapped in the blood, accumulates and becomes toxic.(eg diabetes)
How does insulin allow sugar into a cell?
By interacting with the insulin receptor and opening up the membrane for sugar
Explain how insulin changes from its inactive to active forms.
There are two forms of insulin, a pro-form, which is inactive. It is made as a single polypeptide. It is then processed by enzymes to release two smaller polypeptide pieces.
How do the two active forms of insulin assemble tightly together?
They assemble tightly thanks to the presence of two interchain disulfide bonds.
What is protein denaturation?
Protein denaturation is the unfolding of a protein
Why would a protein denaturate?
Increasing temperature can separate atoms that are non-covalently bonded. A change in pH can change the ionization states of side chains which might remove ionic bonds
How does a protein denature?
The polypeptide remains intact but the secondary structure is alterered to be no longer active - this is done by breaking the non-covalent bonds
Is collagen soluble or insoluble?
Insoluble
What are the functions of collagen?
Provides strength and flexibility to the skin, bone and cartilage.
What is chemically unique about collagen that makes it strong?
It is insoluble with water (providing additional protection to external forces.)
Explain the difference, in terms of structure and function, between procollagen and tropocollagen
Procollagen is the inactive form of collagen. Tropocollagen is the active form of collagen, it is ready to form fibrils. Procollagen and tropocollagen have a triple helix that is tightly wound. However, procollagen contains extra unstructured polypeptide at either end, preventing fibril formation
How is procollagen converted to tropocollagen?
Procollagen peptidase cleaves the ragged ends on procollagen.
What type of secondary structure does tropocollagen have? How many polypeptide chains?
Alpha helical configuration of three polypeptide chains
Explain why glycine is the most abundant amino acid in the sequence of collagen.
The side-chainsof the glycine amino acids point inwards to the core of the three triple helices. There is very little space in this region, so much so that only glycine (which is the smallest of all amino acids) is the only amino acid that fits.
What is hydroxyproline
The compound that occurs in an amino acid sequence of collage, where the side chain of proline has been chemically modified to have a hydroxyl attachment
What is the purpose of hydroxyproline?
Better non-covalent associations for strengthening
What is the roles of prolyl hydroxylase in providing strength to collagen?
Prolyl hydroxylase is the enzyme that attaches hydroxyl to proline.
What is the roles of Vitamin C in providing strength to collagen?
Vitamin C actives prolyl hydroxylase by reducing Fe3+ to Fe2+. Only when Fe2+ is present is prolylhydroxylase active.
Explain why Captain Cook was an advocate for feeding sauerkraut, oranges and limes to his sailors.
Without vitamin C, prolylhydroxlyase is inactive, so proline does not get converted to hydroxyproline. As a result, collagen has less strength and this can lead to a softening of bone, skin and cartlidge in the body. Humans don’t make vitamin C so we need to get it from our diets.
What is meant by chemical cross-linking? How does this step adds strength to collagen. Does collagen become more or less soluble after chemical cross linking?
Amino acid side chain like lysine become covalently linked. The new covalent links provide strength to the fibrils and reduced solubility.


