Mod13: Lung & Corneal Transplantations Flashcards
Lung Transplantation - Overview
What are common indications for Lung Transplantation?
End-stage Parenchymal disease
Severe Pulmonary hypertension
Lung Transplantation - Overview
Candidates for lung Tpx have a poor prognosis. What are they functionally incapacitate by?
Dyspnea
Lung Transplantation - Overview
Which factor is responsible for varying management criteria in lung transplantation?
Primary disease process
Lung Transplantation - Overview
General indications to having a lung Tpx from Barash anesthesia:
End-stage lung dz
Failed maximal medical treatment of lung dz
Age within limits for planned transplant
Life expectancy < 2-3 yrs
Ability to walk and undergo rehabilitation
Sound nutritional status (70%-130% of IBW)
Stable psychosocial profile
No significant comorbid disease

Lung Transplantation - Overview
From Barrish, what are COPD-specific indications for lung Tpx?
FEV1 < 25% of predicted value after bronchodilators and/or
PaCO2 = 55 mmHg and/or
Pulmonary Hypertension (especially with Cor Pulmonale)
Chronic O2 therapy

Lung Transplantation - Overview
From Barrish, what are Cystic Fibrosis-specific indications for lung Tpx?
FEV1 < 30% of predicted
Hypoxemia, hypercarbia, or rapidly declining lung function
Weight loss and hemoptyis
Frequent exacerbations, especially young females
Absence of antibiotic-resistant organisms

Lung Transplantation - Overview
From Barrish, what are Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis-specific indications for lung Tpx?
Vital capacity <60%-65% of predicted
Resting hypoxemia
Progression of disease despite therapy (steroids)

Lung Transplantation - Overview
From Barrish, what are Pulmonary-hypertension-specific indications for lung Tpx?
NYHA functional status class III or IV,
despite Prostacyclin therapy
Mean right atrial pressure < 15 mmHg
Mean pulmonary artery pressure < 55 mmHg
Cardiac Index < 2L/min/m2

Lung Transplantation - Overview
From Barrish, what are Einsenmenger-syndrome-specific indications for lung Tpx?
NYHA class III or IV, despite optimal therapy

Lung Transplantation - Overview
From Barrish, what are Pediatric-specific indications for lung Tpx?
NYHA class III or IV
Disease unresponsive to maximal therapy
Cor pulmonale, cyanosis, low CO

Single vs. Double Lung Transplant
Single-lung transplantation may be performed for selected patients with which medical condition?
COPD
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
Single vs. Double Lung Transplant
Double-lung transplantation is typically performed for patients with which medical conditions?
Cystic fibrosis
Bullous emphysema
Vascular diseases
Single vs. Double Lung Transplant
Why are younger patients more likely to receive bilateral lung transplants?
Disease process tyically involve full lungs
Single Lung Transplantation
Why is Single Lung Transplantation often attempted without CPB?
Can ventilate the other lung (down lung) that is not being transplanted
Double-lumen tube must be used for one-lung (down lung) ventilation
Single Lung Transplantation
Which type of incision is used for Single Lung Transplantation?
Posterior thoracotomy

Single Lung Transplantation
Which clinical signs would indicate the need for CPB during transplantation of one lung?
Arterial hypoxemia (spO2 <88%)
Sudden increase in PA pressures
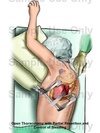
CPB for One Lung Transplantation
When CPB is necessary, where would pt be cannulated during a Left thoracotomy?
Femoral-vein-to-Femoral-artery bypass
CPB for One Lung Transplantation
When CPB is necessary, where would pt be cannulated during a Right thoracotomy?
Right-atrium-to-Aorta bypass
This is the typical approach for open heart surgery

Double-Lung Transplantation
Which type of incision is used for Double-Lung Transplantation?
“Clamshell” transverse sternotomy

Double-Lung Transplantation
True or False: Double-Lung Transplantation is occasionally performed with normothermic CPB
True
As opposed to traditional hypothermic CPB
Double-Lung Transplantation
Why is Sequential bilateral thoracotomies for double-lung transplantation now the preferred approach over the sequential unilateral (one lung at the time) approach?
Sequential bilateral thoracotomies associated with:
Decrease bleeding
Decrease need for tracheal anastomosis
Double-Lung Transplantation
What’s a disadvantage of sequential bilateral thoracotomies
One-lung ventilation not feasable
Henced the need for CPB
Lung Transplantation - Induction of Anesthesia
Which induction technique is appropriate for lung Tpx?
RSI with aspiration prophylaxis
Lung Transplantation - Induction of Anesthesia
Which induction technique would you employ to avoid precipitous drops in blood pressure?
Slow induction with:
Ketamine - Etomidate - Opioids




