Mod IV: Lower Extremity Blocks Flashcards
Lumbosacral Plexus
(see picture)
Lumbosacral Plexus:
You thought the brachial plexus was a pain??

Lumbosacral Plexus:
Lumbosacral Plexus:

The Lumbar Plexus
(see picture)
The Lumbar Plexus:

Lumbar Plexus - Lower extremity distribution
Femoral Plexus Block:
Can achieve block of entire plexus
Advanced block that can be challenging to place with frequent and serious complications
Individual nerve blocks with US can achieve same goals with greatly reduced risks

Lumbar Plexus - Lower extremity distribution
Fascia Iliaca Block (See image)

…

Lumbar Plexus - Lower extremity distribution
Single nerve blocks:
Femoral Nerve
Obturator
Lateral Femoral Cutaneous

Fascia Iliaca Block
AKA: 3 in 1 Block, why?
Femoral Nerve
Lateral Femoral Cutaneous
Obturator (unreliable coverage)

Fascia Iliaca Block
Volume Dependent Compartment Block, why?
40-60ml of LA

Fascia Iliaca Block
Indications:
Anterior Thigh
Knee Surgery
Hip procedures
Femur Fx

Fascia Iliaca Compartment Block
Positioned:
Supine
Fascia Iliaca Compartment Block
setup:
Basic US
Fascia Iliaca Compartment Block
Reliability of NON-US Techniques:
Unreliable!!
Feel “pop-pop” technique
NS 3 in 1
Fascia Iliaca Compartment Block
US technique:
2 approaches with probe
Transverse
Parasagital
Fascia Iliaca Compartment Block
Complications:
Block failure
Hematoma
Toxicity
Nerve damage
Fascia Iliaca Compartment Block
Very safe block to perform, why?
no major nerve or blood vessels near site of injetion
Fascia Iliaca Compartment Block
Transverse Approach:
Probe placed transverse over Femoral artery and slid laterally
Injection to be placed around lateral 1/3 of line between ASIS and pubic tubercle

Fascia Iliaca Compartment Block - Transverse Approach
Lateral Femoral Cutaneous located:
in between Sartorius and Tensor fascia lata muscle in this view

Fascia Iliaca Compartment Block
Parasagittal Approach:
Locate ASIS move probe medially until target picture appears
“Bow Tie” appearance
Needle approach from inferior edge of probe

Fascia Iliaca Compartment Block
Parasagittal Approach - Goal:
Injection of LA below Facia Iliaca between sartorius and internal onliques

Femoral Nerve
Anterior Division:
Cutaneous Branches: Intermediate and Medial femoral cutaneous nerves
Cutaneous innervation to anterior thigh
Muscular Branches
Pectineus and Sartorius

Femoral Nerve
Posterior Division:
Motor innervation to Quadriceps
Rectus Femoris
Vastus muscles
Lateralis - Medialis - Intermedius
Articular Branches
sensory innervation to knee joint

Femoral Nerve Block
Indications:
Anterior thigh
Knee Surgery
ACL, PCL Patellar tendon
Total/partial joint
Has fallen out of favor due to quad weakness and falls
Adductor Canal

Femoral Nerve Block
Anatomy:
Femoral Triangle
NAV or VAN

Femoral Nerve Block - Nerve Stimulator
Supine Position:
Obese pt may need retraction of panniculus

Femoral Nerve Block - Nerve Stimulator
Standard Block Setup:
Monitors, O2, Sedation
Skin asepsis
Skin Anesthesia
Femoral Nerve Block - Nerve Stimulator
Technique:
Femoral Artery palpated in femoral crease
Needle insertion
Lateral to artery
Perpendicular to skin
Slightly cephalic
Goal is Quad twitch
Patellar snap

Femoral Nerve Block
Fascia Iliaca must be pierced for block to work, why?
Femoral Nerve runs in the groove created by iliacus and Psoas muscles below the iliacus fascia

Femoral Nerve Block - Nerve Stimulator
Troubleshooting
Troubleshooting

Femoral Nerve Block
US guided:
Pt supine
Basic US Setup
Probe in femoral crease
Nerve can appear oval or triangular
Usually hyper-echoic
Needle insertion
Lateral => Medial

Femoral Nerve Block
LA must be injected below Facia iliaca
True
Note: LA encircling nerve

Lateral Femoral Cutaneous Nerve Block
Indications:
Lateral thigh
Hip procedures
Tourniquet pain

Lateral Femoral Cutaneous Nerve Block
Technique - position - setup - stimulator use:
Non-US techniques unreliable
Supine or lateral
Standard US setup
Stimulator may be used with goal of paresthesia to lateral thigh

Lateral Femoral Cutaneous Nerve Block
Locating nerve and needling:
LFCN runs between
Tensor Fascia Lata Muscle
Sartorius Muscle
5-10ml of LA used
Injection must dissect facial layer between muscles

Obturator Nerve
Where does it originate?
L2, L3, L4

Obturator Nerve Block
Provides Motor innervation to which muscles:
Adductor muscles
Magnus, Longus, Brevis, Gracilis

Obturator Nerve Block
Provides Sensory innervation to:
Skin: Medial thigh, knee

Medial knee joint
Obturator Nerve Block
Indications:
Knee surgery
Amputations
Tourniquet pain
TURBT surgery

Obturator Nerve Anatomy
Anterior branch:
Motor to adductors
Sensory to medial thigh/knee
Located between longus, brevis, and pectineus

Obturator Nerve Anatomy
Posterior branch:
Primarily motor of Adductors
Sensory: articular braches to medial knee joint
Between Brevis and Magnus

Obturator Nerve Block
Positioning - Setup - Probe - LA volume:
Pt supine leg Abducted slightly ext. rotated
Standard US Set-up
Probe transverse 2-3cm distal to femoral crease
Caution femoral vessels!!!
5-10ml of LA in each location

Obturator Nerve Block
Interfacial approach:
Injecting LA in a facial plane
Longus – Brevis
Brevis – Magnus
NS will produce adduction for both branches

Aponeurotic tunnel in the middle third of the thigh, extending from the apex of the femoral triangle to the opening in the adductor magnus, an the adductor hiatus. This structure is also known as:
Adductor Canal

Adductor Canal block
Originally described as alternate approach to which block?
Saphenous nerve block
Now known to also block sensory to the knee
Motor sparing
Vastus Medialis occasionally blocked

Adductor Canal
Indications:

Knee surgery
Medial leg/Ankle procedures

Adductor Canal
Position - Setup - Probe/Needling - LA:

Pt supine leg Abducted slightly ext. rotated
Standard US setup
Probe transverse, mid thigh
Needle approach A=>P
15-20ml of LA injected

Adductor Canal
Injection of LA should displace:

Sartaurius upward
LA need to be on both sided of Superficial Femoral Artery
Nerve not always visible

Adductor Canal
Continuous Catheter placed above SFA but absolutely needs to be below which muscle?

Sartorius muscle

What’s the largest peripheral nerve in the body?
Sciatic Nerve

Sciatic Nerve
Provides Motor innervation to:
Hamstring muscles
Muscles of the lower leg and foot

Sciatic Nerve
Provides Sensory innervation to:
Posterior thigh
Lower leg and foot
Except <strong>Saphenous</strong>

Sciatic Nerve
Extent of blockade depends on:
Location of block
Note hamstring motor branch early
Tibial and Peroneal components may emerge from plexus as entirely separate nerves

Sciatic Nerve block
Indications:
Knee surgery
Adjunct to Femoral or AC
Surgery of posterior Leg
Hamstring reattachment
Surgery of lower leg or foot
Sciatic Nerve block
Set-up - US Probe - Needle:
Standard NS/US set-up
Curvilinear probe may be needed
Long block needle may be required (100-150mm)
Sciatic Nerve block
Nerve Stimulator Goal:
Twitch of calf, foot, or toes
Hamstring innervation leaves sheath early not a reliable predictor
Sciatic Nerve block
Complications:
Infection
Hematoma
Vascular puncture
LA toxicity
Nerve injury
Tourniquet
Other

Sciatic Nerve Block
Multiple approaches:
Anterior
Trans-Glutial
Sub-Glutial
Mid-Femur
Popliteal
Tibial nerve
Sciatic Nerve - Anterior Approach
Stimulator Technique - Landmark identification:

Line b/t ASIS and Pubic Tubercle
Femoral pulse identified
4-5cm perpendicular from line

Sciatic Nerve - Anterior Approach
Technique:
Needle inserted perpendicular to skin
Advance until twitch of calf, foot , or toes seen
Contact with bone
Frequently due to contact with lesser trochanter
Withdraw needle 1-3cm
Internally rotate leg
Re-advance needle to just past bone
Sciatic Nerve - Anterior Approach
Pearls:
Elevate heel off bed to help identify twitches
Sciatic nerve is prone to injury
Avoid vasoconstrictors in LA
I use Ropivicaine only
Careful needling
Prevent mechanical injuries of an anesthetized limb
Fem or Sciatic first
1st fem then skin you needle for sciatic is anesthetized
Could lead to fem nerve injury??
Sciatic Nerve - Anterior Approach
NS Troubleshooting:
NS Troubleshooting:

Sciatic Nerve Block - US Anterior Approach
Position - US probe - Setup/needle - LA volume:
Supine, leg Abducted
Curvilinear Probe transverse, needle in-plane
Basic US set-up
Long needle 150mm
15-20ml of LA

Sciatic Nerve Block - US Anterior Approach
Indications:
Any sciatic nerve indication
Pt unable to turn lateral or prone

Sciatic Nerve Block - US Anterior Approach
Needling approach:
Can be from medial or lateral side of probe
Be mindful of Femoral A/V!!!
Sliding or tilting probe prox/distal may help visualize SN
Needle can be difficult to drive this deep in tissue

Sciatic Nerve Block - Trans-Gluteal - Stimulator
Position:
Lateral oblique position

Sciatic Nerve Block - Trans-Gluteal - Stimulator
Landmark identification - What are the landmark structures?
Greater trochanter
Posterior Superior Iliac Spine (PSIP)
Needle Insertion 4cm distal to midpoint
Block leg flexed over bottom with foot free to show twitch

Sciatic Nerve Block - Trans-Gluteal - Stimulator - Troubleshooting
Response obtained
- Interpretation*
- Problem*
- Action*

Sciatic Nerve Block - Trans-Gluteal - US
Position:
Lateral position, hips flexed

Sciatic Nerve Block - Trans-Gluteal - US
Probe placed between:
Greater trochanter
Ischium tuberosity

Sciatic Nerve Block - Trans-Gluteal - US
Needle insertion from:
Lateral aspect of probe

Sciatic Nerve Block - Trans-Gluteal - US
Sciatic nerve is predictably located between:
Volume of LA to inject:
Femur and Ischial Tuberosity
below <em>gluteus Maximus</em>
Inject 15-20ml of LA
Ensure good LA coverage

Sciatic Nerve Block - Trans-Gluteal - US
Very similar to trans-gluteal just positioning probe few cm distally
True

Sciatic Nerve Block - Trans-Gluteal - US
Advantages of the US-Guided Trans-Gluteal approach:
Less tissue!!!
May allow for use of linear probe - Less variability
Only need to search lateral and medially to find nerve

Sciatic Nerve Block - Popliteal Approach - Stimulator
Indications:
Foot or Ankle surgery
Analgesia adjunct for knee surgery

Sciatic Nerve Block - Popliteal Approach - Stimulator
Position - LA:
Lateral or Prone position
30-40 ml of LA
Ropivicaine no EPI

Sciatic Nerve Block - Popliteal Approach - Stimulator
Frequently paired with:
Femoral or Adductor Canal
Sciatic Nerve Block - Popliteal Approach - Stimulator
NS goal is:
Foot or Ankle twitch

Sciatic Nerve Block - Popliteal Approach - Stimulator
What can tell you where you are located?
TIPPED
Tibial - Inversion - Plantarflexion
Peroneal - Eversion - Dorsiflexion
Think about what you want numb and move accordingly

Sciatic Nerve Block - Popliteal Approach - Stimulator
You are trying to figuring out whether you are stimulating the Tibial or Peroneal nerve. Which nerve are you stimulating if the response is “Inversion of the foot & Plantarflexion”?

Tibial nerve
“TIP”

Sciatic Nerve Block - Popliteal Approach - Stimulator
You are trying to figuring out whether you are stimulating the Tibial or Peroneal nerve. Which nerve are you stimulating if the response is “Eversion of the foot & Dorsiflexion”?

Peroneal nerve
“PED”

Sciatic Nerve Block - Popliteal Approach - US
Position - Probe - LA:
Supine, Lateral or Prone
Probe transverse
20 – 30 ml of LA

Sciatic Nerve Block - Popliteal Approach - US
Probe transverse:
Start at popliteal crease
Identify: Artery - Vein - Tibial Nerve
Move proximally
Watch tibial and peroneal come together
Place injection when 2 have converged together
Tibial Nerve block
Indication - Volume of LA:
Total knee
Avoids the foot drop seen when peroneal nerve is also anesthetized
5-8ml of LA
Tibial Nerve Block
Setup the same as:
Traditional popliteal
Needle insertion is from medial side
Care taken to only place LA near tibial nerve leaving Peroneal untouched
Ankle Block
Indications - Needle:
Foot and toe surgery
Needle 25ga 1.5 in

Ankle Block
Which 5 Nerves must be anesthetized to achieve Ankle Block?
“SSSPD”
Superficial
Superficial Peroneal - Sural - Saphenous
Deep
Posterior Tibial - Deep Peroneal

Ankle Block - Deep Nerve Blocks
How to block the Deep Peroneal nerve?

Identify Extensor Hallucis Longus
Insert needle just lateral
Advancing until contact with bone
Withdraw 2 mm and inject 2-4 ml of LA

Ankle Block - Deep Nerve Blocks
How to block the Posterior Tibial nerve?
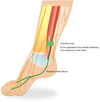
Identify medial malleolus
Insert posterior to and contact bone
Withdraw 2mm and inject 2-4 ml of LA

Ankle Block - Superfical Nerve Blocks
How to blocked the Superfical Nerves (Superficial peroneal, Sureal, Saphenous)?
Creating a SubQ wheel around the entire ankle

Ankle Block - Superfical Nerve Blocks
How to block the Saphenous nerve?

Wheel from tibial ridge directed medially to Achilles

Ankle Block - Superfical Nerve Blocks
How to block the Superficial Peroneal nerve?

Wheel from tibial ridge laterally to lateral malleolus

Ankle Block - Superfical Nerve Blocks
How to block the Sural nerve?

Wheel from lateral malleolus to Achilles

Ankle Block - US Guided
Where is the Superficial Peroneal located?
Nerve Lies superficial to facia
Probe transverse 5cm proximal and anterior to lateral malleolus
Can be blocked with 2-4 ml of LA

Ankle Block - US Guided
Where is the Sural nerve located?
Proximal to lateral malleolus
Runs with small saphenous vein
Can be blocked with 2-4 ml of LA

Ankle Block - US Guided
Where is the Saphenous Nerve located?
Small nerve best visualized 10-15cm proximal to medial malleolus
Runs with the saphenous vein to use as a marker



