MMB-MusicPerception_1a_Acoustics Flashcards
Understand the basics of music perception
- What’s (auditory) perception for?
- Sample current information from the environment
- Integrate together with context and long-term knowledge (e.g. to interpret ambiguous information)
- Complement concurrent information from other senses
- Construct a model of the world which we can act upon
- Communication and expression (speech, music)
- What is Sound?
- Air consists of molecules colliding constantly and randomly
⇒static pressure, uniform in all directions
- Pressure depends on
– Density of medium (air: 100,000 N/m squared) – Temperature - Sound: Variations in pressure in a medium
- Where does sound come from?
- Interaction of an event and an object that results in pressure variations in the air (and hence at our eardrum)
Example: – tuning fork (object) being struck (event)
- How does sound propogate?
The movement produces alternate condensation and rarefaction of air molecules causes
– travelling wave of air pressure
- Draw a model of The spring-and-golf-ball model of sound propagation
- Sound waves are longitudinal waves where air molecules travel in the direction of the wave
- A sine wave is characterised by which three measurements?
- A: (Peak) Amplitude of the pressure variation
- Frequency (or period) of the occilation
- Phase
- Give the wave function to describe amplitude variation over time
- x(t) = Asin(2πft +φ)
A: peak amplitude
f: Frequency in Hertz t: Time in seconds
t: Time in seconds
φ: Phase in degrees or multiples of π
- Describe Frequency (f):
- number of cycles of condensation and rarefaction per second (Hz)
- related to the percept of pitch (more cycles per unit time = higher pitch)
- Related: Period = 1/f => time taken to complete one wave cycle, measured in seconds per cycle
- Related: wave lengths (λ) => distance covered by one complete cycle, measured in metres
- If a sine wave has a frequency of 50Hz how many ms per cycle?
Sine wave with frequency of 50Hz = 50 cycles per second
Period: 1/50cycles per second = 1000ms/50cycles = **20ms/cycle **
- State the equation for finding Wave length (λ)
• Wave length (λ) is speed of sound (c) divided by frequency (f).
λ= c / f
- What is the wave length for sine wave with 50Hz frequency at 20oC (i.e. speed of sound 344m per second)
Wave length (λ) is speed of sound (c) divided by frequency (f).
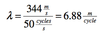
- Exercise 1: Calculate the period of a wave with frequency 440Hz
Frequency of 440Hz = 440 cycles per second
Period: 1/440cycles per second = 1000ms/440cycles = 2.27ms per cycle
- Calculate the frequency of a wave with period 100ms
frequency = 1/period
1000/100 = 10Hz
- Calculate the frequency of a wave with period 15ms
frequency = 1/period
1000/15 = 66.67Hz
- Calculate the frequency of a wave with period 10ms
frequency = 1/period
1000/10 = 100Hz
- Calculate the frequency of a wave with period 5ms
frequency = 1/period
1000/5 = 200Hz
- – Calculate the wave length of a wave with a frequency of 100Hz
λ = wavespeed/frequency
λ = wavespeed/100Hz
λ = (344m/s)/100Hz = 3.44m/cycle
- Calculate the wavelength of a frequency at 800Hz
λ = wavespeed/frequency
λ = wavespeed/800Hz
λ = (344m/s)/800Hz = 0.43m/cycle
- Calculate the wavelength of a frequency at 18kHz
λ = wavespeed/frequency
λ = wavespeed/800Hz
λ = (344m/s)/18kHz = 344m/s)/18000 = 0.0191m/cycle
- The amplitude measurements for a period of a sine wave are (in an arbitrary unit): 0,7,10,7,0,-7,-10,-7
Claculate the rms amplitude
0,7,10,7,0,-7,-10,-7
– Square all amplitude values in time window
0,49,100,49,0,49,100,49
– Take the mean of all squared values
Mean = total / 8 = 49.5
– Take square root of that mean
rms = 7.035624
- Describe Amplitude:
Amplitude = magnitude of pressure variation relative to atmospheric pressure => measured in Newton/m2
• related to the percept of loudness (greater amplitude = louder sound)
Measures:
– Peak or peak to peak pressure
– Root mean square (rms) amplitude
- What are the steps to compute RMS amplitude?
– Pick a period of time window for which you want to calculate the rms amplitude
– Square all amplitude values in time window
– Take the mean of all squared values
– Take square root of that mean
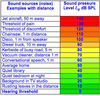
- State some key points about sound intensity
- Sound intensity is a more common concept in psychoacoustics
- Intensity = energy passing through unit area (m2) per second => measured in Watts/ m2
- Intensity is proportionally related to square of rms pressure
- Intensity is expressed relative to absolute hearing threshold
- The reference intensity is 10-12 W/m2
- How much greater is the sound pain threshold than sound at absolute threshold hearing?
Our ears cover huge dynamic range of intensities: Sound at pain threshold is over 10 pascals or 1 trillion times louder than sound at absolute threshold of hearing