ML6: Stage I & II catabolism Flashcards
What are the classes of lipids?
-
Fatty acid derivatives
- Fatty acids – fuel molecules
- Triacylglycerols – fuel storage and insulation
-
Hydroxy-methyl-glutaric acid derivatives
- Ketone bodies (C4) – water soluble fuel molecules
-
Vitamins
- A, D, E, and K
What are triacylglycerides (TAGs)? Are they (overall) hydrophobic, amphipathic, or hydrophilic?
Major dietary and storage lipids
Consist of three fatty acids esterified to glycerol
Overall hydrophobic
What happens to dietary lipids?
-
Lipids are emulsified in the small intestine
Bile salts -
Digestion of lipids by lipases
TAGs – digested by pancreatic lipase
Cholesterol esters – digested by cholesterol esterase
Phospholipids – digested by phospholipases - Absorption by intestinal mucosal cells
-
Transportation to tissues
Consumer tissues – fatty acid oxidation
Adipose tissue – storage
Give an overview of fatty acid catabolism (β-oxidation).
- Occurs in mitochondria
- FA cycles through sequence of reactions
- C2 removed at each cycle
- 1 NADH and 1 FADH2 produced in each cycle
- All intermediates linked to coenzyme-A
Give the stages of fatty acid catabolism (β-oxidation).
-
Activation of fatty acids
Occurs in the cytoplasm
FA actiated by linkage to coenzyme-A
Catalysed by acyl CoA synthetase
fatty acid + coenzyme A → fatty acyl CoA -
Transport of fatty acyl CoA into mitochondria
Fatty acyl group linked to carnitine
Transported across the membrane by translocase protein
Fatty acyl CoA reformed in the matrix
Rate limiting step for faty acid oxidation -
Oxidation of fatty acyl CoA
A series of four reactions
1 NADH, 1 FADH2 and 1 acetyl-CoA are generated in each round
Each round shortens the chain by two carbon atoms
Cycle continues until only acetyl-CoA remains
Overall: released 106 molecules of ATP
What are essential amino acids? Name them.
Amino acids that cannot be synthesised
His, Ile, Leu, Lys, Met, Phe, Thr, Trp, Val
What are the stages of digestion and absorption of proteins?
- Dietary protein digestion begins in the stomach
- Denaturation
- Pepsin
- Further digestion in the lumen of the intestine
- Chymotrypsin, trypsin, carboxypeptidase – pancrease aminopeptidase
- Transport into intestinal cells and into blood
What happens to excess amino acids? Why and how?
They cannot be stored so have to be degraded
-
Transfer of amino group to α-ketoglutarate
Uses aminotransferases -
Dehydrogenation to produce ammonium ion
Uses glutamate dehydrogenase
e. g. aspartate + α-ketoglutarate produces oxaloacetate and glutatamate
e. g. alanine + α-ketoglutarate produces pyruvate + glutatamate
How are ammonium ions removed?
The urea cycle
Toxic NH4+ is converted to urea and excreted
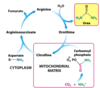
Are proteins produced for a specific function or synthesised as a store of excess amino acids?
They are produced for a specific function
How can energy be provided during starvation?
By breaking down muscle
Explain the nitrogen balance.
Positive nitrogen balance
Intake of nitrogen (protein) > loss
During active growth, pregnancy, tissue repair
Negative nitrogen balance
Intake of nitrogen (protein) < loss
During starvation


