CW2: Amino acid structure Flashcards
Why is rotation around a peptide bond not possible?
The peptide bond is planar due to its partial double-bond character, which limits the rotation angle between amino acids
What is the amino acid with the simplest side chain?
Glycine
What is the name and structure of the intermediate between the two forms of a peptide? Why is it unable to rotate?

Resonance hybrid
It cannot rotate due to the partial double bonds making it a planar molecule

Name the amino acids with polar, positively charged side chains and give their three- and one-letter abbreviations
Lysine / Lys / K
Arginine / Arg / R
Histidine / His / H
Between which bonds in a peptide is free rotation permitted? What is the name of the angles of these bonds, and why are certain values of these angles not permitted?
Free rotation is permitted between:
- Cα –C bond: psi (Ψ) angle
- N–Cα bond: phi (Φ) angle
Certian values aren’t permitted because of steric hindrance (side chains hitting each other).
How can serine and threonine be modified after synthesis? Explain this process if there were a lack of O2 in the cell.
Phosphorylation: adding PO32– to the amino acid
Receptor discovers lack of O2 → Cell nucleus responds with a phosphorylation reaction → Can turn off signal as well using phosphatase (i.e. it is a reversible reaction)
Why are localised pH effects very influential on histidine?
Its pK is 6.5 which is close to a pH of 7, therefore histidine can either accept or donate protins. This means that a small change in pH in either direction can cause a large change in the properties of amino acid chains containing histidine
What are the special properties of proline?
- Not very polar and not very non-polar
- Side chain is chemically linked to the backbone so not very flexible
Name the amino acids with polar, uncharged side chains and give their three- and one-letter abbreviations
Serine / Ser / S
Threonine / Thr / T
Asparagine / Asn / N
Glutamine / Gln / Q
Cysteine / Cys / C
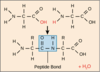
What is the bond between two amino acids? How does it form?
Peptide bond
W
Which amino acids have hydroxyl groups and what influence does this have on their behaviour?
- Tyrosine
- Serine
- Threonine
They can be modified after synthesis (e.g. phosphorylated)
Why do we often say ‘aspartate/glutamate’ not ‘aspartic acid/glutamic acid’?
These amino acids tend to exist negatively charged (because their pKs are approx. 4.4 at pH 7, so they are less protonated (i.e. pH is higher than pK) so protons are given up), hence ‘–ate’
Name the amino acids with non-polar, aromatic side chains and give their three- and one-letter abbreviations
Phenylalanine / Phe / F
Tryptophan / Trp / W
Tyrosine / Tyr / Y
Which amino acids have sulfur in their side chains? What are the differences in their properties?
Methionine and cysteine
The sulfur in methionine is buried in the side chain so has no large bearing on its properties
Cysteine can form dislfide bonds with other amino acids becuase its sulfur is at the end of the side chain
At pH 7, which amino acids have negatively charged side chains? What are their ‘acidic names’?
Aspartate (aspartic acid)
Glutamate (glutamic acid)
Define ‘α-carbon’
The carbon to which the side chain is bonded
What properties would you expect from a non-polar amino acid?
- Hydrophobicity
- Chiral (true of all amino acids except glycine
- Optical isomers (except glycine)
- Folding in aqueous solution to ‘trap’ the hydrophobic regions
Name the amino acids with non-polar, aliphatic side chains and give their three- and one-letter abbreviations
Glycine / Gly / G
Alanine / Ala / A
Valine / Val / V
Leucine / Leu / L
Isoleucine / Ile / I
Proline / Pro / P
Methionine / Met / M
What does the term ‘isoelectric point’ mean?
The pH at which an amino acid will not migrate in an electric field, i.e. the pH where the amino acid is neutral and in its zwitterion form
Why are the variable/side/R groups of amino acids found on alternate sides of a polypeptide backbone?
They are usually bulky groups
Why is a peptide bond planar?
Because it has partial double-bond character which limits the rotation between two amino acids
Name the amino acids with polar, negatively charged side chains and give their three- and one-letter abbreviations
Aspartic Acid / Asp / D
Glutamic Acid / Glu / E
Which amino acid is actually an imino acid? Why?
Proline because it has a secondary amine group (connected to two carbons)


