Midterm III - Helminthology 1 [INCOMPLETE] Flashcards
(170 cards)

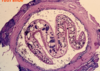
Trematoda: Egg

Trematoda: Miracidium inside the egg

Trematoda: Miracidium (released from egg)

Trematoda: Miracidia

Trematoda: Sporocyst

Trematoda: Sporocyst containing rediae

Trematoda: Sporocyst containing rediae

Trematoda: Redia

Trematoda: Cercaria

Trematoda: Cercaria

Trematoda: Full cercaria
Typical form of the blood flukes
[White spheres]

Trematoda: Metacercariae

Trematoda: Metacercaria

Trematoda: Metacercariae

Trematoda: Metacercaria
Notice the sucker in the middle

Trematoda: Migrant form of a young fluke

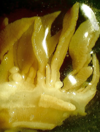
Fasciola hepatica (Common liver fluke)
Acute fasciolosis: Haemorrhages on serosa

Fasciola hepatica (Common liver fluke)
Haemorrhagic tracks in a sheep’s liver

Fasciola hepatica (Common liver fluke)
Haemorrhagic tracks in a sheep’s liver

Fasciola hepatica (Common liver fluke)
Chronic fasciolosis → Flukes are found in the bile duct

Fasciola hepatica (Common liver fluke)
Identifying features:
- Dorsoventrally flattened/Leaf-like
- Grey-brown
- Conical head shape (with shoulders)

Fasciola hepatica (Common liver fluke)
Identifying features:
- Dorsoventrally flattened/Leaf-like
- Grey-brown
- Conical head shape (with shoulders)
[See the yellow eggs]

Fasciola hepatica (Common liver fluke)
Identifying features:
- Dorsoventrally flattened/Leaf-like
- Grey-brown
- Conical head shape (with shoulders)
[Notice the yellow eggs]

Fasciola hepatica (Common liver fluke)
Identifying features:
- Parenchyma with dark intestinal cross-sections