Midterm I - Miscellaneous Photos & Info Flashcards

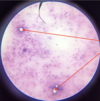
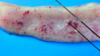
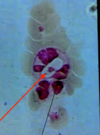
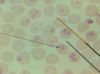
Trypanosoma sp.: Trypomastigotes
Blood smear

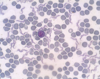
Trypanosoma equiperdum: Trypomastigotes

Trypomastigote in the blood

Trypanosoma sp.: Trypomastigote
Fish blood
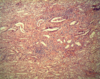
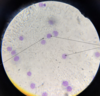
Leishmania sp.: Promastigotes

- Leishmania sp.*: Promastigotes
- Extracellular forms*
Leishmania sp.: Amastigotes
Divided & intracellular - Only in macrophages
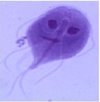
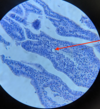
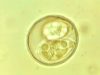
Giardia sp.: Trophozoite
Containing 2 nuclei

Giardia sp.: Trophozoites
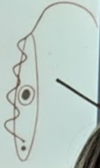
AfricanTrypanosoma sp.: life cycle

Trypanosoma sp.: Form type in the vertebrate host tissue
Amastigotes

Trypanosoma sp.: Form type(s) in insects
- Promastigote
- Epimastigote

Trypanosoma sp.: Form type in the vertebrate host’s blood
Trypomastigote
“Metacyclic form”
Trypanosoma sp.: Symptoms
- Genital & abdominal oedema
- Cachexia
African Trypanosoma sp. “Salivaria”: Vector
Tsetse fly
Males & females
Trypanosoma equiperdum: Life cycle

Trypanosoma cruzi: Life cycle

Leishmania sp.: Life cycle
Passed on by the saliva (not faeces)

Leishmania sp.: Form type In vertebrates
Amastigotes
Leishmania sp.: Form type In insects
Promastigotes
Leishmania sp.: Vector
Female sand fly
Leishmania tropica: Pathological form
Cutaneous form (skin)
Leishmania braziliensis: Pathological form
Mucocutaneous form (oral & nasal cavity)
Leishmania donovani: Pathological form
Visceral form (liver, spleen etc.)
Leishmania infantum: Pathological form
Visceral & cutaneous form
Leishmania chagasi: Pathological form
Visceral & cutaneous form
Giardia sp.: Life cycle
Spreading by cysts


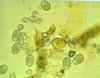
Giardia sp.: Cysts
Giemsa stain not good - Cysts appear empty

Giardia sp.: Cysts
Faecal smear, Poor staining - Nuclei of cysts cannot be seen
Giardia sp.: Cysts
Faecal smear, poor staining - Nuclei of cysts cannot be seen

Giardia sp.: Cysts
Floatation method - not good, empty cysts
Trichomonadida sp.: Life cycle

Trichomonas species are grouped by…
The number of anterior flagella they have

- Trichomonas foetus*
- In cattle*

- Trichomonas gallinae*
- In poultry*
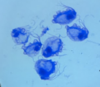
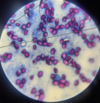
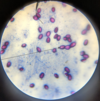
Trichomonas sp.: Trophozoites

Trichomonas sp.: Trophozoites

Trichomonas sp.: Trophozoite

Trichomonas sp.: Trophozoites
Broth culture

Trichomonas gallinae: Necropsy specimen

Trichomonas gallinae: Liver necrosis
Histomonas sp.: Life cycle

Histomonas sp.: Susceptible species
- Turkey
- Partridge
- Quail
- Guinea fowl
- (Chicken)
Histomonas sp.: Forms

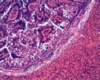
Histomonas sp.: Necropsy findings


- Histomonas meleagridis*: Trophozoite
- Liver, PAS Stain*

Histomonas sp.: Trophozoite

Histomonas meleagirdis: Black head disease
Caused by cyanosis, only becomes black post mortem

Generalised histomosis

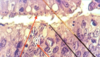
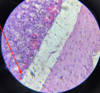
Histomonas meleagirdis: Infection of the caeca of a turkey
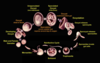
Eimeria sp.: Life cycle
Eimeria sp.: Summarise the zoites
Sporozoites & merozoites
- Unicellular forms
- Asexual form in all apicomplexan parasites
- Lunar shaped

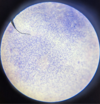
Apicomplexan sporozoites & merozoites
Giemsa stain

Apicomplexan parasite: Sporozoites & merozoites

Apicomplexan parasite: Sporozoites & merozoites

Apicomplexan parasite: Sporozoites & merozoites
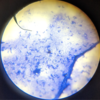
Apicomplexan parasite: Sporozoites & merozoites

Eimeria sp.: Trophozoite

Schizonts
Filled with trophozoites or merozoites

Intracellular schizont

Schizonts: Filled with trophozoites or merozoites

Schizonts: Full of trophozoites or merozoites

Schizonts filled with trophozoites or merozoites
Notice the nucleus pressed to the side

Schizont with other staining
Zoites aren’t visible due to staining

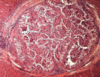
Eimeria sp. infection

- Eimeria sp.*: Schizont
- Zoites can’t be seen inside*
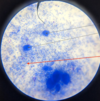
Eimeria sp.: Merozoites

Eimeria sp.: Microgamonts (male)

Eimeria sp.: Macrogamonts (female)

Schizogony

Gametogony

Gametogony

Schizogony

Eimeria sp.: Gamonts
Amongst chicken RBCs
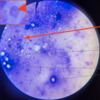
Eimeria sp.: Macrogamonts (female)
Purple appearance
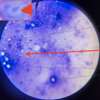
Eimeria sp. infection: Normal chicken RBC
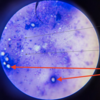
Eimeria sp.: Empty oocysts
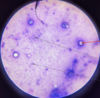
Eimeria sp.: Empty oocyst

Eimeria sp.: Macrogamonts
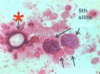
Eimeria sp.: Ripened oocyst
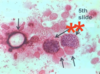
Gamonts

Nuclei of nurse cells

Eimeria sp.: Oocysts shedding into the lumen

Eimeria sp.: Oocysts enter the gut lumen
What is significant about the staining of unsporolated oocysts?
They cannot be stained with standard histological stains
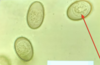
Eimeria sp.: Unsporolated oocysts
Contains a zygote

Eimeria sp.: Unsporolated oocysts
Contains a zygote

Eimeria sp.: Unsporulated oocysts