Mid-term Test Week 5 #MCQ1 Flashcards
(12 cards)
1/ A company has developed a new engine whose average lifetime is unknown. In order to estimate this average, 100 engines are randomly selected from a large production line and tested; their average lifetime is found to be 11 years. The 11 years represents a: #MCQ1
A. Sample.
B. Population.
C. Parameter
D. Statistic.
1/ A company has developed a new engine whose average lifetime is unknown. In order to estimate this average, 100 engines are randomly selected from a large production line and tested; their average lifetime is found to be 11 years. The 11 years represents a: #MCQ1
A. Sample.
B. Population.
C. Parameter
D. Statistic.
2/ The classification of students grades (A, B, C, D and Fail) is an example of: #MCQ1
- Nominal data
- Numerical data
- Ordinal data
- None of the above
The classification of students grades (A, B, C, D and Fail) is an example of: #MCQ1
- Nominal data
- Numerical data
- Ordinal data
- None of the above
3/ The classification of student major (accounting, economics, management, marketing, other) is an example of: #MCQ1
- Nominal data.
- Numerical data.
- Ordinal data.
- None of the above
3/ The classification of student major (accounting, economics, management, marketing, other) is an example of: #MCQ1
- Nominal data.
- Numerical data.
- Ordinal data.
- None of the above
4/ The process of using sample statistics to draw conclusions about population parameters is called: #MCQ1
- Finding the significance level.
- Calculating descriptive statistics.
- Calculating the confidence level.
- Doing inferential statistics.
4/ The process of using sample statistics to draw conclusions about population parameters is called: #MCQ1
- Finding the significance level.
- Calculating descriptive statistics.
- Calculating the confidence level.
- Doing inferential statistics.
6/ In a study of managers at a large firm, managers are categorized into three groups according to their division (field, production, or corporate). A simple random sample is taken from each group, and data are collected on each manager in the sample. This is an example of: #MCQ1
- Simple random sampling.
- Stratified random sampling.
- Cluster sampling.
- None of the above.
6/ In a study of managers at a large firm, managers are categorized into three groups according to their division (field, production, or corporate). A simple random sample is taken from each group, and data are collected on each manager in the sample. This is an example of: #MCQ1
- Simple random sampling.
- Stratified random sampling.
- Cluster sampling.
- None of the above.
6/ Which of the following graphical display can be used to describe relationship between two categorical variables? #MCQ1
- A histogram.
- A scatter diagram.
- A bar chart.
- A pie chart.
6/ Which of the following graphical display can be used to describe relationship between two categorical variables? #MCQ1
- A histogram.
- A scatter diagram.
- A bar chart.
- A pie chart.
Which of the following statements about pie charts is false?
- Pie charts can only be used for nominal data.
- Pie charts are usually used to display the relative sizes of categories for qualitative data.
- Pie charts always have the shape of a circle.
- The area of each slice of a pie chart is proportional to the relative frequency of the corresponding category.
Which of the following statements about pie charts is false?
- Pie charts can only be used for nominal data.
- Pie charts are usually used to display the relative sizes of categories for qualitative data.
- Pie charts always have the shape of a circle.
- The area of each slice of a pie chart is proportional to the relative frequency of the corresponding category.
8/ Which of the following distributions is not symmetric? #MCQ1
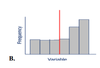
If the median of a distribution is less than the mean, then the distribution is: #MCQ1
A. Bell shaped.
B. Skewed to the left.
C. Symmetrical about its mean.
D. Skewed to the right.
If the median of a distribution is less than the mean, then the distribution is: #MCQ1
A. Bell shaped.
B. Skewed to the left.
C. Symmetrical about its mean.
D. Skewed to the right.
10/ Which of the following summary measures is NOT affected by extreme values?
- The median.
- The range.
- The mean.
- Both the range and the mean.
10/ Which of the following summary measures is NOT affected by extreme values?
- The median.
- The range.
- The mean.
- Both the range and the mean.
11/ The sum of the squared deviations from the sample mean of 16 observations is 60. Which of the following is the variance of the sample? #MCQ1
- 2
- 3.75
- 4
- None of the above
11/ The sum of the squared deviations from the sample mean of 16 observations is 60. Which of the following is the variance of the sample? #MCQ1
- 2
- 3.75
- 4
- None of the above
12/ The price–earnings ratios of a sample of stocks have a mean value of 13.5 and a standard deviation of 2. If the ratios have a bell-shaped distribution, what proportion of ratios do you expect to fall between 9.5 and 17.5? #MCQ1
- Approximately 68%
- Approximately 95%.
- At least 75%
- None of the above
12/ The price–earnings ratios of a sample of stocks have a mean value of 13.5 and a standard deviation of 2. If the ratios have a bell-shaped distribution, what proportion of ratios do you expect to fall between 9.5 and 17.5? #MCQ1
- Approximately 68%
- Approximately 95%.
- At least 75%
- None of the above


