Microbiology Flashcards
Microbiology
Structure of a bacterial cell

Microbiology
What the bacterial cell wall does
Resists environmental stress like osmatic pressure
Acts as a barrier
Provides mechanical strength
Microbiology
Gram positive cell wall structure

Microbiology
Gram negative cell wall structure


Coccus

Bacillus

Vibrio

Spirochete


Microbiology
Which type of bacteria retain the purple dye in the gram stain test?
Gram positive
Microbiology
Polymers that may also be present in the cell walls of gram positive bacteria
Teichic acids
M protein
Mycolic acid
Microbiology
Teichoic acid
May appear in cell walls of gram positive bacteria
Provides rigidity to the cell wall
Microbiology
M protein
May be found in the cell wall of gram positive bacteria
Helps to prevent phagocytosis by immune cells
Microbiology
Mycolic acid
May be found in the cell wall of gram positive bacteria
Waxy lipid
Aids survival in environmental stress
Provides a barrier to antibiotics
Microbiology
Virulence factor that provides a barrier to antibiotics
Mycolic acid
Microbiology
Catalase test
Tests for enzyme catalase
Microbiology
Catalase
Enzyme required by many organisms for the decomposition of hydrogen peroxide to water and oxygen
Microbiology
Gram negative bacteria unique outer membrane of the cell wall is called?
Lipopolysaccharide layer (LPS)
Microbiology
What’s unique about the LPS layer?
It is made up of lipopolysaccharides instead of the standard phospholipid molecules
Microbiology
What are the 2 parts of the LPS layer and their roles?
Lipid A
- Anchors the LPS to the phospolipid bilayer
O polysaccharides
- Carbohydrate chains facing the extracellular fluid
Microbiology
Role of the LPS layer
Acts as a major barrier to the outside world
Offers protection against antiseptics and antibiotics
Acts as an endotoxin
Microbiology
How is an endotoxin released?
When the cell lyses and dies
Microbiology
What is the cause of most symptoms of gram negative bacteria
The LPS which acts as an endotoxin



Microbiology
Four structures of bacteria found outside the cell wall
The capsule
Fimriae and pili
Axail filaments
Flagellum
Microbiology
The capsule
Surrounds the cells of some bacteria
Made of polysaccharides and peptides secreted from the cell
Allows bacteria to stick to surfaces
Can help resist phagocytosis
Microbiology
How does the capsule help resisit phagocytosis?
The capsule inhibits opsinisation and phagocytosis
Microbiology
Opsinisation
Proteins called opsonins are released as part of an immune response
Opsonin targets pathogen and binds to it and then binds to a macrophage
Increases chances of macrophages binding to pathogen
Microbiology
Fimbriae and Pili
Sticky projections involved in sticking to host and other bacterial cells
Move by retacting pili
Microbiology
What are fimbriae and pili made up of?
A single protein called pilin
Microbiology
Axial filaments
Required for motility in spirochetes
Wrap around the cell between the plasma membrane and the outer membrane
Microbiology
Flagullem
Helps bacteria move to favourable conditions
Microbiology
Bacterial movement can be caused by either…
Chemotaxis
Phototaxis
Microbiology
Chemotaxis
Movement in response to chemicals
Microbiology
Phototaxis
Movement in response to light
Microbiology
Main way bacteria reproduce and what that actually means
Binary fission
- Divide by splitting in two
Microbiology
When bacteria reproduce, how similar are the daughter cells to the mother cell?
Identical unless mutation occurs
Microbiology
Bacteial cell divsion steps

Microbiology
What causes a very long cell to occur?
Depletion of FtsZ
FtsZ acts as a contractile ring and cause the two cells to seperate
Microbiology
What gene is responsible for maintaining the rod shape in some bacteria?
MreB gene
Microbiology
What happens when MreB is depleted?
It leads to cocci shapped cells occuring
Microbiology
Endospores
Can survive dormant in harsh conditions such as:
- Extreme heat
- UV radtion
- Antibiotics
Microbiology
Cellular differentation that is involved in endospore formation
Bacterial sporulation
Microbiology
Stages of endospores converting back to a vegative cell
Activation
Germination
Outgrowth
Microbiology
When a endospore germinates, what happens during outgrowth?
Synthesis of RNA, proteins and DNA
Cell begins to divide
Microbiology
Exotoxin
Toxin made in the bacteria and released
Microbiology
Which sort of toxin does a gram positive bacteria produce?
Exotoxin
Microbiology
Which sort of toxin does a gram negative bacteria produce?
Endotoxin
Microbiology
Cytotoxin
Exotoxin
Kills cells that comes in contact with it
Microbiology
Nuerotoxin
Exotoxin
Interferes with neurological signal transmission
Microbiology
Enterotoxin
Targets the linning of the diggestive system
Microbiology
Which type of toxin causes a fever?
Endotoxins
Microbiology
Which type of toxin is unstable at 60oC?
Exotoxins
Microbiology
Which type of toxin requires a large amount to be toxic?
Endotoxin
Microbiology
Which type of toxin only needs a small amount to be toxic?
Exotoxins
Microbiology
Damage to the plamsa membrane can:
Inhibit DNA replication
Destroy the ability to produce energy
Cause loss of membrane integrity and destroy the cell
Microbiology
Ribosomes
Required for protein production
Microbiology
Koch’s postulates
- The same pathogen must be present in every case of the disease
- The pathogen must be isolated from the sick host and purified
- The pure pathogen must cause the same disease when given to uninfected host
- The pathogen must be re-isolated from these newly infected hosts
Microbiology
Who developed the germ theory of disease?
Robert Koch
Microbiology
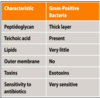
What is the difference between gram positive and gram negative cell walls?
Gram positive has a thick peptidoglycan layer
Gram negative has a thin peptidoglycan layer and outer membrane lipolysaccharide


