Metabolism Flashcards
What is anabolism?
the process of building up larger and more complex molecules from simple precursors

What is catabolism
Breakdown of large molecules and foodstuffs into simpler products

catabolic pathways ___
- all converge into one molecule (acetate (acetyl CoA))

Anabolic pathways ___
- diverge
- acetyl CoA can be used to build things

What is a metabolic pathway
- series of enzyme catalyzed reactions
- converts precursor (A) into product (E) thorugh a series of intermediates known as Metabolites
- each step in a metabolic pathway brings a small chemical specific chemical change
- must be irreversible, thermodynamically very favourable
- are regualred: transcription control level of enzyme, inhibition or activation of enzyme activity
What is elucidation of metabolic pathways
- use of metabolib inhibitors
- if rxn is A -> B -> C -> D , and E2 (between B and C) is inhibited, B will accumulate. then we can isolate it and identify it
- Biochemical genetics
- a) genetic deseases (ex: alkaptonuria: urine in these partients turn black due to accumulaed homogentisic acid, as intermediate of the pathway accumulation seen in urine)
- b) the use of auxutrophic mutants: expose the wild type e.coli (prototrophs) to a mutagen to inactivate a gene encoding a specific gene, auxotrophs can be identified byb their requirement of the end product of the affected pathway
- Use of radioactive labelled substrates
- 14C behaves just like regular carbon, radioisotope always it to be easily seen
- ccan obtain secentive detection of very small amounts even in complex mixtures
What are oxidation reduction reactions
Oxidations = anode = becoming more pos
Reducation =cathode = more neg
- if Aox +Bred <-> Ared + Box
- in order to know which species Box or Aox we need to know STD reduction potentials
- electrons always flow to half reaction w/ higher reduction potential, ie higher EP is th one accepting electrons
if ΔEo’ > 0 rxn will be spon
*oxygen is strongest reducing agent
Explain the Catabolism of Fats
- Fat is the most concentrated store of metabolic energy
*will have higher delta E,
- it is chemically very reduced
- most carbon atoms are CH2, releases the maxiumum amoun of free energy when oxidized to CO2 (most sugars are CH2O), already partially oxidized)
- since hydrophobic, can we stored nearly water free
*the more hydrogens something contains and less oxydens the more reduced something is
What are enzyme cofactors
- “helper molecules”
- some enzymes require help of additional chemical compounds to carry out their functions
ex:
- Inorganic ions: Fe 2+, Mg 2+, Mn 2+, Zn 2+, Cu 2+
- coenzymes complex organic or metalloorganic compounds that act as transient carriers of specific functional groups
*many coenzymes are derivatives of adensosine
What is ATP
- carrier/donor of phosphate groups
- used to phosphorylate many types of molecules: sugars lipids proteins etc
**add picture**
- recall phosphoanhydride bond hydrolysed to drive reaction
WHat is Kinase
enzymes that phosphorylate molecules with help to ATP
What is Coenzyme A (CoA/ CoASH)
- cofactor that acts as a carrier of acyl (acid) groups
- derived from vitamin pantothenic acid (B5)
- The HS is the one acting as nucleophile and involved in reaction
* know reactions it is involved in

What does CoASH form with organic acids
- forms a thioester derivative
- a thioester is the sulfure analogue of an ester
- acid functional group within a molecule is called acyl group
- coenzyme A thioester derivative is called acyl CoA
- in specific case of acetic acid, corresponding coenzyme derivative is called acetyl CoA

What is NAD+ and FAD
- universal electron carriers
- many enxymes that carry out oxidation of different substrates rely only on a few cofactors to act as their electron acceptor
- electrons that are removed from substrates are transferred on to these cofactors reducing them and conserving the energy of oxidation
- cofactors are involved in beta oxidation

What is NAD+ and NADP+
nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+) and nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADP+)
- the pyridine nucleotides derived from vitamin niacin B3
* a niacin deficiency will effects reactions with NAD as a cofactor
* in order to synthesise NAD niacin must be present

What is the redox chemistry of NAD+ and NADP+
- redox reactions occur at the nicotinamide ring
- during oxidation of substrates, two hydrogen atoms are removed from the substrate (Dehydrogenation) *hence name dehydrogenase of enzymes
- oxidized form of the nucleotide NAD+ and NADP+ acepts a hydride ion (;H- , the equivalent of a proton and two electrons) to become reduced NADH or NADPH
*this reaction took in 2 electrons and a proton*

What are the different roles of NAD+ and NADP+
NAD+
- used as the oxidizing agent in catabolic processes
- (fatty acid oxidation)
- resulting NADH is reoxidized via the ETC to generate energy
NADPH
- used as the reducing agent in biosynthesis
What is FAD and FMN
Flavin adenine dinucleotide (FAD) and flavin mono nucleotide (FMN)
- derived from vitamin riboflavin (B2)
- usually found attached or linked to enzymes (prosthetic groups)
*(NAD and NADPH is just folating around)

What is the redox chemistry of flavin nucleotides
- Flavin nucleotides can accept either one or two electrons in the form of one or two hydrogen atoms (each atom, an electron plus a proton)
- the fully reduced forms FADH2 and FMNH2
- when only one elctron is accepted they form stable semiquinone redical (FADH+ and FMNH+)
- due to ability to participate in 1 or 2 electron transfers they are involved in a greater diverstiy of reactions
*can be used in 1 electron oxidation or 2 electron oxidation
*be able to recognize the reducing and oxidizing forms
What are the various energy reservoirs in human body
- goes to most easily accesible first: glucose bc just dissoled in the cell
- glucose suply runs out quickly, then goes to dissolved glycogen (polymer of glucose, need to break the bonds to get glucose)

Where are fatty acids found
- mainly in TAG fat

What is an overview of the complete oxidation of fatty acids to CO2 and H2O
- Beta oxidation: gives rise to acetyl CoA and reduced cofactors
- the Citric acid Cycle
- Electron transport chain
*goal is to get ATP out of this process

Explain the first stage of oxidation of fatty acids
Beta oxidation
- tagged terminal ( ) carbon atom of fatty acids (even and odd chained) with a phenyl group and fed dogs
- aromatic products excreted in urine
- findings showed that fatty acids were cataboliced two carbons at a time

Where does Acyl CoA synthetase occur?
in outer mitochondrial membrane
What is a synthetase vs synthase
- an enzyme that combines two small molecules to form a larger molecule with help of ATP energy
- synthase does same thing but does not require energy
Wht is an overview of oxidation of glucose?
- oxidation to CO2 and H2O acomplished in 3 stages
Stage 1: glycolysis +pyruvate dehydrogenaes
Stage2: TCA cycle
Stage 3: ETC
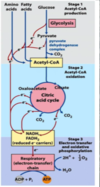
What is an overview of carbohydrate metabolism
- fatty acids only have one process that it can go though, glucose has many

How is glucose transported into cells
- highly polar molecules
- cannot enter cells by passive diffusion across non polar membrane
- transporter proteins called GLUTs (GLUcose transporters) residing in cell membrane, catalyze glucose import
- one of many actions of hormone insulin is to stimulate GLUT-mediated glucose uptake in skeletal muscle and adipose tissue
- in diabetes the body “starves in midst of plenty” ebcause blood glucose is not taken up properly
What are isozymes
two or more enzymes that catalyze the same raction but are encoded by different genes
what is a mutase
- a mutase is a particular subclass of isomerase
- catalyse reactions in which a functional group is shunted between different positions in a molecule

FAD

NAD

CoASH
What cofactor is derived from pantothenic acid
CoA
B5
What CO facor is dervied from niacin
Pyridines (NADH)
B3
What cofactors are derived from riboflavins
flavins (FAD)
B2
Why is there a large and negative Delta G associated with hydroglysis of ATP
- hydrolysis of the electrostatic repulsion amoung negative charges
- the product inorganic phosphate has greater resonance stabilization than does ATP
- ADP2- product radpidly ionizes to release a proton inot a medium of very low [H+] driving the hydrolysis towards completion
What types of carbon molecules have the most energy, which have the least?
most is C-C least are carboxylic acids/carbon diaoxide
- we are oxidizing things, most energy comes from what is least oxidized


