Metabolic bone diseases and osteoporosis Flashcards
what is osteoporossis
reduce bone density and mass
equal loss of mineral and organic matrix
increase risk of fractures
- Bone reportion exceeds formation

what are the risk factors for osteoporosis?
-
Female (lower bone mass and oestorgen decrease in postemenopausla women)
- most bone loss in first 10 years after menopause or oophorectomy
- Genetic
- ethnicity (northern europena and asian)
- Smoking and alcohol
- immobilisation (low physical actiivty)
- durg induced (corticosteriods- inhbit bone formation)
- testerone defivnecy (men)
what are the majro risk factors of osteoporossis
Major- hisotry of fracture as an adulkt
fragility fracture in 1st degree relative
low body weight (<127 lbs)
What is a DEXA scan?
Dual energy Xray absorptiometry
diagnosisa anf assess risk of osteoporosis
measures bone mineral desnity for example before treatmentt hat may have adverse effect on bone density (sec hormeon deprivation breats/prostate cancer)_
what is osteomlacia?
inadequate bone mineralsiation of new born matrix/osteoid (softening of the bones)
ratio of mineral to organic is lowet than normal
what is rickets?
osteomalacia in children
defecit bone mineralsixation at the ephiyseal growth plates
long bones cannot supporot weight of torsoa bones are flexible
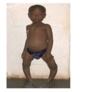
what are the causes of rickets?
defieinctintake or absoprtion of vitamin D
defective 1-alpha hydroxylation (CKD)
primary renal PO4 wasting
inhvitors of minerlalsation
defceitve vitamin D receptors
what are the clinical features of ricekts at birth?
Craniotabes
softening occpital bones
flattened parietal bones can be buckled

in earyl years what are the signs of rickets?
widened epiphyses (wrists)
frontal bossing (squared appearance to head)
Prescen of rickety rosary (beeding at costal chondral joints
Harriosns sulcus
Pigeon chest

what are the symptoms of rickets in older children
Lower limb deformity
myopathy
lumbar lordodsis and bwoing of legs
Hypocalcemia tetany

what are the clinical features of osteomlaaica
usually asymptomatic
symptomatic
- proximal msucle weakness
- widespread bone pain (tendeness)
- dull pain worse on weight bearing
- insuffiency fracture
- wasddling gait

what are the main causes of hypercalcaemia??
-
Primary hypoparathyroidism
- Ca2+ homeotstasi loss due to excessive PTH secretion
- due to benign parathryoid tumoru (adenoma) or hyperplastic parathryoid hormone)
- excessive bone resportion
- excessive PTH- excessive production of 1,2DHCC (more absoprtion from intes and more reasboprtion in kidneys
- depsoit of calcium in heart lungs and soft tissue
-
Malignant disease
- metasses in the bone cause destriction and release of Ca2+ (would see low levekls of PTH in response to hyperclacaemia)
- Metases also secret parahtyroiud hormone related peptide
what are the causes of hypocalacaemia
hypoparathryoidism
pseudohypoparathyoidism
vbitamin D defieicny and dependnecy
renal disease
Inadaqueaet response of VTH-vitamin D axis
how can renal disease result secondary hyperparathrypodms
lose so much calcoium due to kidney disease
get secondary hyperparathyroidsism as the body tries to increase levesl fo calcium in the blood by pulling it from the bones
what is pseudohypoparathryodisim?
target organ resistance to PTH (not hormoen defieiocm)


