Menisceal Injuries Flashcards
Menisceal Tears Menisceal Cysts Discoid meniscus
What is function of the meniscus?
-
Optimise force transmission across the knee by
-
Increasing congruency
- increased contact area -> decreased point loading
-
shock-absorption
- the mensicus is ore ealstic than articualr cartilage so absorbs shock
- Transmits 50% WB load in extension & 85% in flexion
-
Increasing congruency
-
Stability
- meniscus deepens the tibial surface
- acts as secondary stabiliser
- medial meniscus- post horn of medial meniscus is main secondary stabiliser to anterior translation
- lateral meniscus is less stabilising
- has 2x the excursion cf medial m
- ***the meniscus become primary stabilisers in ACL def knee***

What are the meniscus made of?
- Fibroelastic cartilage
- interlacing network of collagen, procollagen, glycoproteins and cellular elements
- 66-75% water
- 90% type 1 collagen
-
fibres- allow the mensicus to expand under compression and increase contact area of joint
- radial
-
longitudinal ( circumferential)
- help dissipate hoop stresses
- vertical matress captures

What is the shape of the medial and lateral meniscus?
Medial
- C shaped w triangular X section
- av width 9-10mm
- av thickness 3-5mm
Lateral
- More circular ( the horns are closer together & approximate at ACL)
- covers a larger portion of the articular surface
- av width 10-12mm
- ab thickness 4-5 mm
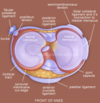
What are the attachment of the meniscus?
-
Transverse ligament
- connects medial and lateral meniscus anteriorly
-
Coronary ligament
- connects mensicus peripherally
- medial mensicus has less mobility w more rigid peripheral fixation cf lateral
-
Meniscofemoral ligaments
- conects meniscus into substance of PCL
- orginate post horn of lateral meniscus
- Ligament of Humphrey ( ant)
- Ligament of Wrisberg (post)
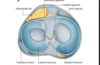
What is the blood supply of the medial and lateral meniscus?
Medial
-
Medial inferior genicular artery
- supplies peripheral 20-30% of medial m
Lateral
-
Lateral inferior genicular artery
- supplies periohery 10-25% lateral m
- central 75% recieves nutrition thru diffusion
What is the innervation of the meniscus?
- Peripheral 2/3rds innervated by type 1 & 11 nerve endings
- Post horn highest concentration of mechanioreceptors
What is the potential of healing of menisceal tears?
- Tears in peripheral 25% red zone
- can heal by fibrocartilage scar formation
- **fibrochondrocyte **is cell responsible for healing
- peripheral tears <4mm have best healing potential
- Tears in central 75%
- have limited or no intrinsic healing potential due to poor blood supply
Describe the movements of the meniscus in knee movements?
- Anterior movement with extension
- Posterior movement with flexion
- lateral meniscus has more mobility than medial due to less ligament attachments
What increases the risk of menisceal tears?
- In an ACL deficient knee
Describe the aetiology of medial mensiceal tears cf lateral ?
- Medial
- More common than lateral
- the exception is in Acute ACL tears when Lateral tears are more common
- Degenerative tears in older pts occur in Posterior horn medial meniscus
How are menisceal tearas classified?
- By location
- Red zone ( outer 3rd, vascularised)
- Red-White sone ( middle 3rd)
- White zone ( inner 3rd, avascular
- Size
-
Pattern
-
Vertical /longitudinal
- common, esp ACL tears
- repair the peripheral
-
Bucket handle
- vertical tear which may displace into notch
-
Oblique/parrot beak
- may cause mechanical locking
- Radial
-
Horizontal
- more common older pts
- assoc w menisceal cysts
- Complex
-
Vertical /longitudinal

What are the presentation of menisceal injury?
- Symptoms
- pain localised medial/lateral
- mechanical locking/clicking
- delayed/intermittent swelling
- Signs
- Joint line tenderness
- effusion
- mcmurray’s test
What is seen on imaging of menisceal injury?
- Xray
- normal in young pts
- menisceal calcifications in crystalline arthropathy
- MRI
- sensitive but high false positive rate
- Double PCL = bucket handle menisceal tear
- paramedial cyst= menisceal tear

What is the tx of menisceal injury?
Non operative
-
rest, NSAIDS, Rehab
- 1st line of tx for degenerative tears
Operative
-
Partial meniscectomy
- tears not amenable to repair
- >80% satisfaction at FU
- 50% have fairbank radiographic changes ( osteophytes, falttening, Joint space narrowing)
- predictors of sucess
- <40 yrs
- normal alignment
- minimal/no arthritis
- single tear
-
Menisceal repair
- for peripheral in red zone
- rim width is the distance form tear to peripheral meniscocapsular junction
- rim width correlates w ability of repair to heal( lower has better blood supply)
- Vertical/longitudinal tear
- 1-4cm length
- combined with ACL reconstruction - greatest success
- 70-95% success
-
Menisceal transplantation
- young pt w near total meniscectomy exp lateral
What are the outcomes of menisceal transplantation?
- Requires 8-12 months for graft to fully heal
- return to sport 6- 9 months
- 10 yr fu
- persistent improvement in subhective pain and functional scores
- most had radiological progression of degenerative chnages
- retears or extrusion common
What are the oucomes of total meniscectomy?
- 20% had significant arthritic lesions and 70% have radiographic changes 3 years post surgery
- 100% arthritis at 20 years
- severity of degeneratiev changes is proportional to % of meniscus that was removed
- Now only historical interest only
How would you repair a menisceal tear?
-
Inside out technique
- gold standard
- medial approach to capsule
- expose capsule by incising sartorius fascia, retracting pes tendons and semimembranosus posteriorly and develop plane between medial gastrocnemius and capsule
- Lateral approach to capsule
- expose capsule by developinf plane between iliotibial band and biceps tendon interval. retract lat head of gastrocnemius posteriorly
-
All inside technique -suture device w plastic /bioabsorbale anchors
- most common
- many complications- device breakage/iatrogenic chondral injury
- Outside in
-
open repair
- uncommon except knee dislocations
-
Technique
- vertical mattress suture strongest co they capture cicrumferential fibres
What are the risk of menisceal tear repair?
- Saphenous nerve and vein ( medial approach)- 7%
- Peroneal neuropathy
- popliteal vessels
- deep infection 1%
- Sterile effusion 2%
- Athrofibrosis 6%
- superifical infection 1%
What is a meniscal cyst?
- a condition characterised by a local collection of synovial fluid within or adjacent to the meniscus
- most commonly assoc with menisceal tear
- location
-
perimeniscal cyst
- medial more common> lat
- Parameniscal cyst- Baker’s cyst
- xtruded fluid outside meniscus
- usually between semimembranosus & medial head of gasronemius
-
perimeniscal cyst

Describe the presentation of meniscal cyst?
- Symptoms
- asymptomatic
- pain
- locking/clicking
- dealyed/intermittent knee swelling
- Exam
- popliteal mass
- crepitus
- joint line tenderness
What imaging is useful and what is seen with a meniscal cyst?
- MRI
- most sensitive
- cyst bright on T2
- xrays normal in young pt with acute meniscal injury

Describe the tx of meniscal cyst?
Non operative
-
Rest, NSAIDS, Rehabilitation
- 1st line
-
Aspiration and steriod injection
- isolated baker’s cyst in young pt
- more outcome in older degenerative tears w cyst
Operative
-
Arthroscopic debridment, cyst decompression & partial meniscal resection
- incomplete meniscal resection-> recurrence
-
Cyst excision using open posterior approach
- paramenisceal cyst
- prone
- curved incision
- interval between semimembraneous and gastronemius
- sharp dissection of cyst margins to capsule
What is a discoid meniscus?
- Abnormal development of the meniscus-> hypertrophic and discoid shaped meniscus
- Discoid meniscus is > than usual
- aka popping knee syndrome
- present 3-5% population
- location
- usual Lateral Meniscus
- 25% bilateral
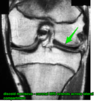
Name and decsribe the classification of Discoid meniscus?
- Watanabe Classification
- Type 1- Complete
- Type 2- Incomplete
- Type 3- Wrisberg ( lack of poor meniscotibial attachment to tibia)

What is the presentation of a discoid meniscus?
- Symptoms
- Clicking, pain and mechanical locking
- often symptomatic in adolscent
- Exam
- mechnical symptoms more pronunced in extension
What is seen on imaging of a discoid meniscus?
- Xrays
- widening of joint space due to widening of cartilage ( up to 11cm)
- Squaring of lateral condyle w cupping of lateral tibial plateau
- hypoplastic lateral intercondylar space
- MRI
- study of choice
- bow tie sign - 3 or more sagittal images w meniscal continuity
- coronal image will show flat meniscus extending across entire lateral compartment

What is the tx of discoid meniscus?
Non operative
-
Observation
- asymptomatic without tears
Operative
-
Partial meniscectomy and saucerization
- for pain and mechanical symptoms
- menisceal tear/ menisceal detachment
- obtain anatomical looking meniscus w debridment
- repair meniscus if detached ( Wrisberg variant)


