Medically Relevant Parasites - SRS Flashcards
Entamoeba histolytica has infected roughly ten percent of the world. The cysts are ingested (>1000) leading to the infective stage. What symptoms does this cause?
Treatment?
•can cause intestinal symptoms with diarrhea or become invasive with liver abscess that resembles:
–anchovy paste on aspiration and right lobe liver
Tx= metronidazole
Key buzzword for Entamoeba histolytica?
Anchovy paste abcess on aspiration and right lobe liver
Blastocystis hominis is found in asymptomatic healthy people and people with diarrhea so debated pathogen.
Apart from diarrhea what are the other symptoms one would endure?
Tx?
Pain
Perianal puritus
excessive flatulence
Tx = metronidazole
This parasitic infection is linked to guinea pigs, and produces a short term cholera-like diarrheal illness in healthy individuals.
In contrast, it can be chronic in the immunocompromised, even causing respiratory disease in AIDS patients.
What is this organism?
Cryptosporidiosis
Cyclospora is a self limited infection, even in HIV if CH4’s are high enough.
What is the contamination vector?
Tx?
Ingestion of contaminated water and food
Tx = sulfa/TMP
Isospora is delivered via water/food. Describe the course of the disease? (natural history)
•Self limited in healthy otherwise months to years (record 26 yrs) and mainly in HIV/AIDS
Name three examples of organisms that cause Primary Amebic Meningoencephalitis (PAM).
- Naegleria fowleri
- Balamuthia mandrillaris
- Acanthamoeba sp.
What is the mechanism of invasion in PAM?
•free living organisms so direct invasion from contact. Usually up nose through cribiform plate.
Tx for PAM?
Mortality rate?
Ampho-B
Very high, >95% mortality for Naegleria
22.5% of people older than age 12 in the US are infected with Toxoplasmosis, and there is world wide distribution. What does this organism infect?
•can infect almost all warm blooded animals but felines are main shedder of infective ooztyes.
–domestic cats 16-80% seroprevalence in US.
The acute form of Toxoplasmosis is typically asymptomatic, but if not… What happens?
–immunocompentent (CD4>100)
•Head/Neck lymphadenopathy over generalized
•can mimic lymphoma or mononucleosis like illness
–Immunocompromised-more severe
•(meningo)encephalitis, pneumonitis, myocarditis, pericarditis, hepatitis, coombs-neg hemolytic anemia or polymyositis
In the chronic form of toxoplasmosis, cysts are formed in what organs?
–cysts any organ but primarily brain, heart and skeletal muscle.
What is the presentation of the chronic form of toxoplasmosis that is common congenitally but rare in adults?
Chorioretinitis
When in pregnancy is transmission the greatest?
The most devastating?
–late pregnancy transmission greatest but early infection more devestating (1st/2nd trimester)
Described the natural history of toxoplasma in infected neonates.
–70% infected neonates asymptomatic at birth but develop ocular or degrees of mental retardation later in life.
- hydrocpehalus,
- microcephaly,
- microphthalmia,
- mental retardation,
- failure to thrive,
- seizures,
- hepatosplenomegaly,
- pnuemonitis,
- fever,
- rash,
- thrombocytopenia,
- chorioretinitis
- blindness.
When HIV patients with toxoplasmosis have CD4 counts under 100, things get bad. What are the most common results of this shit storm?
- CNS, brain lesions common
- –slowly evolving dementia without LOC in conjunction to pathologic effect of HIV.
- Pneumonitis is 2nd most common complication
- –(also seen in kidney transplants)
- –looks like Pneumocystis but more rapid
•A 36-year-old HIV-infected man presented with a 2 to 3 week history of fever and headache and was brought in to the emergency room after having a generalized tonic-clonic seizure. His most recent CD4 count was 14 cells/mm3 and HIV RNA was greater than 500,000 copies/ml. He is known to be IgG seropositive for Toxoplasma. The patient had taken trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole (Bactrim, Septra) and antiretroviral therapy about 1 year ago, but stopped taking all medications 9 months ago. He has a history of Kaposi’s sarcoma. Physical examination shows a confused patient with a temperature of 38.6°C, cutaneous Kaposi’s sarcoma lesions, and no focal abnormalities on a cursory neurologic examination. Contrast brain CT scan demonstrates focal mass lesions (Figure 1) and (Figure 2).
Which of the following is true?
A.The presence of more than one mass lesion rules out CNS lymphoma
B.Approx 10% of primary CNS lymphomas in AIDS pts are associated with EBV
C.Based on clinical presentation, most likely diagnosis is Toxoplasmosa gondii infection and expectation is that it is primarily CNS
D.Based on clinical presentation, most likely diagnosis is toxoplasmosis and HIV therapy should begin before further workup.

C. Based on clinical presentation, most likely diagnosis is Toxoplasmosa gondii infection and expectation is that it is primarily CNS
Toxoplasma gondii is one of the TORCH organisms, What do you commonly see on CT images of the brain with this organism?
What are the non-cat means of infection?

- Ring enhancement CT
- eating undercooked meat esp pork, lamb, venison
What is this condition?
What organisms could be causing this?

Lymphatic Filariasis
•most common is W. bancrofti. also Brugia sp and Loa Loa
W. Bancrofti has a circadian rythym, what is this cycle based on?
The likely release of cortisol in the morning.
How is Onchocera Volvulus transmitted?
What is the common name for this?
- transmitted by black fly
- ‘river blindness’
Your patient who works at the Denver Dumb Friends League, comes in with respiratory distress, x-ray reveals the image attached.
What is the problem here?
How did this happen?
Tx?

Dirofilaria immitis
Normally inhabits dogs and coyotes (hearworm)
•human is not normal host but can happen in pulm arteries causing lesion.
Tx = Surgery for granuloma
Or no treatment
What is the way to treat Dracunculiasis?
Daily turning of a stick to pull it out!
Toxocariasis, aka Visceral Larva Migrans, is carried by cats and dogs. What are the presentation we see with this?
–Visceral 2-3yo , Ocular and neural forms 3-40yo
Blindness
Your 3 y/o patient cannot stop itching their anus through their annual well child check up. What do you think the problem is?
How would you detect this?
Enterobiasis vermicularis - “pinworm”
Detect by adhering scotch tape in the morning to pull off and visualize eggs.
Your patient presents C/O loose mucousy stool with blood during the night especially. You note they have poor hygiene. When you do your exam you find the attached image.
What is the organism responsible for this?

•Trichuris trichiura “whipworm”
(Image is a prolapsed rectum, covered in worms)
Your patient presents with GI disturbances and clear nutritional deficiencies. On physical inspection you find the lesion in the picture.
What is this organism?
What is the route of infection?

Direct invasion of skin
Hookworm -
- Necator americanus
- Ancylostoma duodenale
Your middle age patient presents with wheezing lungs, dry cough, throat irritation and hemoptysis. They have granulomas in the lung. Also they complain of skin reactions - “ground itch”.
What is the likely organism?
Strongyloides stercoralis
You have a mexican patient who presents with sudden onset of siezures.
What is this condition called?
What is the likely organism involved here?
What causes the siezures?
Neurocystercercosis
Taenia solium
–worm dies and causes inflammation
Taenia saginata produces what kind of symptoms?
Mainly GI symptoms
You pull a 15 m tapeworm out of a japanese tourist who came to gamble in the legendary Blackhawk of Colorado.
What is the most likely organism?
Describe the life cycle of this organism.
Diphyllobothrium latum
•complex life cycle with crustaceans, 2 fish and people.
Echinococcosis is a tiny tapeworm found in animals. human infection mainly asymptomatic but cysts can cause issues in what organs?
•lungs and liver and rare brain.
What is a major issue that involves treatment of Echinococcosis?
•Cystic echinococcosis causes hydatid cysts which can cause anaphylaxis when opened
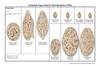
How do you diagnose trematodes?
Based on spine position
Shistosoma Japonicum - no spine
S. Mansoni - lateral spine
S. haematobium - terminal end spine
Describe the two phases of Trichinosis
- GI phase with n/v diarrhea, constipation and pain vs asymptomatic
- muscle invasion phase with triad of myalgia, palpebral edema and eosinophilia
What is a unique aspect of Trichinosis compared to other types of helminthic infections?
Accompanying high fever is somewhat unique
- 12 y/o boy from Egypt came to ER with abdominal pain. 37.5 temp, HR 120 and bp 100/60. silent abdomen but not ‘acute’.
- Hgb 10 and WBC 13k. Eos inc at 12%
. A: Ultrasonography shows multiple, round-shaped structures with a target-like appearance within the small intestine (white arrows); B: In a longitudinal scan of the small intestine, ultrasound shows a tubular structure with two parallel, outer high echogenic lines (black arrows) [“winding hwy”, “railway tracks” or “parallel lines”.] Space between the intestinal wall and the tubular structure was not observed.
What is the organism here?

Ascaris lumbricoides
Describe the typical results of an Ascaris lumbricoides infection.
most asymptomatic or mild with end of infection a couple of months with expulsion of adult worms.
May see intestinal obstruction and/or jaundice particularly in children.
What are the main systems that Schistosomiasis affects? (6)
- –skin (cercarial dermatitis)
- –Intestinal
- –Hepatosplenic
- GU
- Cardiopulmonary
- CNS
What organism causes Katayama fever?
S. japonicum
What do we see in hepatosplenic schistosomiasis?
•granulomas and then portal hypertension 2nd to portal vein vasculitis. In fact, in path specimen, only portal artery and bile ducts are present in the fibrosed area which is pathognomonic.
What organism causes schistosomiasis in the GU system?
What is this associated with an increased incidence of?
- Really only S. haematobium (less japonicum). ‘Sandy patches’ are calcified ova seen through atrophic epithelium = pathognomonic. bloody
- high incident of bladder CA
Not on test (supposedly), but wort mentioning:
•Salmonella in urine is tip off as Schisto colonized with salmonella


