Medically Relevant Bacteria - Gram Negative Curved and Cooccobacilli-LM Flashcards
This is a gram neg, curved rod bacteria with a single polar flagellum. It is a non lactose fermenter but ferments glucose. What is it from this discription and the pictures

Vibrio Cholerae
How is vibrio cholerae transmitted
- Usually a disease of poor sanitation (water with human fecal contamination)
- Large dose is required to produced disease due to acid in stomach killing organisms
V cholerae is a non invasive enterotoxogenic bacterium that produces a potent enterotoxin choleragen? how does it work?
- A domain controls its biologic activity
- A1 peptide enzymatically transfers ADP-ribose from NAD to a GTP regulatory protein which leads to activation of adenylate cyclase and the overproduction of cyclic AMP
- B domain binds the toxin to cellular receptors (GM1 receptor)
How would you Dx cholerae?
Rx?
- Dx- voluminous “rice water stool” presumptive for cholera
- Gram stain stool to see organism or
- Isolation using V. Cholera selective thiosulfate-citrate-bile salts-sucrose (TCBS) agar
- Rx – fluid and electrolyte replacement, doxycycline can shorten disease course

A gram neg, curved rod, is a non lactose fermenter, motile,
•Ingestion of contaminated water, milk or undercooked foods (raw clams) causes.
What is it?

Campylobacter jejuni
How does campylobacter jejuni infection progress?
- Enteroinvasive and after 2-4 day incubation get acute enteritis (fever, loose bloody diarrhea, nausea and abdominal pain)
- Generally self-limiting but may last a week
- Relatively small inoculum is required to cause illness
For C. jejuni, how would you…
DX
RX
?
- Dx - Gram stain may reveal curved (“seagull” or “comma”) shaped organisms, culture at 5% O2, 10% CO2, 85% N2 at 42°
- Rx – early erythromycin treatment may shorten disease course
This picture is showing a gram neg,bacteria that is a non lactose fermenter.
•Lives in the mucus layer above the gastric epithelium and produce urease (buffered from acid)
What in the picture is characteristic of its name?

Helical shape
Helicobacte pylori
H pylori transmits feco-oral or oral-oral; what other conditions is it associated with?
How does it cause these?
- Associated with chronic gastritis, gastric and duodenal ulcers, gastric adenocarcinoma and gastric MALT lymphoma
- Down regulation of somatostatin-producing D cells leads to elevated gastrin levels and enhanced acid secretion
- Chronic superficial gastritis → atrophic gastritis → adenocarcinoma
What would you use to Dx H pylori? think about the fact is produces urease.
Rx.
Breath urea test was highlighted but
- Stool antigen test, urease test on biopsy, breath urea test, IgG serology, visualized microscopically, cultured on chocolate agar in a microaerophilic environment
- Rx – PPI, clarithromycin, and amoxicillin, or metronidazole (clarithromycin-based triple therapy) or a PPI or H2RA, bismuth, metronidazole, and tetracycline (bismuth quadruple therapy)
These are obligate anaerobes so they like to live in abcesses, most encapsulated, non lactose fermenter, gram neg bacilli or cocco bacilli? Does the picture help? What are they?
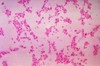
Bacteroids and prevotella
These are all opportunistic with immunosuppression but B fragilis has what virulence factor?
Dx?
Rx?
Anti-phagocytic capsule
- Dx - Gram stain and ANAEROBIC culture
- Rx frequently resistant to many antibiotics and local antibiotic susceptibility patterns are needed as well as antibiotic sensitivity of the patient’s cultured organism
- Debride necrotic tissue, drain pus
Where are Prevotella sp. found?
What can they cause?
Prevotella sp. are similar to, and previously classified as, bacteroides
- Part of the normal oral and vaginal flora
- Can cause obstetric and gynecologic infections, aspiration pneumonia, chronic otitis media and sinusitis, and abscesses in lung, oral cavity, brain abscesses, and human bite wounds
This is a picture of a gram neg coccobacilus, aerobic, non-motile, aquatic. First ID the organism then tell me what is significant about what it produces?
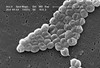
Acinetobacte baumannii
Produces B-lactamase
How does acinetobacter baumannii present?
Dx
Rx
- Nosocomial infections or immunocompromised patients
- Commonly colonizes irrigating and INTRAVENOUS solutions (so can go almost anywhere in body)
- Respiratory tract, CSF, peritoneal fluid, urinary tract infections
- Dx – culture
- Rx – amikacin, minocycline (intrinsically resistant to cephalosporins, macrolides, and penicillins and developing resistance to carbapenems)
Haemophilus is a gram neg coccobacilli whose capsule is a major virulence factor. It is spread by direct contact (day care centers)
What are the types of haemophilus that we learned about?
What type of people must be vaccinated?
Influenzae
Influenzae Type B
Ducreyi
Parainfluenzae
aegypticus
ASPLENIC
How does H influenzae present?
What is special about type B?
•Pneumonia, acute epiglottitis, bacteremia, meningitis, septic arthritis, cellulitis, otitis media, purulent pericarditis, endocarditis, arthritis and osteomyelitis
- H. influenzae type b - most common cause of bacterial meningitis in children 6 months-2 years
- Unencapsulated strains produce ear, sinus and respiratory infections (usually chronic smokers, alcoholics or elderly)
What is this
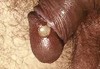
Chancre caused by H ducreyi.
Will also cause this ( painful, unilateral); its called bubbos by the way.

H parainfluenzae,
H aegypticus presentation
pneumonia endocarditis;
conjunctivitis
H. Parainfluenza Dx
Rx
Prevention
- Dx -Gram stain of CSF, capsular antigen detections, culture is fastidious (10% CO2 required) and organisms require factors X (hemin) and/or V (NAD) in media (present in chocolate agar), PCR
- Rx –IV or parenteral third generation cephalosporin
- Prevention – 3 doses of one of the following: MONOVALENT Hib VACCINE, quadrivalent Hib vaccine (Hib + DTP), pentavalent Hib vaccine (Hib + DTP + hepatitis B)
Gram neg coccobacilli that is encapsulated and a strict aerobe? The main one is also called whooping cough, what is it.

Bordetella pertussis- spread by direct contact

What are the exotoxins that Bordetella produces?
- Filamentous hemagglutinin: involved in attachment to host cells
- Pertussis Toxin: adp-ribosyl-transferase that interferes with G-protein signals from cell surface receptors (A subunit) and involved attachment to respiratory epithelia and mφs (B-subunit)
- Invasive adenylate cyclase toxin: increases cAMP, inhibiting immune effector cell functions
- Tracheal cytotoxin: causes ciliostasis and loss of ciliated epithelial cells
- Lethal (dermonecrotic) toxin: heat stable and causes tissue destruction
Whooping cough has stages of the disease can you describe them
Catarrhal
Paroxysmal
Convalescent
- Highly contagious laryngotracheobronchitis usually seen in infants
- 7-14 day asymptomatic incubation period
- Catarrhal stage - fever, rhinorrhea and a highly infectious cough
- Paroxysmal phase - spasmodic “whooping” cough that may last 6 weeks with posttussive vomiting and lymphocytosis accompanied by minimal granulocytosis
- Convalescent phase - secondary complications may occur (encephalopathy, seizures and pneumonia)
Bordetella pretussis Dx
Rx
Prevention
- Dx – clinical symptoms, PCR, grown on Bordet-Gengou agar media, and serologic testing
- Rx – erythromycin can shorten disease course
- Prevention – DTaP vaccine x 5 followed by Tdap( this is important) in adulthood (acellular pertussis not as protective as pre-1997 whole cell preparations DTwP)
Yersinia is a gram neg coccobacilli, what make is different from all the others?
Bipolar stain
Non lactose fermenter
Glucose fermenter

Y. enterocolitica and Y. pseudotuberculosis cause disease via ingestion of contaminated water or food, what symptoms would you see and how would you treat?
- Produces enterotoxin similar to E. coli heat stable toxin
- Enteroinvasive self-limited ileitis, gastroenteritis characterized by fever, abdominal pain that may mimic appendicitis, diarrhea, and mesenteric lymphadenitis
- Dx - culture
- Rx - ampicillin or tetracycline
What kind of Yersinia is called the bubonic plague or black death?
How is it transmitted?
What virulence factors does it have?
- Bubonic plague (black death) maintained among rodent populations (ground squirrels, prairie dogs, great gerbils/black rats for exam questions) transmitted by infected fleas (regurgitate biofilm from gut)
- Facultative intracellular pathogen
- Two antiphagocytic components
- F1 antigen and the V & W antigens (both required for virulence) only produced at 37°, the bacteria are capable of surviving and multiplying within monocyte, and upon emerging from the monocytic host they possess these antigens
- Yops proteins inhibit inflammatory cytokine production
Yersinia pestis causes, what are the presentations
Bubonic plague
Septicemic plague
Pneumonic plague

- Bubonic plague occurs within a week of being bitten by an infected flea, bacterial proliferation produces the “bubo” (swollen, painful lymph node), bacteremia follows, causing death in about 75% in a few days
- Septicemic plague – bacteremia and bacterial endotoxins cause disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC), with bleeding into the skin and other organs; usually fatal
- Pneumonic plague occurs under crowded conditions when contaminated respiratory droplets expelled by infected persons are directly inhaled by another person; shorter incubation period and greater mortality (90% in 1 day) than bubonic plague
Y pestis
Dx
Rx
Prevention
- Dx - Examination of sputum or a lymph node biopsy (Gram-negative, bipolar coccobacilli), culture, immunofluorescence or PCR; P-3 level containment is required
- Rx - Treatment must be rapid and aggressive w/ streptomycin and gentamycin
- Prevention - Vector control and inactivated Y. pestis vaccine for lab personnel handling organism (IM x 3)
Gram neg, pleomorphic coccobacillus, non motile, aerobic, the big clue is that it is intracellular and proliferates in macrophages, what is it?
Francisella tularensis
Primary vectors are ticks and deer flies but Type A and B also have different vectors, what are they?
- F. tularensis tularensis (Type A) found in lagomorphs (rabbits, hares and pikas) in North America
- F. tularensis palaearctica (Type B) in aquatic rodents (beavers, muskrats) in North America and hares and small rodents in northern Eurasia
What are some of the ways to get Tularemia?
Dx
Rx
- Ulceroglandular (most common, via insect bite or handling rabbits ,skin lesion + buboes)
- Glandular
- Oropharyngeal (follows ingestion via food or water)
- Pneumonic (hematogenous or inhalational (dressing rabbit) fever, sore throat, pneumonia and pleuritis)
- Oculoglandular (infection via eyes)
- Typhoidal (via GI tract)
- Dx - culture on buffered charcoal and yeast extract (requires cysteine), PCR, antibodies in the serum (false cross reactivity with Brucella)
- Rx - streptomycin
This is similar to F tularenis and also proliferates in macrophages,
•Generally zoonosis via occupational exposure to infected animal
•Outbreaks via ingestion of unpasteurized milk products and undercooked meat
There are many different types named for their vector can you think of any?

- Worldwide distribution but mostly eradicated in the United States
- Brucella abortus - cows
- B. melitensis – goat, sheep, camels
- Unpasteurized milk caused Malta/undulant/Mediterranean fever
- B. suis - pigs
- B. canus - dogs
- B. ovis (sheep, goats)
- B. neotomae (wood rats), B. pinnipediae (pinnipeds - seals, sea lions, walruses), B. ceti (cetaceans - dolphins, porpoises, whales), B. microti (common vole)
How does Brucellosis present
Dx
Rx
•The organisms may produce a localized abscess, which is followed by bacteremia
•Undulant fever - Flu-like symptoms with limb and back pain, intermittent fever, malaise
•Can cause subacute or chronic disease
•B. melitensis and B. suis are more transmissible to humans
•
Dx -Cultures incubated 3-4 weeks in a 5-10% CO2-enriched environment or Brucella microagglutination test (BMAT)
Rx - Doxycycline (or ciprofloxin) plus rifampin (or streptomycin) MUST treat right away.
SD Schaffner is bit by an animal, maybe a cat and his hand looks like this, what is it?

Pasteurella multicida
Pasteurella multicida comes from numerous animals is a gram neg coccobacilli, non motile, facultative anaerobe.
How does it present?
Dx
Rx
•Cellulitis with bloody drainage from wound, may progress to joint infections, osteomyelitis, meningitis and endocarditis
•Usual infection is from domestic pet bites
•
•Dx – Clinical presentation and culture
•Rx - amoxicillin-clavulanate preferred since bite infections are polymicrobial


