Medically Relevant Fungi - SRS Flashcards
What type of stain is being used on this sample of Cryptococcus?
What does it reveal?
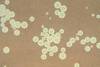
India Ink Stain
Capsule
Cryptococcus infections of the lungs tend to be…
Self limited
Cryptococcus can fairly commonly cause meningitis in HIV patients. What is the treatment for this?
–Treatment is Ampho-B +/- flucytosine followed by fluconazole for a long time (6-12 months to life long)
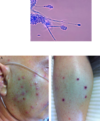
After a sky diving accident your now quadriplegic patient presents with tinea veriscolor with hypopigmentation and seborrheic dermatitis.
You see the rash in the photo and obtain the sample of the organism shown below. What organism is this, and what is the classical description we can expect to see?

Malassezia furfur
•board question is “spaghetti and meatballs” in a patient getting longterm TPN.
What is the most common presentation of histoplasmosis infection?
Acute Pulmonary Illness
What are the other, less common presentations of histoplasmosis infections?
- Rheumatologic syndromes 10%
- Pericarditis 10%
- Chronic Pulmonary Symptoms 10%
- Disseminating disease 10%
Blastomycosis dermatididis is present in soils, and has a similar geography to histoplasmosis. What are the 5 most common presentations of blastomycosis?
- Pulmonary with infiltrates 60-70%
- Cutaneous 40-50%
- Osteoarticular 10-15%
- GU (prostate) 10%
- CNS <10%
What are the yeast forms we covered?
- Candida
- Cryptococcus
- Malassezia
- Trichosporon
What are the mold forms we discussed?
Aspergillus
Zygomycetes
Mucor
Rhizo
Absidia
Fusarium
Pseudoallerscheria boydii/ scedosporium apiospermum
Name six dimorphs
- Histoplasma
- Blastomyces
- Coccidioides
- Paracoccidioides
- Penicillium
- Sporothrix
What component of the fungal cell membrane is unique and targeted by some antifungals?
Ergosterol
What is the only endogenous fungal organism?
Candida
Where is candida found?
GI and GU tracts
Your HIV positive patient presents with the attached physical findings.
What is this condition?
What organism is responsible for this?
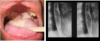
This is an example of mucocutaneous candidiasis presenting as oropharyngeal/esophageal candidiasis. >90% of these will be caused by C. albicans.
Your patient presents with a yeast infection as shown, what is this condition called? What most likely lead to this?

Vulvovaginitis d/t candida.
Typically occurs after a course of antibiotics
This patient developed the rash shown after a course of antibiotics and steroid treatment. What would this fungal infection most likely be?
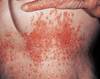
Cutaneous candidiasis
Systemic candidiasis - or candidemia (in the bloodstream) is the 4th most common nosocomial bloodstream infection. It has a 22-38% mortality even with tx.
Who do we see this in?
When do we typically see manifestations?
–Can be seen in severe immunocompromised (ie acute leukemia treatment or bone marrow xplant)
–Usually do not see manifestations until significant neutrophil recovery.
What are the 6 antifungals C. albicans is susceptible to?
- Fluconazole
- Itraconazole
- Voriconazole
- 5-FC
- Amphotericin B
- Echinocandins
Describe the sensitivity of C. glabrata to…
- Flucanazole
- Itraconazole
- Voriconazole
- 5-FC
- Ampho-B
- Enchinocandins
- Flucanazole: S-DD (dose dependent), Resistant
- Itraconazole: S-DD (dose dependent), Resistant
- Voriconazole: S-I (intermediate)
- 5-FC: Susceptible
- Ampho-B: S-I
- Enchinocandins: S
Describe the sensitivity of C. parapsilosis to…
- Flucanazole
- Itraconazole
- Voriconazole
- 5-FC
- Ampho-B
- Enchinocandins
- Flucanazole: S
- Itraconazole: S
- Voriconazole: S
- 5-FC: S
- Ampho-B: S
- Enchinocandins: S-I
Describe the sensitivity of C. krusei to…
- Flucanazole
- Itraconazole
- Voriconazole
- 5-FC
- Ampho-B
- Enchinocandins
Flucanazole: Resistant
Itraconazole: S-DD (dose dependent), Resistant
Voriconazole: S-I (intermediate)
5-FC: I-R
Ampho-B: I-R
Enchinocandins: S
Describe the sensitivity of C. parapsilosis to…
- Flucanazole
- Itraconazole
- Voriconazole
- 5-FC
- Ampho-B
- Enchinocandins
Sensitive to all
This CT scan was taken from a patient with longstanding neutropenia after their neutrophils bounced back. The patient presented with high fever and RUQ pain with nausea, vomiting and anorexia.
What is the name of this condition?

Hepatosplenic (chronic disseminated) candidiasis
You perform a fundoscopic exam on a patient with candidemia and see the attached image. What is this condition?

Endophthalmitis
Known as “valley fever”. Infections with Coccidioidomycosis immitis are asymptomatic in 60% of cases. What happens in the other 40% of cases?
can progress to pneumonia, nodules, cavities
also can disseminate to skin, bones, tendons, CNS
What fungal infection is associated with the lesion shown in the image?
What is the typical vector of infection?
What are the common sequelae of this infection if symptomatic?

This Captains wheel shape is characteristic of Paracoccidioides brasillensis
Inhalation
- bone marrow, organomegaly and Lymphadenopathy common. also intra-abdominal issues
- CNS 10-25%
While tending to his scarlet carson garden, “V” gets pricked by one of the rose bushes. Trusting your capacity for secrecy he comes to you with the skin lesions shown here. You take a sample and visualize the other image microscopically.
What organism is causing this presentation?

Sporothrix schenckii

Sporothrix schenckii has a 1-10 week incubation period after infection, what are the four categories that this organism can present as?
–lymphocutaneous; 75%
–fixed cutaneous
–disseminated
–extracutaneous
What is the function of the black/brown molds?
To return organic material from whence it came
Your 45 y/o male patient with cavitary lung disease. Scans of the patient are attached. A sample of the organism revealed a 45 degree angle branching fungus. What is the organism? What are the structures visible in the scans?
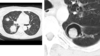
Aspergillus
Aspergilloma
Who do we worry about severe reactions to aspergillus in?
Immunocompromised and neutropenics
Your 43 y/o female patient presents with sudden onset of asthma. Lab tests show IGE levels over 500, and eosinophilia.
What do you suspect is the problem here?
Acute Bronchopulmonary Aspergillosis
(ABPA) AKA farmer’s lung
Microscopy reveals fungi with right angle (90 degree) branching hyphae. What is the organism?
What does the typical patient profile look like?

Zygomycosis
•Typical patient is an uncontrolled DM with sudden onset rhinocerebral necrotizing disease
Characterize the mortality and growth rate of zygomycosis.
Very fast growing
High mortality
What is the best treatment for a zygomycosis infection?
Surgical excision, plus antifungals
In normal host we see this organism in fungal keratitis as well as some other superficial infections. What is this organism?]
What do we see commonly in severely neutropenic hosts?
Fusarium
In neutropenic hosts:
- 60-80% death
–disseminated/fungemia*
–skin*, pneumonia including hemoptysis
Scedosporium apiospermum/Pseudoallersheria boydii can be encountered in soil and contaminated water. What happens to the immunocompromised host?
What are some other presentations?
•immunocompromised hosts tend to get CNS infection and if not aggressively treated upfront, has 75% mortality
other
•Respiratory, keratitis/endophthalmitis and skin/bone infections can be seen.
•also been implicated in sinusitis and lymphadenitis
What are the Scedo and Pseudo forms of Scedosporium apiospermum/Pseudoallersheria boydii?
•Scedo is asexual (perfect) form and Pseudo is sexual (imperfect) form.
Dermatophytes like keratin, so think of nails, hair and skin areas. What are the primary organisms associated with this?
Tinea
–Tinea capitis
–Tinea pedis
–Tinea corporis
–Tinea cruris
–Tinea rubrum
–Tinea unguium
Trychophyton
What would you call this?

Tinea Pedis
What is this?

Tinea corporis
What is this?

Tinea capitis
What is this?

Tinea Cruris
What is this? What causes it?

majocchi granuloma
Tinea Rubrum
What is this?

Tinea Unguium - nails (onychomycosis)
Who do we see pneumocystic jiroveci (carinii) in?
HIV and other immunocompromised patients
Your patient presents with three weeks of non-productive cough, progressive shortness of breath to the point where they have to rest while ascending stairs in their home. Xray and histology images are attached.
What does this person have that is causing their symptoms?
What else do they likely have?
What would be the treatment?
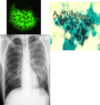
Pneumocystis
Often diagnostic of HIV/AIDS
Treatment is with antibiotics, not antifungals


