Math Flashcards
Rate equation

Range
Difference between the highest and lowest number in a list
Mean (average), median, mode, range
Median: middle value of a list
Mode: occurs most frequently in a list (the “most”)

Ratio box

Rules of exponents: MADSPM
- When equal bases are Multiplied, Add the powers
- When equal bases are Divided, Subtract the powers
- When exponent is raised to a Power, Multiply the powers
Rules of exponents: negative exponents
Raise the reciprocal to the positive power

Rules of exponents: zero exponent
Always equal to zero
Rewriting exponents (beyond 5 rules)
- Rewrite using common bases
- Factor expression

Negative number raised to even power results in a positive or negative number?
positive
Negative number raised to odd power results in a positive or negative number?
Negative
Rules for adding and subtracting square roots

Rules for multiplying and dividing square roots

How to eliminate square roots
Raise to power of 2 (including rest of terms)
How to simplify square roots
Factor number under root that results in a perfect square

Expanded quadratic equations
Variable sqared; variable x coefficient; coefficient
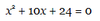
How to factor a quadratic equation
- Separate x2 into: (x ) (x )
- Find factors of third term that, when added or subtracted, yield second term
- Determine operations that correspond to each term (+ or -)
- Solve for both roots (x=0)

What do fully factored quadratic equations look like?
Two sets of (x +/- number) = 0
How to expand a factored quadratic equation
Utilize FOIL: multiply First, Outside, Inside, Last

Common quadratic equations

Inequalities: When multiply or divide by negative number, must…
change direction of inequality symbol.
How to manipulate two equatuons with two variables
Add or subtract entire equation from another to cancel variable out (will most likely have to multiply one equation to get same number associated with variable)
Steps for plugging in numbers
Plug in when variables in problem and answer choices. Check ALL answer choices.
Selecting number:
- Use easy numbers that make sense in context
- Avoid numbers 1 and 0
- Avoid numbers that show up a lot in question or answers
- Avoid plugging in same number for multiple variables
- Avoid plugging in conversion numbers
- Fractions: choose number that works easily with fractions (e.g. product of demoninators)
Signs to plug in the answer (PITA)
- “How much” or “How many” type questions
- Inclination to write algebraic formula
- Answers are in ascending or descending order
- Variables are present
Steps for plugging in the answer (PITA)
Start with C, use “spreadsheet” to stay organized
Plugging in on quantitative comparisons: FROZEN
When variables used, plug in twice using FROZEN:
- Fractions - Repeats - One - Zero - Extremes - Negatives
- (Repeats can be converstion numbers)
Definition of prime number
Only factors are itself and 1
- 0 and 1 are not prime; 2 is only even prime
- Can only by positive integers
Integer divisibility rules
- Integer is divisible by 3 if sum of digits is divisible by 3
- Integer is divisible by 4 if last two digits form number divisible by 4
- Integer is divisible by 6 if divisible by both 2 and 3
- Divisible by 8 if last 3 digits form number divisible by 8
- Divisible by 9 if sum of digits is divisible by 9
P | E | MD | AS
- Parenthesis
- Exponents
- Multiplication & division
- Addition & subtraction
How to add/subtract fractions
Find lowest (or any) common demoninator.
Bowtie method:

How to compare fractions
Bowtie method without multiplying bottom
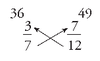
How to convert mixed numbers into fractions
Multiple denominator by integer and add to numerator
Divisor, dividend, and quotient

Definition of remainder
Leftover when one integer is not divisible by another
Percentages in word problems

Percent change equation
Note: For “difference”, always subtract lesser from greater

Distributive law

Types of triangles

Triangle third side rule
Length of any one side of a triangle must be less than sum of other two sides and greater than difference between other two sides.
I.e. L = side length
(L1-L2) < L3 < (L1+L2)
Area of a triangle

Pythagorean theorum and super pythagorean theorum
Pythagorean: a2+b2=c2
Super pythagorean (diagonal in a rectangular solid): a2+b2+c2=d2
30 : 60 : 90 right trangles

45 : 45 : 90 right triangles

Circumference of circle
circumference = 2πr or πd
Circles: chords, arcs and central angles
Arcs and their central angles are always proportional

Area of a circle
Area = πr2
Sum of angles in a polygon
Sum of angles = 180(n-2)
Quadrant numbering

Equation of a line; slope
y = mx+b
slope = rise/run
Surface area and volume of a cylinder
Surface area = 2πr(height)+2(πr2)
Volume = πr2(height)

Surface area and volume of a rectangular solid
Surface area = 2(LW)+2(LH)+2(WH)
Volume = LWH
How to find slope of a perpendicular line
Negative reciprocal
Finding probability of: 1) one event AND another, 2) one event OR another
Probability of A and B = Probability of A x Probability of B
Probability of A or B = Probability of A + Probability of B
Probability of A + Probability of not A =
1
How to deal with factorials
Cancel or factor out, e.g.:

Difference between permutations and combinations
With a combination, the order is irrelevant.
Permutations often ask for arrangements, orders, schedules or lists.
To solve a permutation:
Similar to factorials
- Figure out how many slots
- Write down number of options for each slot
- Multiply
To solve a combination:
* Figure out how many slots
- Fill in slots as you would a permutation
- Divide by factorial of number of slots
E.g.:

How to deal with strange symbols: #*µ⍛
Treat as a f(x) problem and use plug in strategies
Group equation
T = G1 + G2 – B + N
T = total; G1 = first group; G2 = second group; B = members in both groups; N = members in either group


