March 17- Inflammatory Lesions of the Jaw- FINAL Flashcards
What is the most common pathologic condition of the jaw?
Inflammatory Lesions
What is the initial source of inflammation?
Necrotic Pulp
(in the lecture she said that “inflammation can be caused from lesions, pulp damage and trauma” but necrotic pulp is listed as the source of inflammation in the notes)
What is wrong here?

Internal Resorption
What is luxation and avulsion?
Luxation: partial displacement of the tooth due to trauma (intrusion means the tooth looks shorter because it has been displaced inward. Extrusion means the tooth looks longer because it has been partially pulled out).
Avulsion: complete displacement of the tooth due to trauma.
Describe internal resorption and what can cause it?
§ Crown or root
§ Round-to-ovoid radiolucency
§ Asymptomatic
§ Involves pulp chamber, canals and dentin
Cuases: Trauma, Pulp capping, Pulp polyps
What is Wrong here?
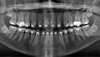
Ortho-related Resorption
(the roots have shrunk!)
What is Wrong here?

External Resorption
Describe External Resorption and what causes it?
It is the resorbing of the actual external root (the apex of the root looks cut off) - confusing in the notes so I am guessing here.
Lamina Dura and bone are abnormal. It cannot be detected clinically and you do not provide treatment.
Causes: Abnormal forces, Trauma, Chronic infl., Cysts, Impacted teeth

What is wrong with the pulp in these teeth?

Pulpal Sclerosis
(Diffuse calcification associated with aginng)
What is wrong with the pulp in this tooth?

Pulpal Stone
What is wrong with the teeth here and how doe sit happen?

Pulpal Obliteration
- Irritation of the pulp 2. Stimulaon of secondary dentin 3. Obliteration of the pulp cavity 4. Tooth is Non vital (No treatment)
Name 4 causes fro inflammatroy lesions of the Jaw.
Periapical Lesions
Osteomyelitis
Osteoradionecrosis
Bisphosphonate related jaw necrosis
Name the cardinal signs of Inflammation
Pain
Redness
Swelling
Heat
Loss of function
Define Rarefraction and Sclerosis
Rarefraction: condition of being less dense
Sclerosis: diffuse increase in density, increase “radiopacity” of a tissue
Rarefying Osteitis refers to 3 histopathological entities:
- Radicular abscess
- Radicular granuloma
- Radicular Cyst
(impossible to differentiat radiographically)
Define Sclerosing/Condensing Oteitis
localized inflammatory response of bone to pulpal necrosis or periodontal disease - radiopaque lesion (mineral content) - radiographic images is not a good judge - earliest evidence of pulpal necrosis… In dental images… increase of the PLS width
What is worng with the bone here?

Rarifying Osteitis
Condensing osteitis
Furcation Involvement
What is worng with the bone here?

Rarifying Osteitis
What is wrong with the bone here

Rarifying osteitis
Huge condensing osteitis
What is the most common pathologic condition of the jaw? Describe it.
Periapical inflammatory lesions
Teeth are direct pathway. Bone invasion from from caries and periodontal disease. Around apex of the root. Radiolucent or Radiopaque. Can’t be evaluated on a clinical basis… Initial source of the lesion is the necrotic pulp
What is the difference between chronic and acute periapical lesions?
Acute usually have no radiographic findings while chronic lesions do in the form of granulomas, cysts, abcess and bone changes.
What are the different changes that can occur in inflammation of the Jaw?
- Removal of bone mineral content (rarefration)
- Deposition of bone mineral content (sclerosis)
- Enlargement of bone
- Resoption of tooth roots
- Deposition of cementum (hypercementosis)
What is the radioluscency here?

Radicular Cyst
What are combined Perio-Endo lesions and what do they always present with radiographically?
Periodontal lesions > inflammatory lesion in bone Extension into bone from the overlying sot tissues
+
Periapical lesions > necrotic pulp (caries/trauma)
Always present with rarifying osteitis
What kind of Lesion is this?
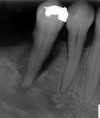
Perio - Endo Lesion
Describe a Periapical Abscess
Localized collection of pus
Acute = pain (intense, throbbing constant)
Chronic = long-standing, long-grade, pus-producing process… can produce a fistula
What is Pericoronitis?
Pericoronitis: Inflammation disorder affecting tissues surrounding the crown of a partially erupted tooth
What is wrong here?

Sclerosing Osteitis
What is wrong here?

Osteosclerosis
(Note: not sclerosing osteitis! The teeth look vital without caries. There are continuous borders to the radiopacity and there is no radioluscent outline. Therefore the lesion is not linked to the tooth)
What is wrong here?

Osteosclerosis
(Note: not sclerosing osteitis! The teeth look vital without caries. There are continuous borders to the radiopacity and there is no radioluscent outline. Therefore the lesion is not linked to the tooth)
Describe a Granuloma
Radulscent
Ruptured Lamina dura
Chronic
Can be Asymptomatic
Previous sensibility to heat and cold
Evolution to cyst or abscess
Widened of periodontal space
Lamina dura not visible
What is happening here?

Hypercementosis
(note that there is increased thickness on the INSIDE of the PDL space)
What is this?

Loculus of Maxillary sinus (normal anatomy)
What is the unlabelled arrow?
Nasopalatine Foramen (normal anatomy)
What is this?

Mental Foramen
(radioluscency in between mandibular premolars)
Describe Condensing Osteitis
- Well-defined
- Long-standing pulpitis
- Low-grade infl./mild irritation
- Most common radiopacity
- Physiologic reaction to infl.
- No treatment in the area
- Will have widening of PDL space and lamina dura
What is this?

Lateral Periodontal Cyst
(longstanding so has cortical bone barriers)
What is this due to?

Malignancy
What is the difference between osteitis and osteomyelitis?
“osteitis” – inflammation of bone
“osteomyelitis” – infection of the substance of bone by pyogenic organisms
More on osteomyelitis: - Is when the infection spreads in the bone marrow and is no longer contained to the vicinity of the tooth root apex. - Generalized inflammatory response of bone that may involve cortical and cancellous bone, bone marrow and the periosteum. - May arise from: odontogenic inf.; infected fractures; hematogenous spread of infection (distant site).
Describe radiograpbhic and clinical findings of osteomyelitis
Radiographically no changes from pre-exosting periapical lesion
Clincially: Purulent drainage, war, skin, fever
Describe radiographic findings in osteomyelitis
Relatively localized chronic osteomyelitis - persistence of outline of socket, sclerosis of adjacent bone, small sequestrum near bottom of original socket
What is wrong here?

Osteomyelitis
(bone sequestration and less bone density on the left)
What is wrong with the left mandible

Chronic OSteomyelitis
How does osteoradionecrosis and bisphophate related ostenecrosis differ from osteomyelitis radiographically?
They dont really. Need history.
What made this grown man cry?

Oral Candida
What is a “poop canal”?
Google Image result of Poop Canal:



