Male Repro Flashcards
FSH in males
to Sertoli cells
make sperm
diploid to haploid

emission mechanism
sympathetic T10-L2
contraction of seminal vesicles and prostate
expulsion of sperm/seminal fluid into posterior urethra
erect penis mechanism
parasympathetic
- smooth muscle relaxation, blood flow into corpus cavernosa, sinusoidal spaces fill, veins that enable outflow forced shut and trapped
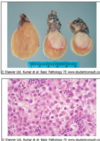
what area of prostate gets bigger in nodular hyperplasia
transition zone
L: small transition zone younger person (blue)
R: can see much larger transition zone, taking up 90% of prostate
Causes partial urinary obstruction
So passing urine gets harder in older men- incomplete emptying of bladder
Stroma form small nodules– net effect is to block urethra
Effects: incomplete emptying of bladder leading to nocturia
Causes bladder to hypertrophy and thicken muscle
Predisposition to bacterial infection bc don’t empty bladder totally
flaccid penis mechanism
sympathetic
- , constant suppress to penis so remain flaccid – flaccid by smooth muscle contraction
- flaccid: 2 corpus cavernosa w low blood flow
5ARI
prevent t to DHT (potent in prostate!)
decrease prostate volume
intracavernosal injection
- has to go into corpora cavernosa
- pure prostaglandin
- pain with erection (more than pain with injection)
- highly effective – mimics natural physiology
- do it with Doppler evalulation
- disadvantages –
- can hit vein and bruise
- pain at injection site
- cumbersome if poor dexterity
- can be sensitive to small doses
- some people are tired of using it all the time
T and prostate cancer?
most show no association
treamtent MAy stim growith in previously undaignosed tmros
neurotransmitters in ejaculation
serotonin
dopamine
oxytocin
GABA
3 types of intratesticular ducts
- straight tubules
- rete testes
- efferent ductules
epithelium of glans
•Glans of penis, as compared to rest of penile urethra, is lined by a stratified squamous epithelium compared to the vast majority of the penile urethra which is a pseudo-stratified columnar epithelium

DHT inhibitors for BPH
DHT inhibitor– GH inhibitor to debulk prostate
PDE5 inhibitors
- increase intracellular Ca – erection: cell relaxed by sequestration of Ca à drive Ca into ER (relax)
- reset: phosphodiesterase 5 – breaks down cAMP, GMP – turn off event
- if inhib PDE 5 – perpetuates cycle for longer
- need all of the first things!! sexual stimualation etc
- enable smooth muscle relaxation in the cells of the penis (upstream stuff has to work)
- all side effects from other PDE in the body
- Cialis – in body for longer
- look like cGMP – binde PDE5 – prevents PDE from binding cGMP, does work for a longer time!!
leydig cells
secrete T under LH

- LH stimulates Leydig
- FSH stimulates Sertoli
- Then negative-feedback loop to hypothalamus
- As androgen-binding proteins rise, the Sertoli cells secrete inhibin which goes back to cause inhibition of FSH from anterior pituitary
male hormonal changes with age
decreased total and free T
increased SHBG
increased FSH, LH
clomid
increase FSH and LH centrally
won’t work if testicles failed
no neg impact on sperm making - use for decreased sperm cunt for hormonal reasons and fertility
what kind of cancer is on the penis
- Squamous cell carcinoma:
- etiology (HPV), growth,
- Spread (inguinal nodes)

black arrow

•Would find spermatogonia right up against basal part (black arrow)
adverse events with transdermal gel
risk for transfer to partner and kids

- Flat line cells that would be straight tubules (black arrow)
- At the top you can see scalloped appearance (blue arrow)
- As well as development of smooth muscles in tunica propria
- This is beginning of efferent ductules
what hormones to check in hypogonadism patients
FSH
LH
Estradiol (T conversion in periphery - obese)
DHEA
prolactin (inhibits GnRH)
thyroid
How does T travel in the blood?
free T is very low - bind AR, activate, go to nucleus
falls apart easily –> hard to measure - const disappearing
free T
albumin-bound (liver)
sex hormone binding globulin (liver)
What if High T, low FSH + low LH
exogenous - taking illicit steroids –> infertile don’t want to come off steroids
treaments for hypogonadism
oral (not in US - first pass to liver) - but can give clomid (increase FSH and LH = won’t work if tests fail, no neg impact in sperm making, give form sperm making!)
transdermal - patch and gel
injectable
long term