Male Ext Genitalia; Clinical Correlation to Urethral Injury Flashcards
Sscrotum fascia- what are their extensions and attachments?
-
Ext oblique extends to form the ext spermatic fascia
- Attaches to the borders of the external inguinal ring.
-
Int oblique extends to form the cremaster muscle & fascia
-
Attaches to the
- inguinal ligament & iliopsoas laterally
- pubic tubercle medially.
-
Attaches to the
- Transversalis fascia becomes the int spermatic fascia in the scrotum
Layers of testis
Some Dirty Englishmen Called It Testis
- Skin
- Dartos fascia (has smooth muscle) - continues with Colle’s and Scarpa’s
- Ext spermatic fascia
- Cremasteric fascia
- Internal spermatic fascia
- Testis

Anatomy of epididymus
- Head, body, and tail
- Tail is continuous with ductus deferens
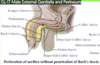
Course & contents of spermatic cord
Spermatic cord travels through the inguinal canal into the scrotum
- Testicular artery
- Cremaster
- Genitofemoral nerve femoral branch
- Pampiniform plexus of veins
- Testis

Scrotal lymphatics
- Does not cross the median raphe
- Drains into the superficial inguinal nodes on the ipsilateral side
*
The smooth muscle of the dartos fascia is continuous with what other fascia?
Colles fascia
Scarpa’s fascia
Darto’s fascia of penis

As scarpa’s fascia goes downward, it becomes what ?
Darto’s fascia- the outermost fascia.

The deep/buck’s fascia surrounding the penis envelops the
wraps around the corpus cavernosa and corpus spongiosum individually

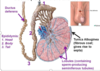
Anterior distal urethral lesion results in extravasation where and between what fascia?
Into scrotum and abdomen under Scarpa’s/Dartos

The fascia of scrotum connect via the tunica vaginalis (extension of parietal peritoneum) that surrounds the testis
Parietal peritoneal surface of the tunica can produce fluid, but if it’s not absorbed –> hydrocele
Course of the vas deferens
Goes from tail of epididymus, up the spermatic cord, through the superficial & deep inguinal rings, posterior to the inferior epigastric artery, anterior to the ureter, and joins with the duct of the seminal vesicles to drain into the ejaculatory ducts.
Cut in vasectomy
Anatomy of testis
- Comes down from spermatic cord
- Has epididymis on anterior surface
- Has small body at its upper pole called the appendix testis

Vascular supply of the testicle
-
Testicular (internal spermatic) artery - biggest
- From abdominal aorta
- Transverses in retroperitoneum, then through inguinal ring
-
Artery of vas deferens/Deferential artery
- From internal iliac artery OR superior vesical artery
-
Cremasteric (external spermatic) artery
- From inferior epigastric artery
- Primarily supplies tunica vaginalis

Testicular venous drainage (not an LO)
Pampiniform plexus: group of veins anastomose with each other and the deferential veins.

Left testis drains into the left renal vein
Right testis drains into anterior surface of the IVC
Where do lymphatics from the testis drain? Difference in the course between right and left?
Left testis lymphatics drain into the para-aortic and interaortocaval lymph nodes to drain in the thoracic duct.
Right testis lymphatics runs along the vena cava and then move to the left side of your body to reach those nodes.
Thus, the left doesn’t cross over, but the right will cross to the left due to generalized lymphatic flow and thoracic duct
Testicular tumor - what approach do you use and why?
You take the inguinal approach instead of the scrotal appraoch to avoid spreading the tumor via the differences in lymphatic drainage.
Testicular cancer (micrometastatic or residual disease) follow what lymph node chain?
Ipsilateral lymph node chain
Ultrasounds for scrotal contents - uses
- Can use high frq because testicles are so close to skin
- Determine if theres a hydrocele or testicular torsion
3 layers of scrotum seen on ultrasound
- Outer hyper-reflective layer (skin)
- Hypo-reflective intermediate
- Hyper-reflective inner layer (tunica albuginea)
The testicle itself is a smooth, homogenous structure

Mediastinum testis - what does it do and what does it look like on an ultrasound?
Mediastinum testis drains the seminiferous tubules into the rete testes
On an ultrasound, it’s a highly reflective linear structure at the posterior superior aspect of the testicle

Cremasteric Reflex
- Stroking the inner thigh stimulates the ilioinguinal nerve (L1)
- Activates motor neurons in the genital branch of the genitofemoral nerve
- Ipsilateral cremasteric contraction & Testicular elevation
Structure of penis
-
Corpus cavernosa: paired erectile bodies that prolongate proximally as the crus and attaches to the pubic arch
- Separated by a septum proximally, but is permeable distally to allow free communication between their vascular spaces
-
Urethra travels through the corpus spongiosum, with its proximal segment known as the bulb
- Reaches into the glans penis: expansion of corpus spongiosum

Cross-section of the penis
- In the dartos, you see the superficial dorsal veins
- Buck’s fascia goes around the corpora cavernosa and the corpus spongiosum
- Urethra is inside the corpus spongiosum
- Cavernosal artery runs through the middle of the corpora cavernosa to supply the erectile tissue
- Tunica albuginea (holds rigidity of erections) has an outer longitudinal layer and an inner circular layer.

Tunica albuginea
Tunica albiginea: tough, collagenous connective tissue layer that envelops the corpora cavernosa; holds rigidity of erections
- Circular inner layer bundles support and contain the cavernous tissue
-
Intracavernous pillars radiating from the inner layer act as struts to support the erectile tissue during erection
- The corpus spongiosum lacks this to ensure a low-pressure structure during erection
-
Longitudinal outer-layer bundles extend from the glans to the proximal crura
- Insert into the inferior pubic rami, but absent at the 5’ and 7’ o clock positions