Lumbar, Sacrum, and Innominate HVLA Flashcards
HVLA Superior Innominate Shear
Patient is supine with feet off the table
Physician is at the foot of the table grasping the tib fib superior to the ankle
- Abduct and internally rotate the patients leg
- Lean back and induce axial traction
- Instruct the patient to inhale and exhale; increasing traction in the first 2-3 breaths
- Apply a thurst at the end of exhlation
- Reassess

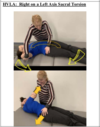
HVLA Inferior Innominate Shear
Patient is lateral recumbent with the affeted side UP and the phsycian behind the patient
Physician has cephalad hand on the PSIS and caudal hand on the ASIS
- Provide lateral distraction to gap SI joint
- Instruct the patient to inhale and exhale for 2-3 cycles increasing force on exhlation
- Exert a cephalad force through the ASIS and PSIS
- Recheck
***See the OSCE for the other treatment option

HVLA Anterior Innominate Rotation
Patient is lateral recumbent with the dys side up facing physician
Cephalad hand is between L5 and S1
Caudal hand flexes the hips and knees until L5 and S1 are separate
- Drop the pts legs off the table
- Place cephalad hand on the bicep just above the elbow with forearm on the shoulder
- Place the caudal forearm on the femur between the PSIS and trochanter
- Roll pelvis anterior to induce axial rotation and movement in SI joint
- Apply a force with the forearm that is directed DOWN the shaft of the femur
- Recheck

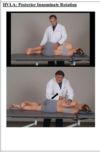
HVLA Posterior Innominate Rotation
Patient is lateral recumbent with dys side up facing the patient
Cephalad hand is between L5 and S1
Caudal hand flexes the hips and knees until motion is felt at the SI
- Straighten the patients bottom leg and place distal to popliteal fossa
- Cephalad hand moves to bicep just above elbow
- Caudal forearm on the PSIS and the iliac crest
- Roll pelvis anteriot to induce axial rotation until movement in the SI joint is felt
- Apply force
- Recheck
HVLA pubic restriction
Patient is supine with knees flexed and feet flat on the table
- Alternate MET between Adduction and Abduction of the knees
- With the final Abduction apply a force towards further abduction while patient is still ADducting
- Recheck

HVLA Bilateral sacral flexion
Patient is prone with the physician beside the patient
- Abduct the legs until motion is felt at the SI joint and internally rotate the legs
- Place hand on the apex of the sacrum
- Have the patient breathe in and resist exhalation
- As the patient inhales, apply and anterior and superior thrust
- Reassess

HVLA Bilateral Sacral Extension
Patient is prone in the TV watching postition and the physician is bside the patient
- Abduct the legs and externally rotate
- PLace heel of hand on the base of sacrum
- Have patient breathe in and out several times and resist inhalation
- As the patient exhales, apply a foce that is anterior/inferior
- Recheck

HVLA R/L Sacral Torsion
Patient is supine with hands clasped behind the neck
Physician is on the side of the axis
- Side bend the patient into a “c” shape AWAY from you
- Place the thenar eminence of the caudal hand on the ASIS opposite the axis
- Place cephalad hand on the patients lateral bicept
- Induce rotation of upper torso by pulling on the patients arm toward you and PREVENTING ASIS motion
- Have the patient breathe in and out. On EXHALATION apply a posterior thurst on ASIS while rotating
- Recheck
L1-L5 “Extension/Neutral” dysfunction: Long Lever, Rotational Emphasis
Pateint is supine with hands clasped behind neck; physician is opposite the PTP
- C-bend the patient AWAY (neutral) or TOWARD (non-neutral extension)
- cephalad hand is grasping the bicep
- Caudal hand stabilizes the ASIS
- Patients trunk rotates into the rotational barrier
- On exhalation exert a rotational thurst while stabilizing the ASIS
- Recheck

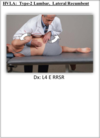
HVLA Type 1 Lumbar; lateral recumbent
Patient is lateral recumbent PTP up facing the physician
- Monitor the apex of the curve with the caudal hand
- Grasp the patients bottom arm and pull anteriorly and cephalad
- Flex hips and knees until motion is felt; straighten bottom leg, top leg at the popliteal space
- Cephalad hand against shoulder
- Caudal forearm contacts the line between the PSIS and greater trochanter
- Push the shoulder posterioly and toll the pelvis, having the patient inhale deeply
- At the end of exhalation, thust
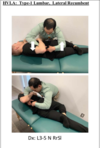
HVLA Type 2 lumbar; lateral recumbent
Patient is lateral recumbent with the PTP side up and facing the physician
- Grasp the patients bottom arm and pull anteriorly to rotate the dysfunctional segment caudally
- Flex hips and knees until motion is felt
- EXTENDED: leave the bottom leg slightly bent with superior leg crossed over the bottom
FLEXED: patient straightens the bottom leg and places the foot into the popliteal space
- Caudal forearm to the posterior aspect of the pelvis from SI joint to the greater trochanter
- Cephalad arm contacts the anterior shoulder
- Roll the pelvis to barrier and inhale
- At the end of exhlalation, rotate the patients pelvis towards the table
- Recheck