Lower limb random questions Flashcards
(185 cards)
To prevent the joint space from being obscured by the magnified shadow of the medial femoral condyle in the lateral projection of the knee, the radiographer should: a. Angle the central ray 5 degrees cephalad b. Place the knee joint in 90 degree flexion c. Rotate the knee so that the patella forms a 45 degree angle to the film d. Fully extend the patients lower leg
a. Angle the central ray 5 degrees cephalad
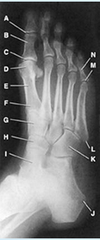
The bone identified in the figure attached is the:
a. tibia
b. cuboid
c. talus
d. navicular

Talus
To perform this position, the central ray is angled:
a. 5-7 degrees cephalic
b. 5-7 degrees caudad
c. angulation depends on the patient
d. There is no angulation in this position

5-7 degrees cephalic
The tibial plateaus slope:
a. anteriorly 10-20 degrees
b. posteriorly 10-20 degrees
c. laterally 10-20 degrees
d. medially 10-20 degrees
posteriorly 10-20
In which of the following positions can the sesamoid bones of the foot be demonstrated free of superimposition with the metatarsals or phalanges?
a. dorsoplantar metatarsals/toes
b. tangential metatarsals/toes
c. 30 degrees medial oblique foot
d. 30 degrees lateral oblique foot
tangential metatarsals/toes
Where does the CR enter the knee for a lateral projection of the patella?
a. posterior margin of the medial epicondyle
b. anterior margin of the medial epicondyle
c. through the patellofemoral joint space
d. directly to the lateral aspect of the patella
Through the patellofemoral joint space
For a lateral projection of the ankle, the CR must enter the:
a. navicular
b. tibiofibular joint
c. medial malleolus
d. lateral malleolus
medial malleolus
The bone part identified in the figure attached is the:
a. lateral condyle
b. medial condyle
c. lateral malleolus
d. medial malleolus

lateral malleolus
The talus articulates with how many bones:
a. 1
b. 2
c. 3
d. 4
4
Which of the following projections of the calcaneous is obtained with the leg extended, the plantar surface of the foot vertical and perpendicular to the IR, and the central ray directed 40 degrees caudad?
a. Axial plantodorsal projection
b. Axial dorsoplantar projection
c. Lateral projection
d. Weight-bearing lateral projection
Axial dorsoplantar projection
How far should the IR extend below the knee for a lateral projection of the femur?
a. 1 in
b. 2 in
c. 3 in
d. 4 in
2 in
What is the CR angle for an AP projection of the leg?
a. 0
b. 5 degrees caudad
c. 7 degrees caudad
d. 5-7 degrees cephalad
0 degrees
What is the CR angulation for the axial (plantodorsal) projection of the calcaneous?
a. 25 degrees
b. 30 degrees
c. 35 degrees
d. 40 degrees
40 degrees
The best projection to demonstrate the articular surfaces of the femoropatellar articulation is the:
a. AP knee
b. PA knee
c. tangential (“sunrise”) projection
d. “tunnel” view
tangential (“sunrise”) projection
In the lateral projection of the ankle, the:
- talotibial joint is visualized
- talofigular joint is visualized
- tibia and fibula are superimposed
1 and 3 only
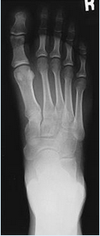
In the attached image, the central ray is directed to:
a. The PIP joint of the third digit
b. The head of the third metatarsal
c. The base of the third metatarsal
d. The PIP joint of the digit of interest

The head of the third metatarsal
Which of the following bones participate in the formation of the acetabulum?
- Illium
- Ischium
- Pubis
1, 2 and 3
Which of the following is recommended to better demonstrate the tarsometatarsal joints in the dorsoplantar projection of the foot?
a. Invert the foot
b. Evert the foot
c. Angle the central ray 10 degrees posteriorly
d. Angle the central ray 10 degrees anteriorly
Angle the central ray 10 degrees posteriorly
How many tarsal bones are there in the foot?
a. 4
b. 5
c. 6
d. 7
7
The most commonly performed oblique projection of the foot is the:
a. AP oblique in medial rotation
b. AP oblique in lateral rotation
c. PA oblique in medial rotation
d. PA oblique Grashey method
AP oblique in medial rotation
For an AP oblique projection of the knee, the limb is rotated:
a. 25 degrees
b. 30 degrees
c. 45 degrees
d. 30-40 degrees
45 degrees
For a plantodorsal projection of the toes, the central ray should be directed to enter the anatomy at the:
a. 1st metatarsophalangeal joint
b. 3rd metatarsophalangeal joint
c. 2nd metatarsophalangeal joint
d. navicular bone
3rd metatarsophalangeal joint
In which of the following projection is the talofibular joint best demonstrated:
a. AP
b. Lateral oblique
c. Medial oblique
d. Lateral
Medial oblique
All of the following bones area associated with condyles except the:
a. femur
b. tibia
c. fibula
d. madible
fibula