Leukaemia Flashcards
(23 cards)
What is principle site of blood cell formation?
The bone marrow
What is the average lifespand of a RBC?
100 days
What is Leukaemia?
It is cancer of the blood.
What are the symptoms of Leukaemia?
- Reduced platelets - Abnormal bruising/bleeding
- Suppressed/dysfunctional white cells - increased risk of infection
- RBC deficiency - anaemia, shortness of breath and fatigue
What are the four classes of Leukaemia?
ALL - Acute Lymphocytic Leukaemia
AML - Acute Myelogenous Leukaemia
CLL - Chronic Lymphocytic Leukaemia
CML - Chronic Myelogenous Leukaemia
What two lineages can leukaemias arise from?
Myeloid - Eosinophils, Basophils, Neutrophils, Monocytes, Platelets, RBC
Lymphoid - T and B cells
What is the origin of most Leukaemias in children?
Acute Lymphoid
80% are ALL, 20% AML
Which lineage do most leukaemias in children orginate from?
The B-cell lineage
What percentage of acute leukaemias are involved in chromosomal translocations?
65%
What is a driving force in a large proportion of acute leukaemias?
65% of acute leukaemias involve chromosomal translocations.
What are the most frequent targets of chromosomal translocations in acute leukaemias?
Transcription factors or components of signalling pathways
This results in either
- the inappropriate expression of a gene in the wrong cell
- expression of a novel gene
What are the two primary functions of the blood system?
To carry oxygen around the body
Immune system
What is the difference between acute and chronic tumours?
Acute tumours develop very rapidly
Chronic tumours develop over a long time
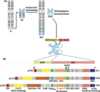
What is the Philadelphia chromosome?
It is found in almost all cases of chronic myeloid leukaemia.
Almost always a key step in this particular type of leukaemia.
It was discovered in Philadelphia.
P chromosome is a tiny fragment. Reciprocal translocation between Ch9 and Ch22. This swap results in a slightly bigger Ch9 and a tiny Ch22.
The Philadelphia Ch is the tiny Ch22.

What are the two genes that are involved in the formation of the Philadelphia chromosome?
abl and bcr genes.
The position of break in the bcr gene is variable.

What two chromosome join and translocate to form the Philadelphia chromosome?
Chromosome 9
Chromsome 22

What is the oncogenic product of the fusion event between Ch9 and Ch22?
Hybrid Bcr-Abl protein

What arises from the translocation between ablandbcr?
A hybrid Bcr-Abl protein that acts as a constitutively activated tyrosine kinase.
It phosphorylates targets inappropriately, this triggers oncogenic events.
What pathways does bcr/abl fusion activate?
Ras pathway
PI3K pathway
Jak-STAT pathway
What transcription factors are affected by bcr/abl fusion?
bcr/abl fusion can activate transcription factors including Jun, Myc and NF-KB.
How many break points are there in bcr?
Three
These can produce three different fusion proteins depending on where the break occurs.
ALL Acute Lymphoblastic Leukaemia
CML Chronic Myelogenous Leukaemia
CNL Chronic Neutrophili Leukaemia
Why do leukaemias exhibit specific translocations?
Either…
Translocations are random, and the effect of some can be selected for in the expansion of clones
OR
Translocations are non-random and some cause clonal expansion
In blood cells what machinery binds
There is a higher frequency of DNA recombination in the blood


