Lecture 4.2: ECG Hypertrophy of Atria and Ventricles Flashcards
What are 4 best leads to see atrial enlargement?
I, II, III, and V1

What is the p-wave like in RAE and is taller in which lead?
Tall, pointed; taller in III than in I

What is the p-wave like in LAE and is taller in which lead?
Wide, notched (“M” shape); taller in I than in III

RAE is associated with what 2 etiologies?
- Tricuspid valvular disease
- Pulmonary HTN

In RAE the tall peaked P waves will have amplitude greater than ______mm in leads II, III, and aVF
>2.5 mm
What are 2 etiologies causing LAE?
Mitral stenosis and Mitral regurgitation

In LAE the second half of the P wave will be negative in which leads?
V1 or III

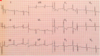
Interpret this EKG

LAE with 1st degree AV block
What is the most common cause of LVH?
Other causes?
- HTN = most common
- Also, AS, AI, hypertrophic cardiomyopathy and coarcatation of aorta
How does hypertrophy of the LV affect the electrical transmission as it passes through it and arrives at epicardial surface?
Effect on the QRS complex?
- Impulse will take longer = voltage and interval of QRS will increase
- Taller R waves over LV + deeper S waves over RV

Which feature of the ventricle is the main determinant of QRS voltage?
Total muscle mass
Criteria for LVH lack _______ (specificity/sensitivity), but are ______(sensitive/specific)
Criteria for LVH lack sensitivity, but are specific
Using the Romhilt-Estes Scoring System for LVH how many points is considered probably LVH and how many for dx of LVH?
- Probably LVH = 4
- LVH = 5
Using the Romhilt-Estes Scoring System for LVH, what size R or S in the limb leads, V1-V3, and V5-V6 is considered 3 points?
- R or S in limb lead = 20 mm or more
- S in V1-V3 = 25 mm or more
- R in V5-V6 = 30 mm or more
Using the Romhilt-Estes Scoring System for LVH, what type of axis deviation is worth 2 points?
LAD -30° or more